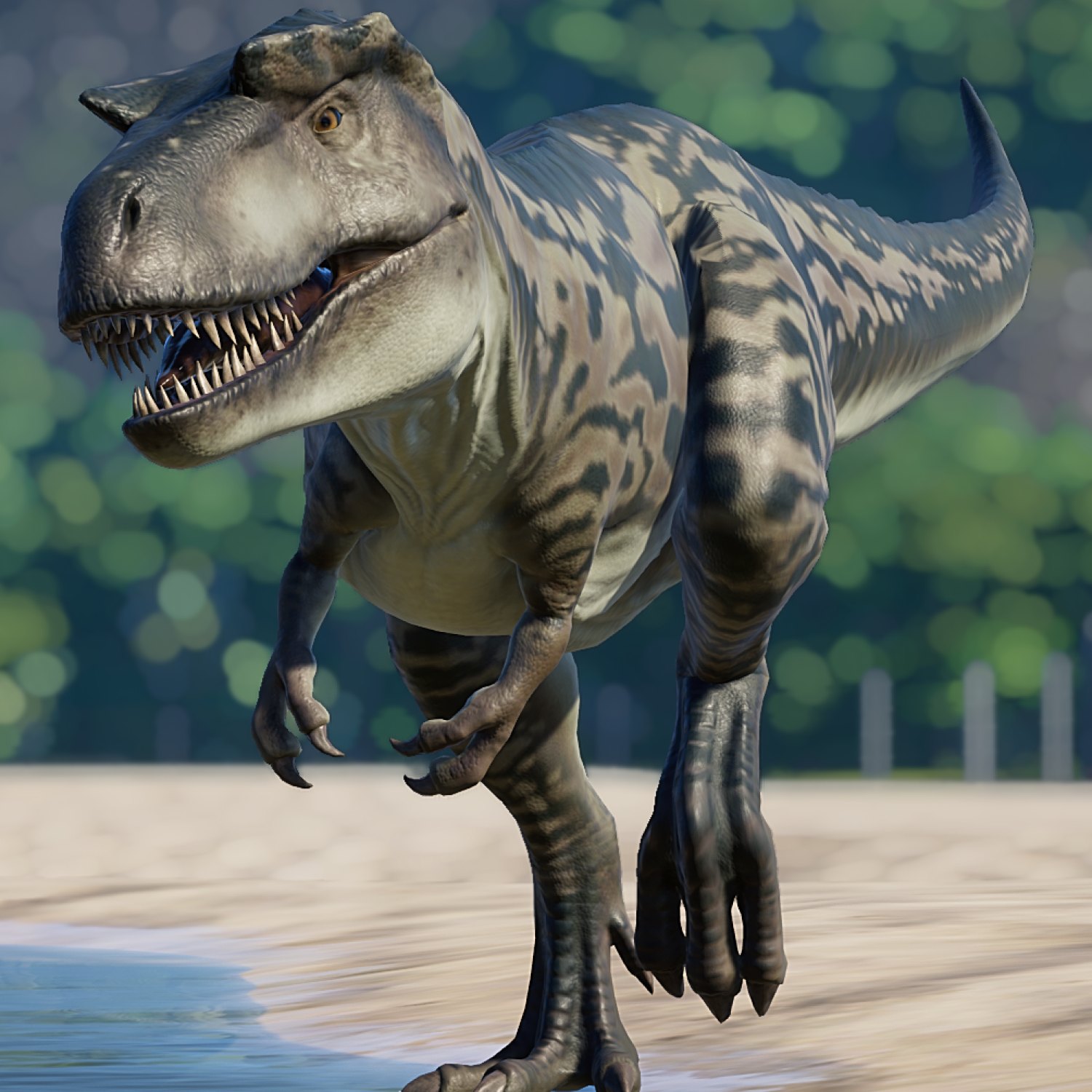
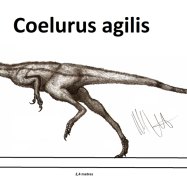
Albertosaurus
Unknown
Did you know that the Albertosaurus, a predatory dinosaur, roamed western North America during the Late Cretaceous period? Its skin color remains a mystery, but scientists believe it was a swift hunter, capable of catching prey with unknown speed. #Albertosaurus #dinosaurs
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Albertosaurus
Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
Feeding Behavior: Active predator
The Fierce Predator of the Late Cretaceous: Albertosaurus
Albertosaurus, a name that may not be as well-known as its larger cousin Tyrannosaurus Rex, but equally as formidable and fascinating. This dinosaur roamed the lands of Western North America during the Late Cretaceous period, approximately 70 million years ago. With its sharp, serrated teeth, impressive size, and cunning hunting abilities, Albertosaurus was a top predator in its native habitat. Let's delve deeper into the features that make Albertosaurus a standout amongst its prehistoric counterparts Albertosaurus.A Name with Significance
Scientifically known as Albertosaurus sarcophagus, this dinosaur was named after the location where its first fossil was discovered - Alberta, Canada. The name Albertosaurus translates to "Alberta lizard," while its species name, sarcophagus, means "flesh-eating." This carnivorous beast certainly lived up to its name, and paleontologists have uncovered numerous fossils of Albertosaurus, providing a wealth of information about this captivating species.Size, Height, and Weight
One of the most noticeable features of Albertosaurus is its large size. This dinosaur measured around 9 to 10 meters in length, making it shorter in comparison to its more famous cousin, the T-Rex, which could reach lengths of up to 12 meters. However, Albertosaurus made up for its slightly smaller length with an impressive height of 3-4 meters, and it was estimated to weigh between 2 to 3 tons. To put that into perspective, it was approximately as heavy as a modern-day African elephant.A Carnivorous Diet
As a carnivorous dinosaur, Albertosaurus had a distinctly different diet from its herbivorous counterparts. Instead of feeding on plant matter, this predator hunted and consumed other dinosaurs, small mammals, and possibly even other reptiles Australodocus. Its strong jaws and sharp, serrated teeth were perfectly designed for tearing through flesh, making it a fearsome and efficient hunter.Active Predator and Group Hunting
Unlike other dinosaurs that may have been passive hunters, Albertosaurus was an active predator that actively pursued its prey. This behavior was further enhanced by its ability to hunt cooperatively in groups. Yes, you read that right - Albertosaurus were social creatures that lived and hunted in packs. This made them an even more effective predator, especially when targeting larger and more dangerous prey.The King of Its Territory
Albertosaurus was a dominant species in its native habitat, which spanned across Western North America. This region was mostly covered in forests, with temperate to subtropical climates, making it an ideal environment for this dinosaur to flourish. With the abundance of food sources, including other dinosaurs, this predator ruled the land with its hunting prowess.The Mystery of Their Speed and Skin Color
One of the challenges of studying extinct creatures like dinosaurs is piecing together information from fossils and other evidence. Unfortunately, when it comes to Albertosaurus, there is not much known about its speed or skin color. Paleontologists have not yet discovered any evidence that can provide an accurate estimate of how fast it could move, but some speculate it could run at a speed of up to 40-45 kilometers per hour. As for its skin color, scientists have been unable to determine it due to the limited preservation of soft tissue in fossils.A Survivor Until the End
The Late Cretaceous period was a time of great change and instability, and many species of dinosaurs struggled to adapt to the rapidly changing environment. However, Albertosaurus was a resilient species, and it survived until the very end of the Cretaceous period, when a massive extinction event wiped out 75% of all animal and plant species on Earth, including the non-avian dinosaurs.In Conclusion
Albertosaurus may not have the same recognition as other dinosaurs, but its unique features and hunting abilities make it a fascinating subject of study. With its sharp, serrated teeth, impressive size, and social hunting behavior, this predator was a formidable force in the Late Cretaceous period. Although many mysteries still surround this species, it is clear that Albertosaurus was a fierce and successful predator that roamed the lands of Western North America with confidence and dominance.
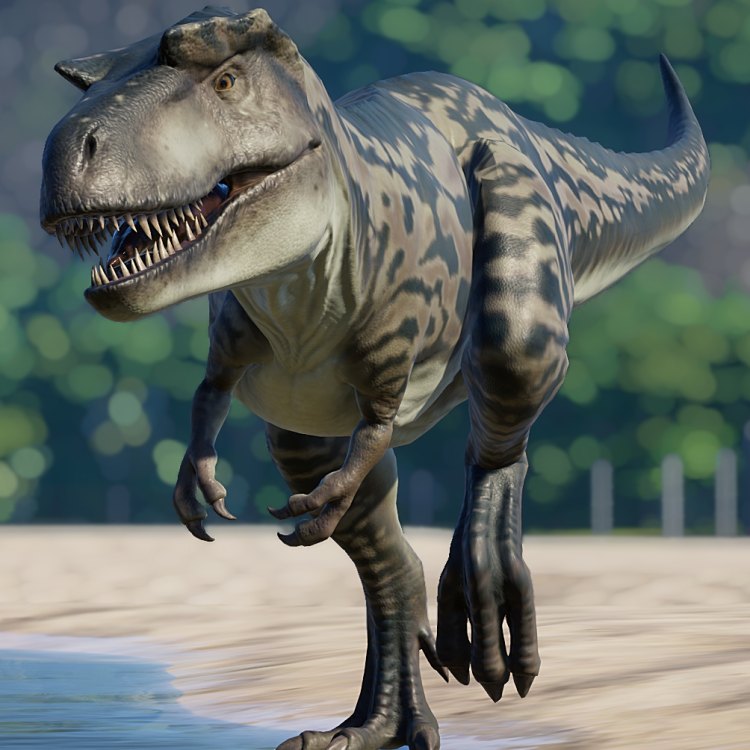

Albertosaurus
Dinosaur Details Albertosaurus - Scientific Name: Albertosaurus sarcophagus
- Category: Dinosaurs A
- Scientific Name: Albertosaurus sarcophagus
- Common Name: Albertosaurus
- Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
- Length: 9-10 meters
- Height: 3-4 meters
- Weight: 2-3 tons
- Diet: Carnivorous
- Feeding Behavior: Active predator
- Predatory Behavior: Hunting in groups
- Tooth Structure: Sharp and serrated
- Native Habitat: North America
- Geographical Distribution: Western North America
- Preferred Temperature: Temperate to subtropical
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown

Albertosaurus
- Bone Structure: Light and hollow bones
- Reproduction Type: Egg-laying
- Activity Period: Diurnal
- Distinctive Features: Narrow skull and long lower legs
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Large size and powerful jaws
- Largest Species: Albertosaurus sarcophagus
- Smallest Species: Unknown
- Fossil Characteristics: Fossilized bones
- Role in Ecosystem: Top predator in its ecosystem
- Unique Facts: Close relative of Tyrannosaurus rex
- Predator Status: Apex predator
- Discovery Location: Alberta, Canada
- Discovery Year: 1884
- Discoverer's Name: Joseph Burr Tyrrell

Albertosaurus sarcophagus
The Mighty Albertosaurus: A Top Predator of Prehistoric Times
The world of dinosaurs is a fascinating one, filled with towering creatures that roamed the earth millions of years ago. Among these ancient giants is the Albertosaurus, a fierce predator that ruled the North American landscape during the Late Cretaceous period. The name Albertosaurus, derived from the Latin word "Alberta" (the Canadian province where it was first discovered) and the Greek word "sauros" (meaning lizard), is a fitting title for this remarkable creature.Albertosaurus, scientifically known as Albertosaurus sarcophagus, is a unique genus of theropod dinosaur from the tyrannosaur family OnTimeAiraz.Com. It is famous for its close relation to the iconic Tyrannosaurus rex, often referred to as its "younger cousin." However, despite this association, the Albertosaurus has many distinctive features that set it apart from other tyrannosaurs.
One of the most striking characteristics of the Albertosaurus is its bone structure. Unlike other theropods, it had light and hollow bones, similar to those of birds. This adaptation made it lightweight, allowing it to move swiftly and efficiently while hunting its prey. Additionally, the hollow bones aided in regulating its body temperature, making it easier for the Albertosaurus to survive in diverse environments.
Another significant aspect of the Albertosaurus is its reproductive method. This theropod was an egg-laying species, meaning it laid eggs to reproduce. Fossil evidence suggests that the Albertosaurus built nests to incubate and protect its eggs, much like modern-day birds Atrociraptor. This fact highlights yet another connection between the Albertosaurus and birds, further solidifying its classification as a feathered theropod.
The Albertosaurus was also a diurnal creature, active during the day. This means that it was awake and active while the sun was up and rested at night. This could have been a survival adaptation to avoid competing with other carnivorous dinosaurs, such as the larger and more powerful Tyrannosaurus rex, which is believed to have been primarily active at night.
One of the most distinctive features of the Albertosaurus is its narrow skull and long lower legs. The skull was significantly shorter and narrower than that of its relative, the T. rex, but still had a formidable bite force. Its long legs made it an agile and fast-moving predator, capable of chasing down its prey with ease. The combination of these features made the Albertosaurus a fearsome and efficient hunter.
Despite being a dominant predator, very little is known about the communication methods of the Albertosaurus. Unlike other species of dinosaurs, such as the recently discovered raptor Vocalizations of the Albertosaurus remain a mystery, with only speculation and theories to go by.
One of the most notable survival adaptations of the Albertosaurus was its size and powerful jaws. Standing at an average of 9 meters in length and weighing over 2,000 kilograms, it was one of the largest theropods of its time. Its powerful jaws, equipped with sharp teeth, allowed it to take down even the largest of prey, making it a top predator in its ecosystem.
The Albertosaurus sarcophagus was the largest known species of the genus, with smaller species being unknown. However, the discovery of juvenile fossils suggests that the Albertosaurus had a significant size difference between genders, with females being smaller than males. This theory has been supported by the discovery of a previous "largest species" that was later proven to be a male Albertosaurus.
The discovery of Albertosaurus fossils has been instrumental in understanding the role this carnivorous dinosaur played in its ecosystem. As a top predator, it was an essential part of the food chain, regulating the populations of herbivorous dinosaurs such as Edmontosaurus and hadrosaurs. Its presence would have had a significant influence on the structure and balance of the ecosystem.
Another unique fact about the Albertosaurus is its close relation to the Tyrannosaurus rex, arguably the most famous dinosaur of all time. Although smaller and with some physical differences, the two are closely related and share many similarities. This has led to the belief that the Albertosaurus served as an evolutionary link between smaller tyrannosaurs and the formidable T. rex.
As an apex predator, the Albertosaurus was at the top of the food chain, with no natural predators to worry about. Its powerful jaws and sharp teeth made it a formidable opponent, dominating the landscape as the ultimate predator. This fact, combined with its size, made the Albertosaurus a feared and respected creature in prehistoric times.
The first Albertosaurus fossil was discovered in 1884 by a young Canadian geologist and explorer, Joseph Burr Tyrrell. While on an expedition in the Red Deer Valley of Alberta, Canada, Tyrrell uncovered a tooth, which he initially thought belonged to a carnivorous marine reptile. However, further excavation led to the discovery of more fossils, and in 1889, paleontologist Henry Fairfield Osborn officially named the new species Albertosaurus sarcophagus.
Since then, numerous fossils of the Albertosaurus have been discovered in the Western United States and Canada, including the famous Dinosaur Provincial Park in Alberta. These fossils have provided a wealth of information about this remarkable predator, allowing scientists to piece together its history, behavior, and appearance.
In conclusion, the Albertosaurus was a formidable creature, known for its size, unique bone structure, and powerful jaws. Its close relation to the iconic T. rex and its influence on the ecosystem of its time has earned it a well-deserved place in the spotlight. Thanks to the tireless work of scientists, we continue to learn more about this incredible predator, further expanding our understanding of the wonderful world of dinosaurs.

The Fierce Predator of the Late Cretaceous: Albertosaurus
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.