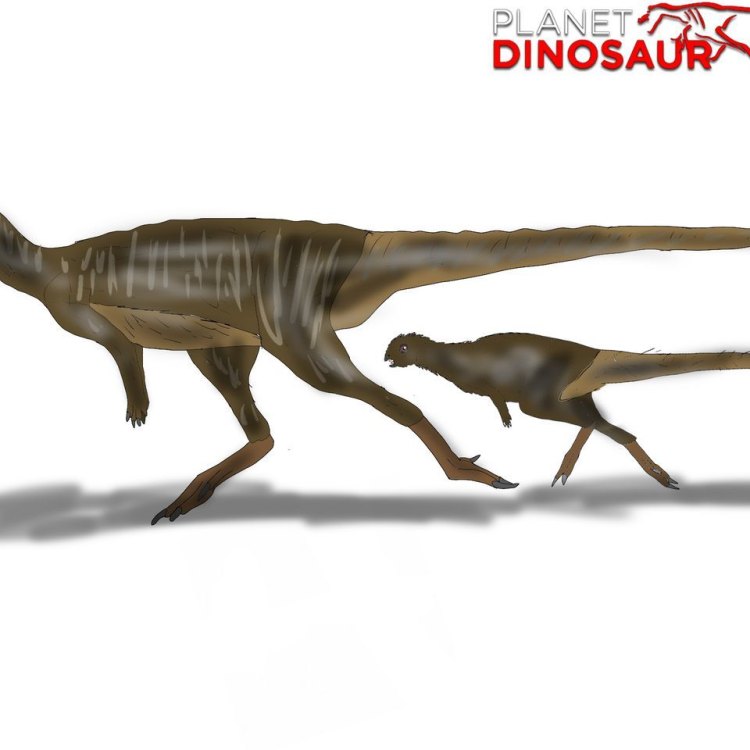
Jeholosaurus
Unknown
Meet Jeholosaurus - a mysterious herbivorous dinosaur from China. Its name means Jehol lizard, named after the fossil-rich Jehol Group in China. Although its skin color and maximum speed remain a mystery, its diet is known to consist of plants. Discover more about this enigmatic dinosaur from the land of the Great Wall. #Jeholosaurus #ChinaDinosaurs #HerbivorousDinosaur
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Jeholosaurus
Geological Era: Early Cretaceous
Feeding Behavior: Browsing
Jeholosaurus: Unpacking the Mysteries of the Fossilized Forest Giant
In today's world, few creatures capture our imagination quite like dinosaurs. These ancient reptiles have long been the subject of fascination, and their remains continue to be unearthed, providing a glimpse into a world that existed long before humans walked the earth. One such dinosaur that has caused a stir in the scientific community is the Jeholosaurus.Named after the Jehol Province in China where its fossils were discovered, the Jeholosaurus is a herbivorous dinosaur that lived during the early Cretaceous period, approximately 130 million years ago Jeholosaurus. While it may not be as well-known as some other dinosaur species, its unique characteristics and mysterious nature make it a fascinating creature to unravel. So, let's take a trip back in time and explore the world of Jeholosaurus.
Uncovering the Basics: What We Know About Jeholosaurus
As with many paleontological discoveries, much of what we know about Jeholosaurus is based on its fossilized remains. But from these remains, scientists have been able to piece together a relatively detailed understanding of this prehistoric creature.
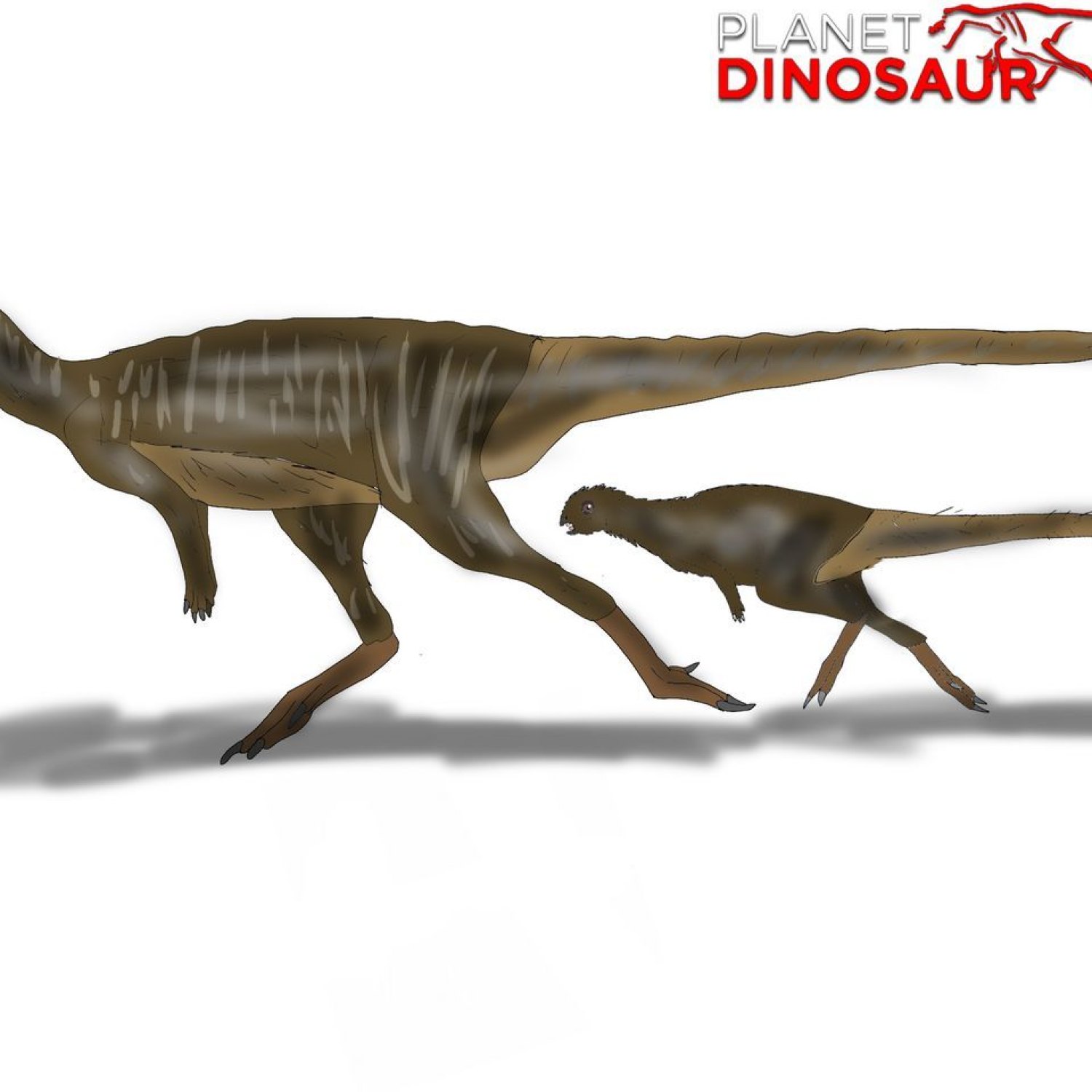
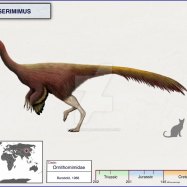
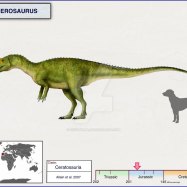
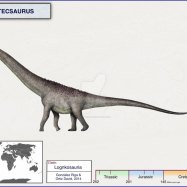
Like many dinosaurs, Jeholosaurus was a bipedal animal, meaning it walked on two legs. It measured around 3 meters in length and stood at approximately 1.5 meters tall. Its estimated weight was around 500 kilograms, making it a medium-sized dinosaur. It is believed to have a compact and robust body, with strong hind legs for walking and running Jainosaurus.
Jeholosaurus was a herbivore, which means it primarily fed on plants. Its tooth structure consisted of leaf-shaped teeth, indicating that it was well-equipped for browsing and consuming vegetation. This suggests that it may have lived in a forest environment, as this type of tooth structure is commonly found in modern-day herbivorous forest-dwelling animals.
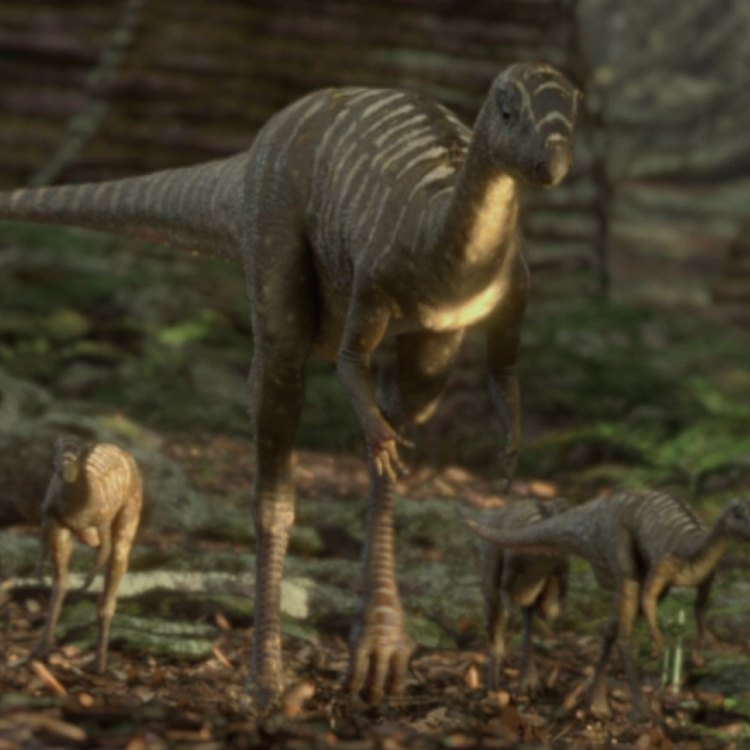
Speaking of its habitat, Jeholosaurus is native to China and is thought to have lived in the Jehol Province during the Early Cretaceous period. At the time, this region was a lush, green paradise teeming with diverse plant and animal life. The presence of Jeholosaurus fossils in this area suggests that it was a suitable habitat for this creature.
The Mystery of Jeholosaurus: Unraveling Its Behavior & Physiology
While we may have a good grasp of Jeholosaurus' physical characteristics, there is much that remains unknown about its behavior and physiology. As with most extinct creatures, the only way to piece together this information is through studying its fossils.
Based on its tooth structure, it is likely that Jeholosaurus had a browsing feeding behavior. This means that it would have consumed a variety of plants, including leaves, twigs, and possibly fruits. Scientists also speculate that it may have had a specialized digestive system to break down tough plant material, similar to modern-day herbivores such as elephants and rhinos.
But what about its predatory behavior? While many dinosaurs were fierce predators, there is evidence to suggest that Jeholosaurus may not have been one of them. Its lack of typical predatory characteristics, such as sharp teeth and claws, leads scientists to believe that it likely did not hunt other animals for food. This aligns with its herbivorous diet, indicating that Jeholosaurus was a non-predatory dinosaur.
Another intriguing mystery surrounding Jeholosaurus is its maximum speed. Unfortunately, due to the nature of fossil evidence, it is impossible to say how fast this dinosaur could run. However, based on its robust body structure and strong hind legs, it is likely that it was a relatively fast animal. This may have been beneficial for escaping from predators or quickly traversing its forest habitat.
Challenges in Studying Jeholosaurus: Overcoming the Limitations of Fossil Evidence
One of the biggest challenges when it comes to studying Jeholosaurus is the limitation of the fossil record. Unlike living animals, we cannot observe or study these creatures directly. Instead, scientists rely on rare and often incomplete fossilized bones to piece together an understanding of an animal that lived millions of years ago.
In the case of Jeholosaurus, there have been limited fossil findings. This makes it challenging for scientists to draw definitive conclusions about its behavior, physiology, and even its appearance. For example, while we know that it was a forest-dwelling herbivore, we can only speculate on its skin color and other physical features.
Additionally, as with many dinosaurs, there is significant debate surrounding the classification of Jeholosaurus. Some scientists believe it to be a member of the Iguanodontidae family, while others argue that it belongs to the Hadrosauridae family. These ongoing debates highlight the complexities of paleontology and the difficulties in accurately identifying and classifying extinct animals.
Bringing Jeholosaurus Back to Life: The Role of Technology in Understanding This Dinosaur
Despite the limitations of fossil evidence, technology has played a crucial role in helping scientists understand Jeholosaurus and other dinosaurs. In recent years, advancements in technology have allowed for better preservation and analysis of fossilized remains, providing new insights into these ancient creatures.
One of the most significant advancements in paleontology is the use of computer modeling and 3D imaging. With these techniques, scientists can recreate the bones and skeletons of extinct animals and study them in detail. This has allowed for a more accurate understanding of Jeholosaurus' physical characteristics and behavior.
Furthermore, technology has also been instrumental in recreating a realistic depiction of what Jeholosaurus may have looked like. Through the use of advanced imaging software, scientists have been able to map out the muscles and skin texture of this dinosaur, giving us a glimpse into its possible appearance.
Extinction and Legacy: What Happened to Jeholosaurus?
Like all dinosaurs, Jeholosaurus eventually became extinct. While the exact cause of its extinction is unknown, it is believed to have occurred around 120 million years ago, during the Early Cretaceous period. It is possible that climate change, environmental factors, or competition with other dinosaurs all played a role in its decline and ultimate extinction.
Despite its relatively unknown status, Jeholosaurus has made significant contributions to our understanding of dinosaurs. Its discovery has provided valuable insights into the diversity of plant-eating dinosaurs and the forest habitats of the early Cretaceous period. And with ongoing research and advancements in technology, we may uncover even more about this mysterious and elusive creature.
Discovering the World of Jeholosaurus: A Final Word
Dinosaurs may have roamed the earth millions of years ago, but their legacy continues to capture our imagination. From their sheer size to their unique characteristics, these creatures are a testament to the incredible diversity of life on our planet.
Jeholosaurus may not be as well-known as some other dinosaur species, but its impact on paleontology is undeniable. In many ways, it represents the challenges and wonder of studying extinct creatures and the importance of technology in unlocking their secrets. And while there may always be mysteries surrounding Jeholosaurus, its presence reminds us of the incredible diversity and beauty of the natural world.

Jeholosaurus
Dinosaur Details Jeholosaurus - Scientific Name: Jeholosaurus
- Category: Dinosaurs J
- Scientific Name: Jeholosaurus
- Common Name: Jeholosaurus
- Geological Era: Early Cretaceous
- Length: 3 meters
- Height: 1.5 meters
- Weight: 500 kilograms
- Diet: Herbivore
- Feeding Behavior: Browsing
- Predatory Behavior: Non-predatory
- Tooth Structure: Leaf-shaped teeth
- Native Habitat: Forest
- Geographical Distribution: China
- Preferred Temperature: Temperate
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown

Jeholosaurus
- Bone Structure: Unknown
- Reproduction Type: Unknown
- Activity Period: Unknown
- Distinctive Features: Large head with a toothless beak, long neck, and short tail
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Unknown
- Largest Species: Unknown
- Smallest Species: Unknown
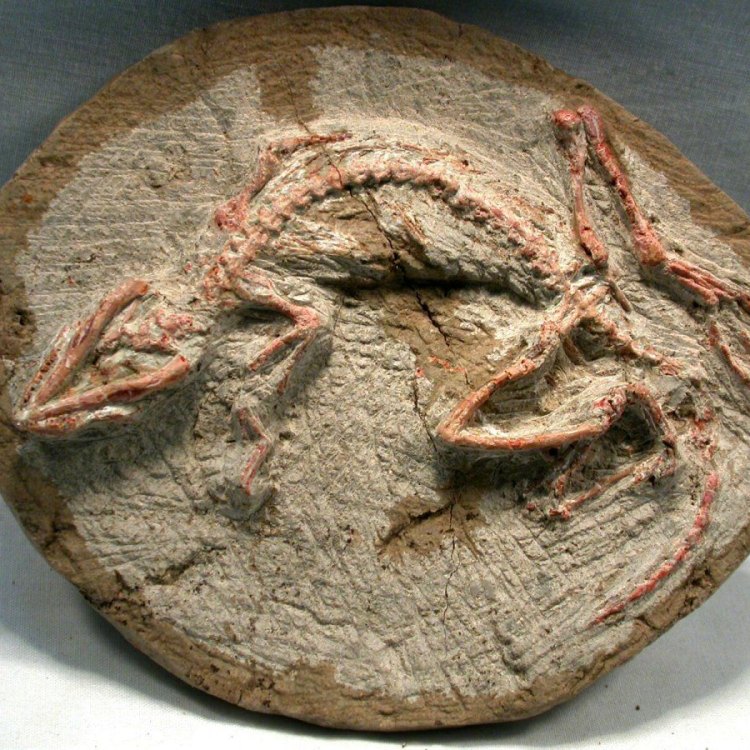
- Fossil Characteristics: Nearly complete skeletons
- Role in Ecosystem: Herbivorous dinosaur, part of the Early Cretaceous ecosystem
- Unique Facts: One of the most primitive ceratopsian dinosaurs
- Predator Status: Non-predatory
- Discovery Location: Liaoning Province, China
- Discovery Year: 2000
- Discoverer's Name: Wang

Jeholosaurus
The Journey of Jeholosaurus: Uncovering the Secrets of an Ancient Dinosaur
Deep in the heart of Liaoning Province in China, a team of researchers made an extraordinary discovery in the year 2000. They stumbled upon an almost complete skeleton of an unknown dinosaur species, giving us a glimpse into the past and unlocking the secrets of an ancient ecosystem.This incredible creature was later identified as Jeholosaurus, and since its discovery, it has intrigued scientists and researchers alike. With its distinctive features and mysterious bone structures, Jeholosaurus has paved the way for new discoveries about the early Cretaceous period, around 120 million years ago OnTimeAiraz.Com.
But who was Jeholosaurus? What made it unique? And what can we learn from its existence? Let's embark on a journey to uncover the secrets of this primitive ceratopsian dinosaur.
Unknown Bone Structure and Reproduction Type
One of the most fascinating aspects of Jeholosaurus is its bone structure, which remains a mystery to this day. Unlike other well-known dinosaurs such as the Tyrannosaurus Rex or the Velociraptor, not much is known about the internal anatomy of Jeholosaurus.
But what we do know is that Jeholosaurus belonged to the ceratopsian family, which includes famous species like the Triceratops and the Styracosaurus. These dinosaurs were known for their distinct facial features, such as horns and frills, but Jeholosaurus was quite different.
The most distinctive feature of Jeholosaurus was its large head with a toothless beak, resembling that of a modern-day parrot. This suggests that Jeholosaurus was an herbivorous dinosaur, relying on plants for survival. Its long neck and short tail also imply that it could reach high vegetation, making it a dominant species in its ecosystem.
Unfortunately, the reproductive habits of Jeholosaurus remain a mystery too Jaxartosaurus. Since no eggs or nests have been discovered, scientists are unable to determine if Jeholosaurus laid eggs like most dinosaurs or if it gave birth to live offspring.
The Unknown Activity Period and Survival Adaptations of Jeholosaurus
Another aspect that remains a mystery is Jeholosaurus's activity period and its survival adaptations. We can only speculate based on its physical features and fossil evidence, but the truth is yet to be uncovered.
Given that Jeholosaurus roamed the Earth during the early Cretaceous period, it is likely that it was most active during the day. This is supported by the fact that many of its relatives, such as the Triceratops, were diurnal animals.
However, its survival adaptations are still a topic of debate. Some theories suggest that Jeholosaurus may have had a thick skin or armor-like plates for protection, but since no fossil evidence has been found, this remains a mystery.
The Mysterious Communication Method of Jeholosaurus
Another intriguing aspect of Jeholosaurus is its communication method. Dinosaurs are known for their vocal communication, with some species producing loud roars and others using calls and honks to communicate with each other.
But with Jeholosaurus, its communication method remains unknown. Its toothless beak, lacking the vocal apparatus, casts doubt on whether it could vocalize at all. Perhaps, it used visual signals or body language to communicate, like some birds today.
Unknown Species Size and Fossil Characteristics
As we continue to uncover more about Jeholosaurus, it is important to note that its size and fossil characteristics are still unknown. Since only nearly complete skeletons have been discovered, it is challenging to determine the exact size range of Jeholosaurus.
Some estimates suggest that it could have been as small as a chicken, while others believe it could have grown up to the size of a sheep. Until more fossils are discovered, it is impossible to determine the largest and smallest species of Jeholosaurus.
However, one thing that has been established is that the fossil characteristics of Jeholosaurus are impressive. The nearly complete skeletons that have been unearthed give us a complete look at the anatomy and structure of this ancient dinosaur, providing valuable information about its way of life.
The Role of Jeholosaurus in the Ecosystem
As an herbivorous dinosaur, Jeholosaurus played a crucial role in the early Cretaceous ecosystem. Its diet consisted of plants, and as a large-bodied animal, it would have played a significant role in the distribution and shaping of vegetation in its environment.
It could have also served as prey for larger predators, such as the carnivorous theropods, or as a competitor for vegetation with other herbivorous species. With its unique features, Jeholosaurus added diversity and richness to the early Cretaceous ecosystem, making it a crucial species for understanding this time period.
The Unique Facts and Non-Predatory Status of Jeholosaurus
Among the many unique facts about Jeholosaurus, one stands out the most - it is one of the most primitive ceratopsian dinosaurs ever discovered. This means that Jeholosaurus belonged to one of the earliest branches of the ceratopsian family tree, making it a crucial species for understanding the evolution and diversification of these dinosaurs.
Moreover, it is believed that Jeholosaurus was a non-predatory species, meaning it did not hunt or prey on other animals. Instead, it survived by feeding on plants and utilizing its physical features for defense against predators.
The Discovery and Discoverer of Jeholosaurus
As we dive deeper into the mysteries surrounding Jeholosaurus, it is worth mentioning the incredible discovery that led to its recognition as a new dinosaur species. In 2000, a man named Wang accidentally stumbled upon a nearly complete skeleton of Jeholosaurus while searching for fossils in China's Liaoning Province.
After careful analysis, researchers were able to conclude that this was a new and unique species, adding to the diversity of dinosaurs during the early Cretaceous period. Since then, some other Jeholosaurus fossils have been discovered, shedding more light on this extraordinary creature.
In Conclusion
Jeholosaurus is a prime example of how every new discovery brings us one step closer to understanding the mysteries of our planet's past. Its distinctive features, unknown bone structure and reproductive type, and mysterious communication and survival adaptations continue to captivate scientists and researchers worldwide.
As we continue to uncover more fossils and make new discoveries, we are sure to learn more about Jeholosaurus and its role in the early Cretaceous ecosystem. Its unique status as one of the most primitive ceratopsian dinosaurs makes it a crucial species in our understanding of dinosaur evolution and the rich diversity of life on Earth.
So let's continue to dig, explore, and discover, for who knows what other incredible creatures await us in the depths of our planet's history.

Jeholosaurus: Unpacking the Mysteries of the Fossilized Forest Giant
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.