Ampelosaurus
Unknown
Ampelosaurus, a herbivorous dinosaur found in Southern Europe, is shrouded in mystery with an unknown skin color and maximum speed. Despite this, its discovery in Cretaceous fossils has provided valuable insights into the diversity of dinosaurs in Europe. Join us as we unravel the enigma of Ampelosaurus and its importance in the world of paleontology. #DinosaurFact #Ampeloasaurus #SouthernEurope #Herbivore
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Ampelosaurus
Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
Feeding Behavior: Browsing
The Magnificent Ampelosaurus: A Giant of the Late Cretaceous
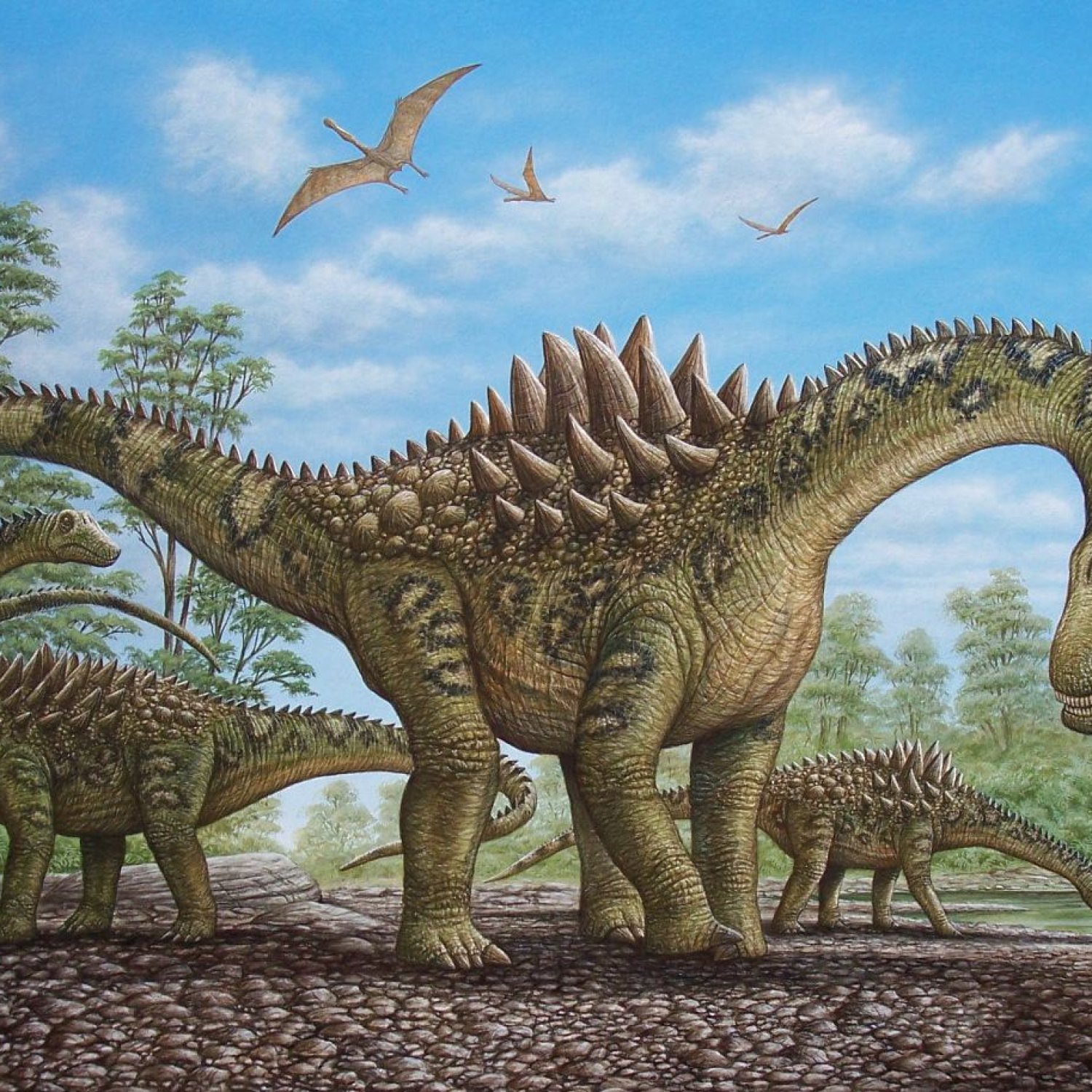
Ampelosaurus – it might be a name that you have never heard before, but this majestic dinosaur is certainly one worth knowing about. With a length of 12 meters, a height of 4 meters, and a weight of 6 tons, the Ampelosaurus was truly a giant of its era, the Late Cretaceous. This herbivorous behemoth roamed the woodlands of Southern Europe, its leaf-shaped teeth perfectly adapted for browsing on the plentiful vegetation.In this article, we will delve into the world of the Ampelosaurus, exploring its physical characteristics, behavior, and habitat Ampelosaurus. So, let's get started and discover the wonders of this magnificent creature.
Meet the Ampelosaurus: Scientific Name, Geological Era, and Distribution
The Ampelosaurus was first discovered in 1989 in the town of Cruzy, in the Hérault region of France. Its scientific name, Ampelosaurus, comes from the Greek words “ampelos” meaning vine and “sauros” meaning lizard, a nod to the fact that its fossils were found in a vineyard.
This impressive dinosaur lived during the Late Cretaceous period, which spans from 99 to 66 million years ago. This era was dominated by dinosaurs, including the famous T-Rex and Triceratops. However, the Ampelosaurus was not the biggest of its kind, as it coexisted with other larger sauropods, such as Argentinosaurus and Alamosaurus.
The Ampelosaurus was mainly found in Southern Europe, specifically in France and Spain. This geographical distribution suggests that this dinosaur preferred a warmer climate, but the exact temperature range it thrived in is still unknown. Its fossils were preserved in the woodlands, providing us with a glimpse into its native habitat Amargasaurus.
Size and Appearance: A Giant of the Late Cretaceous
As mentioned earlier, the Ampelosaurus was no tiny creature. Its estimated size of 12 meters in length could rival some of the biggest dinosaurs of its time. With a height of 4 meters, it stood as tall as a two-story building, and its weight of 6 tons was equivalent to the weight of approximately four cars.
Despite its massive size, the Ampelosaurus was relatively lightweight for a sauropod, mainly due to its slender body. Its long neck, which made up half of its body length, allowed it to reach for the vegetation and browse on plants with ease.
This dinosaur had a distinctive feature that truly made it stand out – its leaf-shaped teeth. These teeth were adapted for grinding and shredding plants, which made them perfectly suited for the Ampelosaurus's herbivorous diet. While we do not know its exact feeding behavior, it is believed to have been a browser, slowly moving through the woodlands to find the best plants to eat.
Not a Hunter, but Not Hunted Either: The Predatory Behavior of the Ampelosaurus
Despite its impressive size, the Ampelosaurus was not a predator. It was a peaceful herbivore that spent its days peacefully browsing on plants. It did not possess any traits that would have made it a successful hunter, such as sharp teeth or claws.
However, this does not mean that the Ampelosaurus was completely defenseless. Its massive size alone would have served as a deterrent to any potential predators. Additionally, its strong, muscular tail could have been used as a weapon to fend off any attackers.
Mysterious Skin Color and Unknown Maximum Speed: What We Still Don't Know About the Ampelosaurus
While we have learned a lot about the Ampelosaurus, there is still much that we do not know. For example, we have no idea what color its skin was. Without fossil evidence, it is hard to determine the skin color of any dinosaur, and the Ampelosaurus is no exception.
Another mystery surrounding this dinosaur is its maximum speed. Without complete skeletal remains, it is difficult to estimate its walking or running speed. However, researchers believe that it would not have been the fastest sauropod, with its heavy body size and slow, browsing behavior.
Incredible Adaptations: How the Ampelosaurus Survived in Its Environment
Despite not having any obvious predator defenses, the Ampelosaurus still managed to dominate its environment. How did it survive in such a dangerous world?
One theory suggests that the Ampelosaurus lived in herds, an adaptation that would have increased its survival chances. By living in groups, the dinosaurs would have been able to look out for each other and warn of potential danger. Additionally, this behavior would have helped them reproduce, ensuring the survival of their species.
Furthermore, the Ampelosaurus had a unique adaptation for a sauropod – its teeth. Its leaf-shaped teeth were an excellent tool for grinding plants, allowing the dinosaur to maximize its food intake. This would have been especially beneficial during the dry season when food may have been scarce.
Reviving the Past: How Science Is Uncovering the Secrets of the Ampelosaurus
Thanks to advancements in technology and the hard work of paleontologists, we are getting a better understanding of the Ampelosaurus with each passing day. Through the use of computer models and 3D imaging, scientists are able to reconstruct the dinosaur's appearance, behavior, and even its habitat.
Additionally, the discovery of new fossils, such as a nearly complete skeleton in 2007, is providing valuable insights into this giant from the Late Cretaceous. By piecing together these discoveries, we are able to unravel more of the mysteries surrounding the Ampelosaurus and gain a better understanding of this remarkable creature.
In Conclusion
Ampelosaurus – a name that may not roll off the tongue but is certainly one worth knowing about. With its impressive size, unique teeth, and peaceful nature, this sauropod was an incredible creature that roamed the woodlands of Southern Europe during the Late Cretaceous period. Although there is still much that we do not know about the Ampelosaurus, science continues to unravel its mysteries, allowing us to get a glimpse into the fascinating world of this magnificent dinosaur.
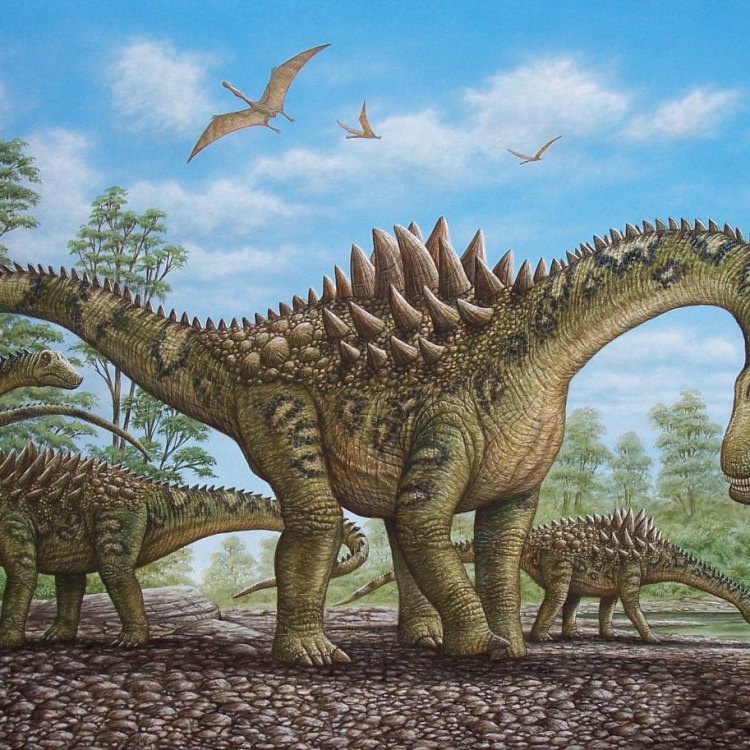

Ampelosaurus
Dinosaur Details Ampelosaurus - Scientific Name: Ampelosaurus
- Category: Dinosaurs A
- Scientific Name: Ampelosaurus
- Common Name: Ampelosaurus
- Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
- Length: 12 meters
- Height: 4 meters
- Weight: 6 tons
- Diet: Herbivorous
- Feeding Behavior: Browsing
- Predatory Behavior: Non-predatory
- Tooth Structure: Leaf-shaped teeth
- Native Habitat: Woodlands
- Geographical Distribution: Southern Europe
- Preferred Temperature: Unknown
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown
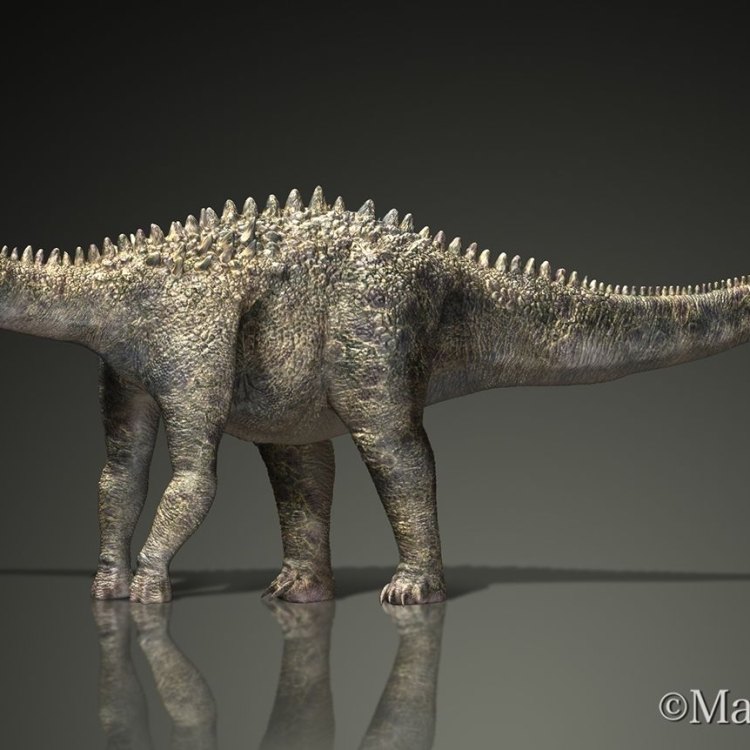

Ampelosaurus
- Bone Structure: Sauropod-like
- Reproduction Type: Egg-laying
- Activity Period: Diurnal
- Distinctive Features: Long neck, long tail, four-legged
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Unknown
- Largest Species: Ampelosaurus atacis
- Smallest Species: Unknown
- Fossil Characteristics: Incomplete fossil remains
- Role in Ecosystem: Herbivore, part of the food chain
- Unique Facts: One of the last surviving sauropods in Europe
- Predator Status: Non-predatory
- Discovery Location: France
- Discovery Year: 1989
- Discoverer's Name: Sanz, et al.
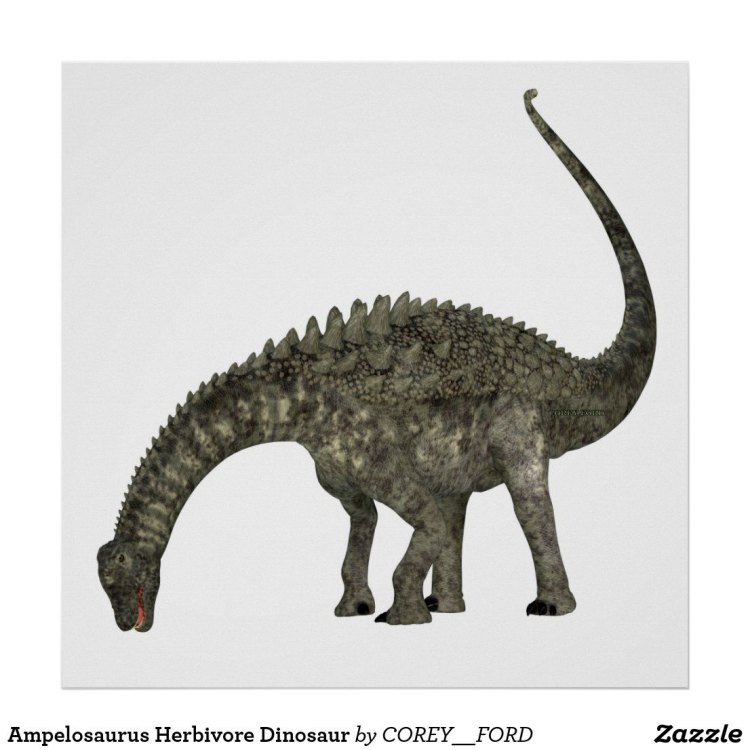

Ampelosaurus
The Last of the European Sauropods: The Enigmatic Ampelosaurus
The prehistoric world was once dominated by immense, long-necked giants known as sauropods. These massive creatures roamed the earth for over 140 million years, from the Late Triassic to the end of the Cretaceous period. While most sauropods were found in North America and Africa, there were also a few species that inhabited Europe. Of all the European sauropods, Ampelosaurus stands out as one of the last and most enigmatic survivors OnTimeAiraz.Com. In this article, we will dive into the fascinating world of Ampelosaurus and uncover some of its unique features and mysteries.Bone Structure and Identification
Ampelosaurus, which translates to "vineyard lizard," is a genus of herbivorous sauropod dinosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous period, around 70-66 million years ago. Its fossil remains were first discovered in Southern France in 1989 by paleontologist Josep Antoni Sanz and his team. The genus name is derived from "Ampelos," the Greek word for vine, as the bones were found in an area that was once used for growing grapes.Being a sauropod, Ampelosaurus had a distinctively long neck, measuring about 13 feet, and a long tail to counterbalance its large body. Its four-legged structure was characteristic of all sauropods, with the hind legs being longer than the front. This structure allowed them to stand upright and reach for foliage high up in trees. Ampelosaurus is estimated to have grown to about 50-60 feet in length and weighed around 10-15 tons, making it one of the largest sauropods in Europe.
Reproduction and Activity
Ampelosaurus, like all sauropods, was egg-laying, or oviparous Agustinia. This means that they laid eggs instead of giving birth to live young. The eggs were small, about the size of a watermelon, and were usually laid in clusters or buried in nests. The exact number of eggs laid by Ampelosaurus is unknown, but it is estimated to be between 20-40 eggs per clutch.Ampelosaurus was also diurnal, meaning that it was most active during the day and slept at night. This is a common characteristic among herbivorous dinosaurs as they needed to constantly forage for food. Being diurnal also meant that they had to deal with the threat of predators during the day, which influenced their behavior and survival adaptations.
Communication and Survival Adaptations
The communication method of Ampelosaurus is unknown, as is the case with many long-extinct species. Some scientists believe that they communicated through low-frequency vocalizations, while others suggest that they may have used visual displays such as head movements and tail flicking. Whatever the case may be, communication was essential for Ampelosaurus to interact with its own kind and for potential mating purposes.Survival adaptations of Ampelosaurus are also somewhat of a mystery. Being a large herbivore, it certainly faced the threat of predators such as theropod dinosaurs. To protect itself, Ampelosaurus may have used its long neck and tail to make it difficult for predators to attack or reach its vital organs. It may have also traveled in herds to increase its chances of survival, as being in a group offers more eyes and protection against predators.
Largest and Smallest Species
The largest known species of Ampelosaurus is the Ampelosaurus atacis, which was discovered in southern France and named in 2007. This species is estimated to have grown to a length of 60 feet and weighed around 20 tons, making it a true giant among European dinosaurs.The smallest species of Ampelosaurus is currently unknown. Since the fossil record for this genus is incomplete, it is challenging to determine the size of smaller species accurately. However, scientists believe that there may have been smaller species of Ampelosaurus that have yet to be discovered.
Fossil Characteristics and Discoverer
The main reason why so little is known about Ampelosaurus is because of the incomplete fossil remains. Most of the fossils discovered so far consist of incomplete or fragmentary bones, making it difficult to fully understand this species. Only a few fairly intact specimens have been found, and even those lack certain crucial parts, such as the skull and teeth.The first fossils of Ampelosaurus were found in the southern French village of Campagne-sur-Aude in 1989 by a team of paleontologists led by Josep Antoni Sanz. These remains were classified as a new species and were named Ampelosaurus atacis in 2007. Since then, several more fossil discoveries have been made, but there is still much to be learned about this elusive dinosaur.
Role in the Ecosystem
As a herbivore, Ampelosaurus played an essential role in the ecosystem as part of the food chain. Its diet consisted of plants, including conifers, cycads, ferns, and various flowering plants. Being a large sauropod, it likely consumed large quantities of vegetation, helping to shape and control the plant life in its environment. It is also possible that it served as a seed disperser, unintentionally spreading seeds through its droppings.Ampelosaurus was also prey for larger predators, such as theropod dinosaurs, which kept the herbivore population in check and maintained balance in the ecosystem. The discovery of the well-preserved remains of a juvenile Ampelosaurus, with signs of being attacked by a theropod, is evidence that it was indeed a potential target for predators.
Unique Facts
Ampelosaurus is one of the last surviving sauropods in Europe, living near the end of the Cretaceous period. This makes it a crucial link in the understanding of the evolution and extinction of sauropods, which are some of the most iconic and mysterious creatures to ever walk the earth. Its discovery has shed light on the diversity and distribution of these giant dinosaurs, providing significant insights into their world and their place in history.Apart from being one of the last sauropods in Europe, Ampelosaurus is also unique because of its discovery location and the circumstances surrounding it. The fossils were found in a vineyard, which is not a typical area for paleontologists to search for dinosaur remains. This adds an interesting element to the story behind the discovery and showcases how fossils can be found in the most unexpected places.
Predator Status
Ampelosaurus is classified as a non-predatory dinosaur, meaning that it did not hunt or actively prey on other animals. Its sharp, peg-like teeth were primarily used for grazing and chewing plant matter. However, young or weakened Ampelosaurus may have been at risk of becoming prey for larger predators, highlighting the harsh reality of survival in the prehistoric world.Conclusion
In conclusion, Ampelosaurus is a fascinating dinosaur with many unique features and mysteries. Its bone structure, egg-laying, and diurnal activity set it apart from other sauropods, making it an intriguing subject for paleontologists. The incomplete fossil remains pose a challenge to fully understanding this species, but its role in the ecosystem and its place in history cannot be denied. With ongoing research and future fossil discoveries, we may uncover even more about this enigmatic dinosaur and its incredible story.
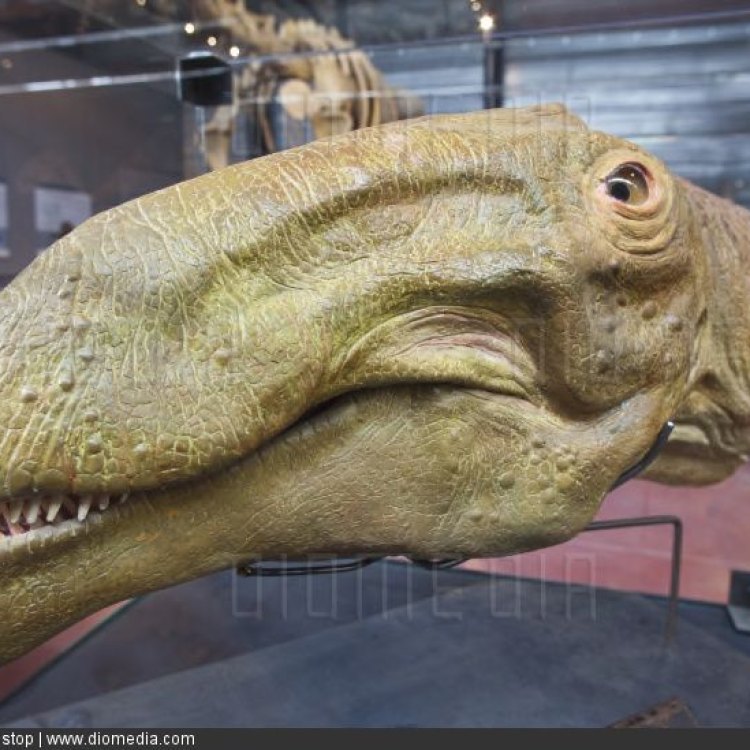

The Magnificent Ampelosaurus: A Giant of the Late Cretaceous
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.