Archaeornithomimus
Unknown
Meet the Archaeornithomimus, a dinosaur from the Cretaceous period known for its swift speed and herbivorous diet. Native to Mongolia, this dinosaur's skin color remains a mystery. Discover more about this fascinating creature and its place in history! #Dinosaur #Archaeornithomimus #Paleontology
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Archaeornithomimus
Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
Feeding Behavior: Omnivorous
Unveiling the Mysteries of the Archaeornithomimus: A Fascinating Herbivore of the Late Cretaceous Period
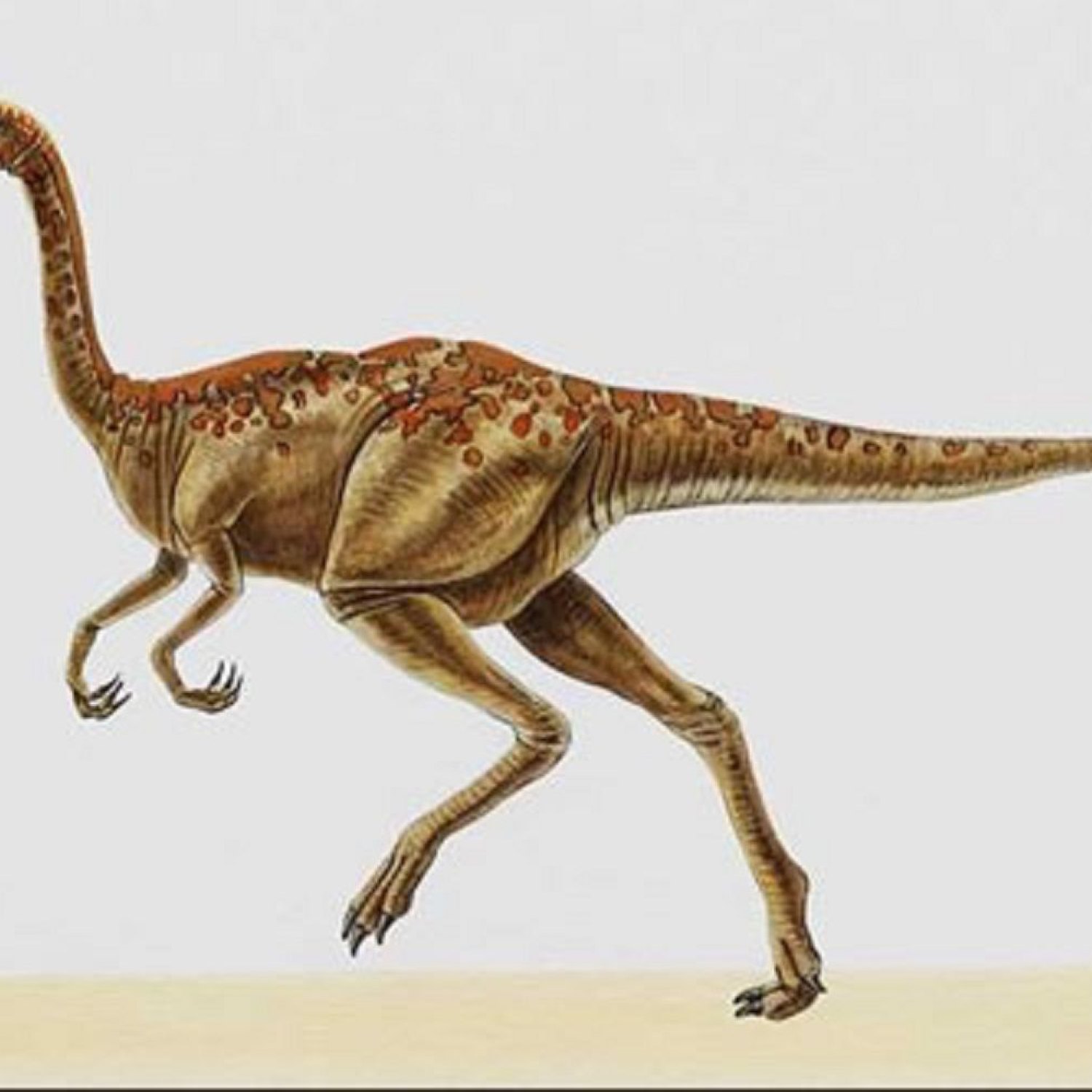
In the vast expanse of the Late Cretaceous period, a time when dinosaurs roamed the Earth, there was a creature that stood out among its counterparts. Introducing the Archaeornithomimus - a herbivorous dinosaur that dwelled in the plains and forests of Mongolia. The name Archaeornithomimus is derived from the Greek words "archaios" meaning ancient, "ornithos" meaning bird, and "mimos" meaning mimic. This translates to “ancient bird mimic,” which accurately describes this remarkable creature's appearance Archaeornithomimus.Belonging to the family Ornithomimidae, the Archaeornithomimus was a bipedal dinosaur that shared many similarities with modern-day birds. With a length of 3-4 meters and a height of 1-1.5 meters, it was a moderate-sized dinosaur, weighing between 200-400 kilograms. Its large size allowed it to graze on vegetation from ground level, making it an easy target for predators. However, its unique characteristics helped it survive and thrive in its native habitat.
Physical Features and Behavior
At first glance, the Archaeornithomimus might seem like just another bird-like dinosaur, but a closer look reveals its distinctive features. Starting with its toothless beak, it is clear that this dinosaur was a herbivore. Its beak was specialized for plucking and stripping leaves, a behavior similar to modern-day birds like turkeys and chickens. Its feeding behavior was also omnivorous, meaning it consumed a variety of plant material, including seeds, fruits, and nuts Albalophosaurus.Unlike some of its carnivorous counterparts, the Archaeornithomimus was non-predatory. It was a peaceful and gentle creature that relied on its speed and agility to escape from potential threats. Unfortunately, due to the lack of fossil evidence, it is still unknown how fast this dinosaur could run, but its body proportions and limb structure suggest that it could have traveled at high speeds.
The Archaeornithomimus had an elongated and slender body, similar to ostriches, but with longer legs. Its hind limbs were powerful, and its feet were specialized with long, sharp claws that helped it maintain balance and traction when running. These adaptations demonstrate the dinosaur's ability to move efficiently on both flat and uneven terrain, making it a formidable prey.
Native Habitat and Distribution
The plains and forests of Mongolia were the primary home of the Archaeornithomimus. These regions were rich in vegetation, providing an abundant food source for the herbivorous dinosaur. Its geographical distribution was limited to this area, with no evidence of its existence being found in any other part of the world.During the Late Cretaceous period, the climate in Mongolia was warm and humid, with a moderate temperature that was suitable for the Archaeornithomimus. Being a cold-blooded reptile, this dinosaur relied on the external environment to maintain its body temperature, making the temperature fluctuations too cold or too hot for its survival.
Uncovering the Mysteries and Experiments
Despite the numerous fossil records of the Archaeornithomimus that have been discovered, there are still many mysteries surrounding this fascinating creature. One of the biggest questions is its maximum speed, which is still unknown, leaving room for speculation and debates among experts.To uncover more information about this dinosaur, experiments have been conducted to analyze its physical abilities. Through computer-simulated models, researchers have estimated that the Archaeornithomimus could run at a speed of 64 kilometers per hour, making it one of the fastest dinosaurs of its time. However, these findings are not conclusive and remain a topic of ongoing research.
The Importance of the Archaeornithomimus
The Archaeornithomimus may not be as well-known as other famous dinosaurs like Tyrannosaurus Rex or Velociraptor, but its significance is undeniable. It provides invaluable insights and knowledge about the evolution and adaptation of dinosaurs, especially regarding their similarities to modern birds. Its unique tooth structure and feeding behavior have also helped scientists better understand and classify other herbivorous dinosaurs.Moreover, the Archaeornithomimus plays an essential role in educating and fascinating people about the fascinating world of dinosaurs. Its bird-like characteristics and peaceful nature have made it a fan-favorite among children and adults alike, with its image often being featured in books, movies, and other forms of media.
In Conclusion
The Archaeornithomimus may have lived during the Late Cretaceous period, but its existence continues to pique the interest and curiosity of people even today. With its bird-like features and herbivorous diet, this dinosaur was a unique and fascinating creature that roamed the Earth millions of years ago. Its discovery has contributed immensely to the field of paleontology, helping us better understand the wonders of the prehistoric world.The mysteries surrounding the Archaeornithomimus may not all be revealed yet, but its legacy will continue to captivate and educate generations to come. So, the next time you see a bird, remember that they have a distant relative who once roamed the plains and forests of Mongolia as a majestic and awe-inspiring dinosaur – the incredible Archaeornithomimus.
Archaeornithomimus
Dinosaur Details Archaeornithomimus - Scientific Name: Archaeornithomimus
- Category: Dinosaurs A
- Scientific Name: Archaeornithomimus
- Common Name: Archaeornithomimus
- Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
- Length: 3-4 meters
- Height: 1-1.5 meters
- Weight: 200-400 kilograms
- Diet: Herbivorous
- Feeding Behavior: Omnivorous
- Predatory Behavior: Non-predatory
- Tooth Structure: Toothless
- Native Habitat: Plains and forests
- Geographical Distribution: Mongolia
- Preferred Temperature: Moderate
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown

Archaeornithomimus
- Bone Structure: Lightweight
- Reproduction Type: Egg-laying
- Activity Period: Diurnal
- Distinctive Features: Long limbs and hind feet for fast running
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Fast and agile for defense
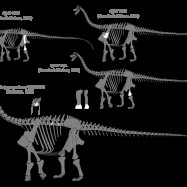
- Largest Species: Archaeornithomimus asiaticus
- Smallest Species: Archaeornithomimus senticolis
- Fossil Characteristics: Complete skeletons and trace fossils
- Role in Ecosystem: Herbivore in Late Cretaceous ecosystems
- Unique Facts: May have been able to run at high speeds
- Predator Status: Non-predatory
- Discovery Location: Mongolia
- Discovery Year: 1972
- Discoverer's Name: Sergei Mironovich Kurzanov
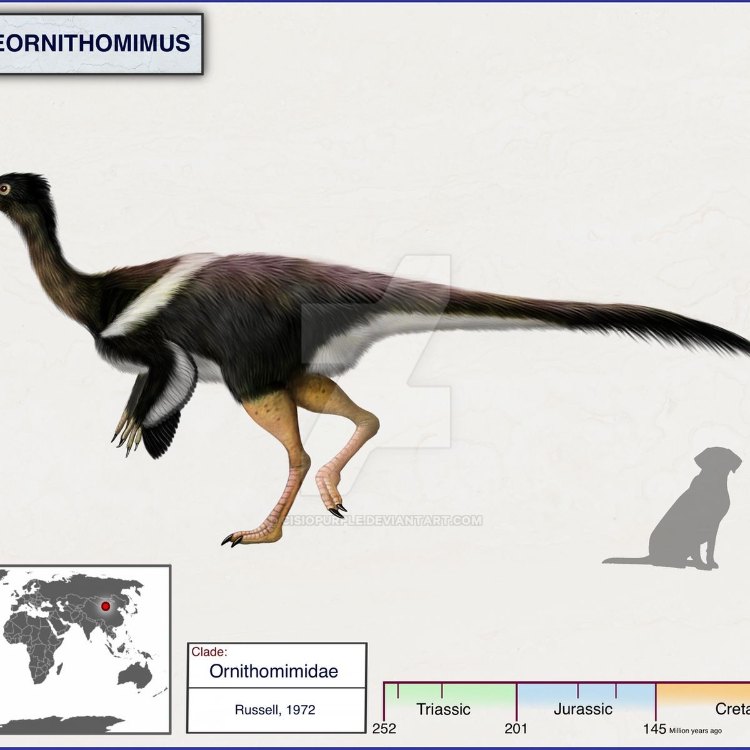
Archaeornithomimus
The Fascinating World of Archaeornithomimus: The Fast and Agile Herbivore of Late Cretaceous Ecosystems
The world of dinosaurs is filled with a wide variety of fascinating creatures, each one with its unique features and adaptations. One such creature that sparks curiosity is the Archaeornithomimus. Its name might be a mouthful, but its significance in the field of paleontology is undeniable. Often referred to as "bird mimic", this species is one of the most well-known and studied members of the ornithomimid family OnTimeAiraz.Com. But what sets this dinosaur apart from the rest? Let's dive into the unique features and characteristics of Archaeornithomimus and discover its role in the Late Cretaceous ecosystems.Archaeornithomimus, meaning "ancient bird mimic", roamed the Earth nearly 70 million years ago during the Late Cretaceous period. Its fossils have been found primarily in Mongolia, and its discovery in 1972 by Russian paleontologist Sergei Mironovich Kurzanov has shed light on how this species lived and evolved. It is believed that this dinosaur evolved from a more primitive species called Pelecanimimus, which had more prominent teeth and longer arms.
One of the most notable characteristics of this species is its bone structure, which is remarkably lightweight. This feature is shared by other ornithomimis such as Gallimimus and Struthiomimus, which were also known for their fast running abilities. Lightweight bones meant that Archaeornithomimus could reach high speeds without putting excess strain on its body. Its long limbs and hind feet also played a crucial role in its speed and agility, allowing it to cover great distances in search of food and escape potential predators.
Speaking of food, Archaeornithomimus was an herbivore, which means it fed on plants and vegetation Anchisaurus. Its slender, beak-like mouth was perfect for plucking leaves and fruits, making it an important part of the Late Cretaceous ecosystem. As a diurnal species, it was active during the day, taking advantage of the ample sunlight to locate and gather food. Its lightweight body also enabled it to move swiftly between feeding areas, giving it an edge over other dinosaurs.
While we know that Archaeornithomimus was an herbivore, its reproductive type remains a mystery. Due to a lack of evidence, scientists have not been able to determine whether this species laid eggs like most dinosaurs or had a different method of reproduction. Research is ongoing, and scientists hope to uncover more information about this aspect of the species in the future.
Interestingly, though this species had been studied extensively, there is still a lot we do not know about it, including its communication methods. We do not have any evidence of vocalizations, so it is still unclear how these dinosaurs communicated with each other. Scientists believe that they may have used visual cues or scents, but this remains a subject of speculation.
Apart from its remarkable speed and lightweight bone structure, Archaeornithomimus had another survival adaptation that played a crucial role in its defense. Its long limbs and agile body allowed it to outrun potential predators. Being non-predatory, this species was constantly on the lookout for predators, relying on its speed and agility to avoid any potential danger. Additionally, its lightweight bones also made it easier to escape if it was ever caught in a dangerous situation.
The largest species of Archaeornithomimus, known as Archaeornithomimus asiaticus, could grow up to 13 feet long and reach a substantial speed of 40 miles per hour. On the other hand, the smallest species, Archaeornithomimus senticolis, was about half the length of its larger counterpart and possessed similar features. While the larger species is believed to have been faster, the smaller species may have been able to maneuver more effectively in dense forest areas.
The fossil record of Archaeornithomimus is quite impressive, with complete skeletons and trace fossils being discovered. These fossils have given scientists valuable insight into the anatomy and behavior of this species. Complete skeletons have allowed scientists to study the bone structure and estimate the size and speed of the species. On the other hand, trace fossils, such as footprints, have provided evidence of the size and behavior of these dinosaurs in their natural habitat.
Archaeornithomimus holds a crucial place in Late Cretaceous ecosystems, and its role as an herbivorous species cannot be overstated. Its long legs and fast running abilities allowed it to cover great distances and forage for a variety of plants. As a part of the food chain, it helped in maintaining a balance in the ecosystem by grazing on plants, and in turn, providing food for predators.
Apart from its unique physical features, Archaeornithomimus also has some interesting and unique facts attached to its name. Scientists believe that due to its long legs and lightweight body, it may have been able to run at high speeds, similar to modern-day ostriches. This theory has not been proven yet, but it is something exciting for paleontologists to explore in the future.
In conclusion, Archaeornithomimus is a fascinating and unique species with distinctive features that have captured the attention of scientists and dinosaur enthusiasts alike. Its lightweight bone structure, long limbs, and agility make it stand out from other dinosaurs, and its role as an herbivore in Late Cretaceous ecosystems cannot be overlooked. While there is still much to learn about this species, its discovery and study have contributed significantly to our understanding of the world of dinosaurs. With continued research and exploration, we can hope to uncover more secrets and mysteries of this ancient and incredible bird mimic.

Unveiling the Mysteries of the Archaeornithomimus: A Fascinating Herbivore of the Late Cretaceous Period
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.