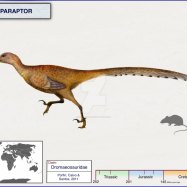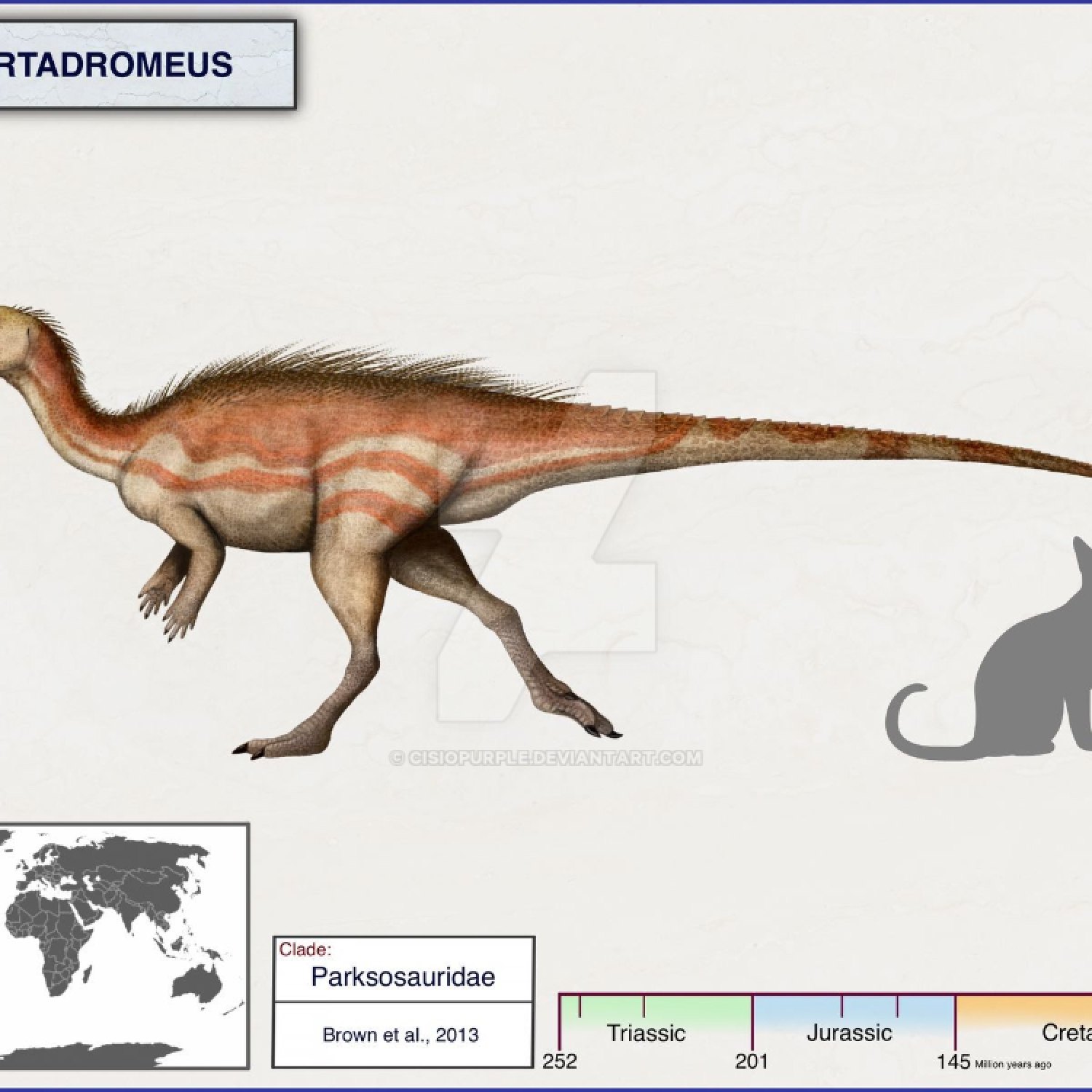
Albertadromeus
Unknown
Discover Albertadromeus, a small, herbivorous dinosaur found in North America. Its striking skin color may remain a mystery, but its maximum speed is not to be underestimated. Learn more about this unique dinosaur and its role in the prehistoric world. #Albertadromeus #dinosaur #herbivore #NorthAmerica #prehistoric #amazinganimals
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Albertadromeus
Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
Feeding Behavior: Herbivore
Dinosaur Discovery: Unveiling the Secrets of Albertadromeus
Imagine a world filled with a diverse range of plants, animals, and dinosaurs. Now, picture a small, agile herbivore roaming around the woodlands and forests of North America during the Late Cretaceous period. This was the world of Albertadromeus, a fascinating and unique species of dinosaur that has recently captured the attention of paleontologists and enthusiasts alike.Meet Albertadromeus, a dinosaur with a scientific name that's just as intriguing as its origin Albertadromeus. Its scientific name, Albertadromeus, is derived from "Alberta," the Canadian province where its fossils were discovered, and "dromeus," which means "runner" in Greek. This small herbivore, measuring about 2 meters in length and standing at a height of 0.6 meters, weighed around 10 kilograms. While it may seem like just another ordinary dinosaur, Albertadromeus has some remarkable characteristics that set it apart from the rest.
Herbivorous Feeding Behavior
One of the key features that make Albertadromeus stand out is its herbivorous diet. While most dinosaurs were either carnivorous or omnivorous, Albertadromeus solely relied on plants for sustenance. Its diet consisted of leaves, fruits, and other vegetation found in its native habitat of woodlands and forests.This feeding behavior also gives us an insight into the ecosystem and food chain during the Late Cretaceous period. It shows that different species of dinosaurs could coexist and thrive while having different diets and occupying different niches in their environment Abydosaurus.
Leaf-shaped Teeth and Non-Predatory Behavior
One might wonder how Albertadromeus, being a herbivore, managed to feed on plants with its sharp and pointed teeth. However, unlike carnivorous dinosaurs that used their teeth for hunting and tearing flesh, Albertadromeus had leaf-shaped teeth that were ideal for grinding vegetation.Its non-predatory behavior and tooth structure served as an adaptation to its herbivorous diet. These features also suggest that it was not a direct ancestor of any modern-day herbivorous dinosaurs. Instead, it was a unique species that evolved to survive and thrive in its environment.
Natural Habitat and Geographical Distribution
The fossils of Albertadromeus were discovered in the Late Cretaceous rocks of Alberta, Canada, hence its scientific name. These rocks were dated to be around 76 million years old, making Albertadromeus one of the youngest dinosaurs to be discovered in this region.Based on its fossil remains, scientists hypothesize that Albertadromeus lived in a woodland and forest environment with moderate temperatures. This suggests that the region where it lived was neither too hot nor too cold, making it ideal for this small herbivore to survive.
The Mystery of its Speed and Skin Color
As with most dinosaur species, there are still some unanswered questions when it comes to Albertadromeus. One of them being its maximum speed. Due to its size and herbivorous nature, it is unlikely that Albertadromeus was a fast runner. However, its agile and light built could have still allowed it to move swiftly to evade predators.Another mystery surrounding this dinosaur is its skin color. Most dinosaur fossils are found without any trace of skin, making it challenging to speculate what colors they might have been. As for Albertadromeus, there is no evidence to suggest its skin color, leaving it to our imaginations.
In Conclusion
Albertadromeus is a perfect example of how even the smallest and seemingly ordinary creatures can have a significant impact on our understanding of the prehistoric world. Its unique features, such as its herbivorous diet, leaf-shaped teeth, and non-predatory behavior, provide us with valuable information about the ecosystems and food chains during the Late Cretaceous period.The discovery of Albertadromeus also serves as a reminder that there is still so much to learn and uncover about our planet's past. With ongoing research and discoveries, who knows what other wonders the world of dinosaurs holds for us.
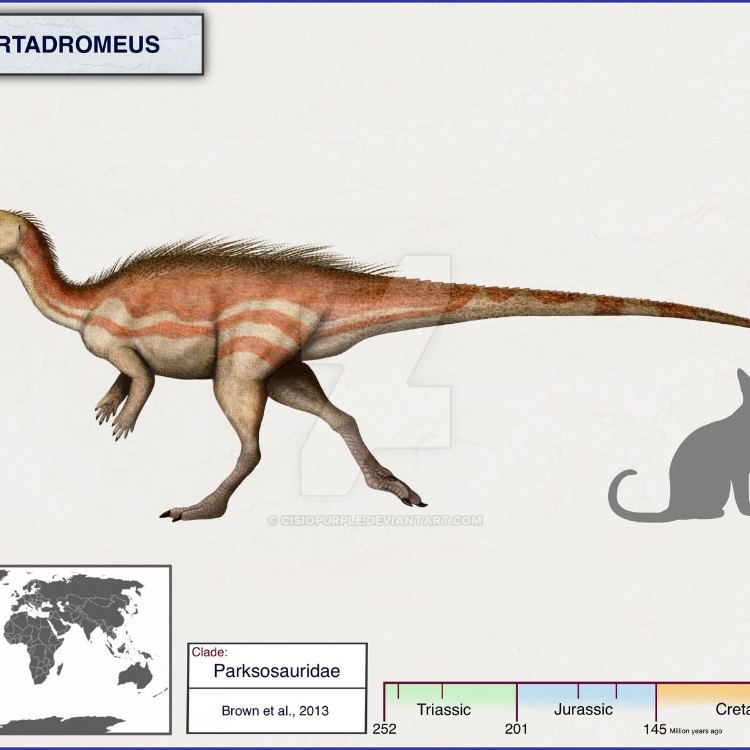
Albertadromeus
Dinosaur Details Albertadromeus - Scientific Name: Albertadromeus
- Category: Dinosaurs A
- Scientific Name: Albertadromeus
- Common Name: Albertadromeus
- Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
- Length: about 2 meters
- Height: about 0.6 meters
- Weight: about 10 kilograms
- Diet: Herbivore
- Feeding Behavior: Herbivore
- Predatory Behavior: Non-predatory
- Tooth Structure: Leaf-shaped teeth
- Native Habitat: Woodlands and forests
- Geographical Distribution: North America
- Preferred Temperature: Moderate
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown
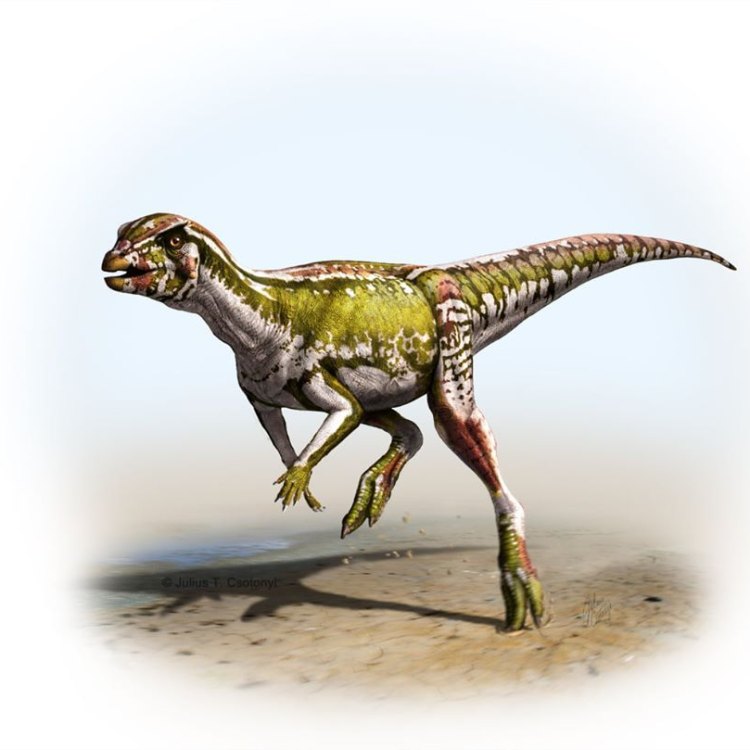

Albertadromeus
- Bone Structure: Lightweight
- Reproduction Type: Egg-laying
- Activity Period: Diurnal
- Distinctive Features: Large eyes, long hindlimbs
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Unknown
- Largest Species: Unknown
- Smallest Species: Unknown
- Fossil Characteristics: Fragmentary remains
- Role in Ecosystem: Unknown
- Unique Facts: The most complete individual found has only a fragment of the skull and a few vertebrae.
- Predator Status: Non-predatory
- Discovery Location: Montana, United States
- Discovery Year: 2012
- Discoverer's Name: Anthony Romilio
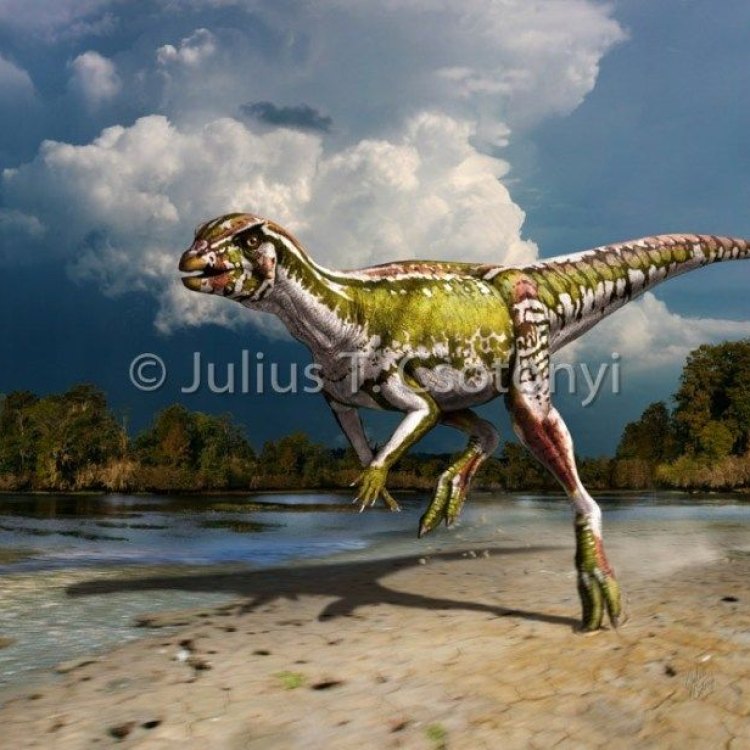

Albertadromeus
The Mysterious and Unique Albertadromeus: Uncovering the Secrets of an Ancient Dinosaur
In 2012, paleontologist Anthony Romilio unearthed a partial skeleton of a small, unknown dinosaur species in Montana, United States. This new discovery would soon be known as Albertadromeus, a name derived from the Latin word "Alberta," the place where it was found, and the Greek word "dromeus," meaning runner. From the little that is known about this ancient creature, one thing is for sure: Albertadromeus is unlike any other dinosaur ever discovered.Bone Structure: Lightweight and Agile
One of the most distinctive features of Albertadromeus is its lightweight bone structure OnTimeAiraz.Com. Unlike its larger and more massive dinosaur cousins, this creature had light and hollow bones, making it agile and swift on its feet. The exact reason for this adaptation is still unknown, but researchers believe it may have been necessary for survival in the competitive and crowded environment of its time.
Reproduction Type: Egg-laying and Diurnal Activity
Like most dinosaurs, Albertadromeus is believed to be an egg-laying species. This means that it would have laid eggs instead of giving birth to live young. Based on the fossil remains found, it is also believed to have been diurnal, meaning it was active during the daytime. This aligns with its lightweight bone structure, which would have provided it with the ability to move quickly during daylight hours.
Distinctive Features: Large Eyes and Long Hindlimbs
Albertadromeus had several unique features that set it apart from other dinosaurs. Its most striking feature was its large eyes, which were positioned towards the sides of its head, giving it a wide field of vision. This adaptation would have been useful in detecting predators or finding food in its environment Albertonykus. Additionally, its long hindlimbs would have enabled it to move quickly and cover long distances, particularly during its active daytime period.
Communication Method: Unknown
While some dinosaurs may have had distinctive calls or other communication methods, nothing is known about how Albertadromeus communicated with other members of its species. Its fragmentary fossil remains offer little clues to its communication methods, leaving this aspect of its behavior as a mystery for researchers to unravel.
Survival Adaptation: Unknown
The exact reason for Albertadromeus' lightweight bone structure and other unique features is still unknown. Researchers can only speculate that these adaptations were necessary for its survival, but what exactly it was adapting to remains a mystery. Some theories suggest that it may have evolved to survive in a fast-moving environment or to evade predators.
Largest and Smallest Species: Unknown
With only a partial skeleton of Albertadromeus discovered, it is challenging to determine the largest and smallest species. These details would require a more complete fossil find, which has yet to be discovered. It is believed that Albertadromeus was a small dinosaur, possibly measuring only a few feet in height, but its exact size remains unknown.
Fossil Characteristics: Fragmentary Remains
Despite the significance of the discovery of an unknown dinosaur species, the most complete Albertadromeus specimen found has only a fragment of the skull and a few vertebrae. This suggests that the remains were most likely scattered after the creature's death, making it challenging to gather a complete understanding of its physical characteristics and behavior. This is also one of the reasons why so little is known about Albertadromeus.
Role in the Ecosystem: Unknown
Without a complete understanding of its anatomy and behavioral patterns, it is challenging to determine Albertadromeus' role in the ecosystem. It is hypothesized that it may have been a herbivore, possibly foraging on smaller plants and vegetation due to its small size. On the other hand, some researchers speculate that it may have been a scavenger, feeding on remnants of larger dinosaur's kills to survive. Until more fossil evidence is discovered, the exact role of Albertadromeus in its ecosystem remains unknown.
Unique Facts: Fragmentary Fossils and Non-predatory Behavior
The most fascinating and unique fact about Albertadromeus is that the most complete individual found was only a fragment of the skull and a few vertebrae. This makes it one of the most elusive and mysterious dinosaurs ever discovered. Moreover, it is believed to have been a non-predatory species, meaning it was not a dominant predator in its environment. Instead, it may have played a different, yet unknown, role in the ecosystem.
Predator Status: Non-predatory
From the fragmentary remains of Albertadromeus, it is difficult to determine its predator status. However, based on its small size and lack of evidence of hunting or predatory behavior, it is considered a non-predatory species. It is more likely that this small dinosaur was a prey species, hunted by larger predators for survival.
Discovery Location and Year: Montana, United States, 2012
In 2012, Anthony Romilio discovered the first partial skeleton of Albertadromeus in Montana, United States. This finding was significant as it marked the discovery of an entirely new dinosaur species, one that had not been seen or studied before. This also meant that there was much to be learned and uncovered about this creature and its place in prehistoric history.
Discoverer's Name: Anthony Romilio
The discovery of Albertadromeus can be attributed to Anthony Romilio, a paleontologist and assistant professor at the University of Queensland. Romilio's passion for the prehistoric world and his expertise in paleontology led him to this groundbreaking discovery, forever cementing his name in the history books of dinosaur discoveries.
In conclusion, the discovery of Albertadromeus has opened up a world of possibilities and mysteries. This small, agile, and elusive dinosaur has intrigued and captivated researchers, paleontologists, and dinosaur enthusiasts alike. With only fragmentary remains to study, it may be challenging to uncover all of its secrets, but it also makes the search all the more exciting. As more discoveries are made and further research is conducted, one thing is for sure: Albertadromeus will continue to fascinate and amaze us with its uniqueness and mysterious past.

Dinosaur Discovery: Unveiling the Secrets of Albertadromeus
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.