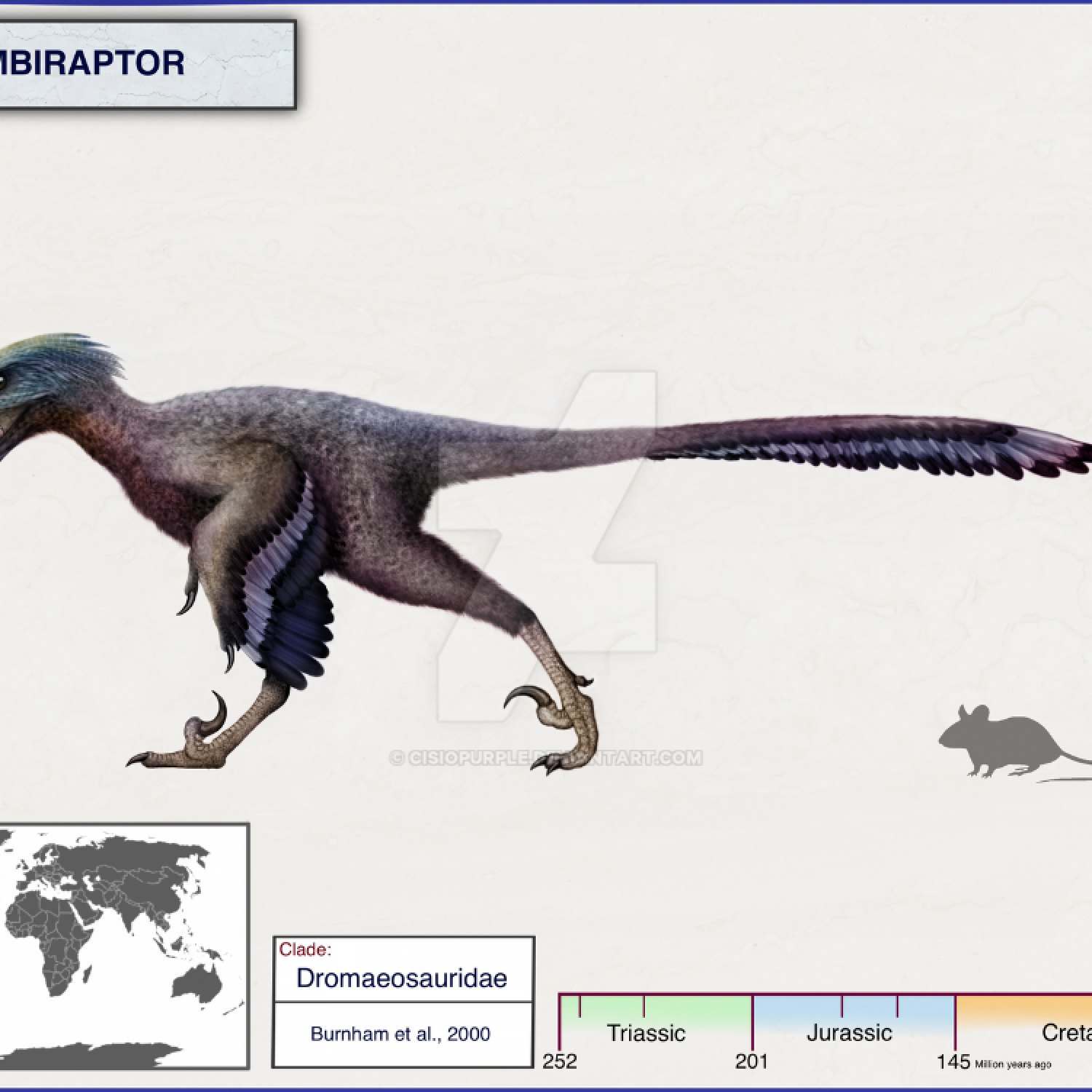
Bambiraptor
Unknown
Meet Bambiraptor, a fierce carnivorous dinosaur that roamed North America millions of years ago. Its skin color remains a mystery, but its speed and hunting tactics were top-notch. Join us as we uncover more about this compact raptor in our latest blog post! #Bambiraptor #Dinosaurs #NorthAmerica
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Bambiraptor
Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
Feeding Behavior: Active predator
Bambiraptor: The Fierce, yet Adorable, Dinosaur from Late Cretaceous Period
In the vast and diverse world of dinosaurs, there are some that are known for their massive size, while others are known for their ferocious predatory skills. And then there is Bambiraptor - a dinosaur that may not be as big as a T-Rex, but its story is just as intriguing and one-of-a-kind.Found during a paleontological expedition in Montana, USA, in 1994, Bambiraptor is one of the most well-preserved and unique dinosaur fossils ever discovered. Its name is a combination of two words - "Bambi," due to its small size and "raptor," a reference to its belonging to the family of swift and agile predatory dinosaurs Bambiraptor.
Bambiraptor, with its scientific name also being Bambiraptor, lived during the Late Cretaceous period, about 75 million years ago. Its fossils were found in layers of sedimentary rocks, indicating its presence in the last stages of the Mesozoic Era. Its name may be reminiscent of the cute and lovable Disney character, but make no mistake, Bambiraptor was a fierce predator.
In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of Bambiraptor, its physical characteristics, behavior, and habitat. Get ready to travel back in time and delve into the exciting world of this small yet unique dinosaur.
Physical Characteristics
First things first, let's talk about the physical appearance of Bambiraptor. From the data summary, we know that it was about 1 meter in length, 30 centimeters in height, and weighed around 2 kilograms. This makes it a relatively small dinosaur compared to its cousins such as the Velociraptor or Deinonychus.Despite its small size, Bambiraptor was an agile and nimble creature with sharp claws and teeth Barilium. Its front limbs were relatively short, with three fingers, while its hind legs were long and muscular, allowing it to run at high speeds. Its tail was long and used for balance while hunting or moving around.
Bambiraptor's most distinguishable feature was its sharp and serrated teeth, which were perfect for hunting and tearing through its prey. Its jaws were powerful and could exert a tremendous amount of force, enabling it to kill its victims quickly.
Diet and Feeding Behavior
Based on the data, we know that Bambiraptor was a carnivorous dinosaur, meaning it fed on meat. But what type of prey did it hunt? Due to its small size, it is believed that Bambiraptor hunted small prey, such as rodents, small mammals, and possibly even insects.Its feeding behavior is described as that of an active predator - constantly on the move, looking for its next meal. Its sharp claws and swift movements helped it to catch its prey quickly. Bambiraptor was also believed to have had binocular vision, allowing it to have depth perception and accurately target its prey.
Predatory Behavior
As mentioned earlier, Bambiraptor was a fierce predator. But how did it hunt its prey? Unlike other dinosaurs with massive jaws and teeth, Bambiraptor relied on its speed and agility rather than brute force.It is believed that Bambiraptor hunted in packs, similar to other raptor dinosaurs. Working together, they would surround their prey, then one would distract it while the others went in for the kill. This tactic is known as "pack hunting" and is still seen in present-day predators such as wolves or lions.
Bambiraptor's sharp claws and serrated teeth were its primary weapons, used to take down its prey. Its front claws were especially long and pointed, making them ideal for stabbing and slashing. Its serrated teeth were responsible for shredding its prey's flesh, making it easier for Bambiraptor to consume.
Habitat and Geographical Distribution
Bambiraptor's native habitat was believed to be in the woodlands, based on the location of where its fossils were found. During the Late Cretaceous period, much of North America was covered in woodlands, providing the perfect habitat for Bambiraptor to thrive.Speaking of North America, this brings us to the geographical distribution of Bambiraptor. Fossils of this dinosaur have been found exclusively in North America, with most sites being in Montana, USA. This indicates that Bambiraptor was native to this region, and did not roam beyond its borders.
Preferred Temperature and Speed
As we know, Bambiraptor lived in the Late Cretaceous period, a time when the Earth's climate was very different from what it is now. The climate was much warmer, and it is believed that Bambiraptor preferred a tropical to subtropical climate.However, the data summary states that Bambiraptor's maximum speed is unknown. This is because the level of mobility in its joints cannot be determined solely from fossil evidence. However, based on its physical characteristics, it is believed that Bambiraptor was a fast and agile dinosaur, capable of running at high speeds to catch its prey or escape from danger.
Discovering Bambiraptor Fossils
The discovery of Bambiraptor fossils is an intriguing story in itself. In 1994, a team of paleontologists was excavating a site in Montana, USA, when they stumbled upon a small but well-preserved fossil skeleton. At first, they thought it was a baby dinosaur, but after further analysis, they realized that it was a fully grown Bambiraptor.This discovery was a significant breakthrough in the study of dinosaurs. Not only did it provide valuable insight into the physical characteristics and behavior of Bambiraptor, but it also opened up new research possibilities into the evolution and diversity of dinosaurs during the Late Cretaceous period.
Fun Facts about Bambiraptor
Now that we have learned about its physical characteristics, behavior, and habitat, let's take a look at some fun facts about Bambiraptor:- Despite its name, Bambiraptor is not related to the deer-like animal from Disney's animated movie.
- The fossils discovered were from an individual that was estimated to be about one year old, making it a young adult.
- Bambiraptor's binocular vision was essential for hunting, but also gave it excellent depth perception, making it an ideal climber and jumper.
- Its teeth were so sharp that scientists believe that they were likely replaced rapidly, perhaps to keep up with its rapid growth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Bambiraptor may not have been as famous or large as some of its dinosaur relatives, but it was a remarkable creature in its own right. With its fierce predatory skills, sharp teeth and claws, and swift movements, it was a formidable hunter in the woodlands of North America during the Late Cretaceous period.The discovery of Bambiraptor's fossils has provided valuable insight into the world of dinosaurs, and has contributed to our understanding of their evolution and diversity. Its unique name, adorable appearance, and intriguing story make it a standout dinosaur that continues to capture the imagination of paleontologists and enthusiasts alike.
So the next time you think of a T-Rex or Velociraptor, remember Bambiraptor - the fierce, yet adorable, dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous period. Its small size may deceive you, but it was a true predator, and its story is a testament to the remarkable creatures that once roamed the Earth.
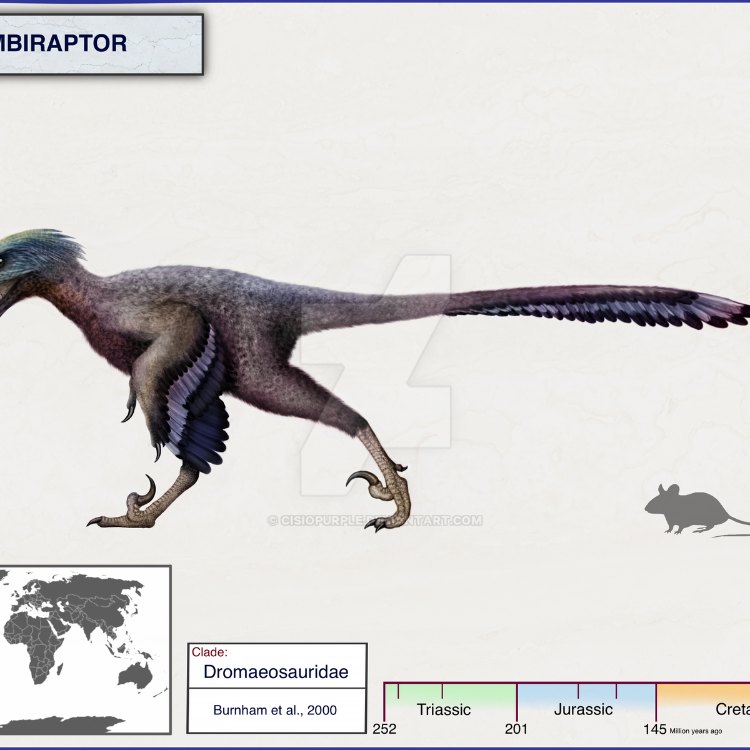
Bambiraptor
Dinosaur Details Bambiraptor - Scientific Name: Bambiraptor
- Category: Dinosaurs B
- Scientific Name: Bambiraptor
- Common Name: Bambiraptor
- Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
- Length: 1 meter
- Height: 30 centimeters
- Weight: 2 kilograms
- Diet: Carnivorous
- Feeding Behavior: Active predator
- Predatory Behavior: Hunted small prey
- Tooth Structure: Sharp and serrated
- Native Habitat: Woodlands
- Geographical Distribution: North America
- Preferred Temperature: Tropical to subtropical
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown
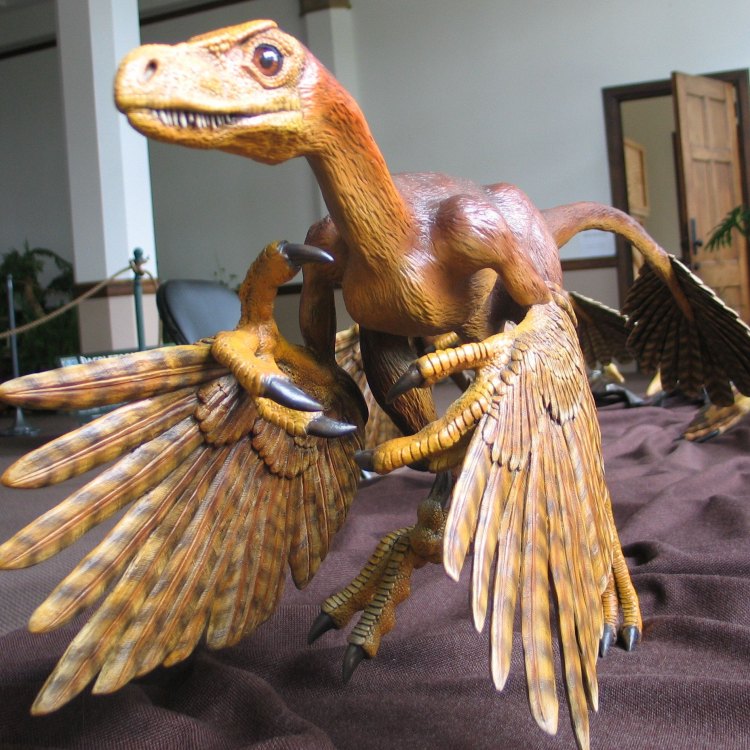

Bambiraptor
- Bone Structure: Lightweight
- Reproduction Type: Egg laying
- Activity Period: Diurnal
- Distinctive Features: Long legs, sharp claws
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Quick and agile
- Largest Species: Unknown
- Smallest Species: Unknown
- Fossil Characteristics: Well-preserved fossils
- Role in Ecosystem: Top predator in its environment
- Unique Facts: Named after the Disney character Bambi
- Predator Status: Carnivore
- Discovery Location: Montana
- Discovery Year: 1993
- Discoverer's Name: David Burnham

Bambiraptor
The Ferocious Bambiraptor: Uncovering the Lightweight Predator of Montana
In the vast landscapes of Montana, a tiny but mighty predator once roamed the earth. With its distinctive long legs and sharp claws, the Bambiraptor has captured the imagination of scientists and dinosaur enthusiasts alike. Named after the classic Disney character Bambi, this small but fierce creature has left its mark in the field of paleontology.But what makes the Bambiraptor so unique? From its bone structure to its role in the ecosystem, let’s dive into the fascinating world of this diurnal, egg-laying dinosaur OnTimeAiraz.Com.
A Bone Structure Fit for Speed and Agility
One of the first things that sets the Bambiraptor apart is its lightweight bone structure. This ancient creature had hollow bones, much like those of modern birds, making it lighter and more agile than other dinosaurs of its time. This adaptation allowed the Bambiraptor to move swiftly and efficiently, making it a formidable predator in its environment.But the lightweight bone structure was not the only physical feature that aided this creature in its hunt for survival.
Distinctive Features that Helped the Bambiraptor Succeed
The Bambiraptor was a small dinosaur, measuring just over three feet long and weighing around six pounds. Despite its small size, it had long, slender legs and sharp, curved claws that were perfectly designed for a swift and precise attack. These sharp claws also enabled the Bambiraptor to grip onto and climb trees, giving it an advantage over its prey.Another distinctive feature of the Bambiraptor was its large eyes, indicating that it was active during the day, a diurnal animal. This would have allowed it to take advantage of the daylight and hunt efficiently, while most other predatory dinosaurs were asleep Bagaceratops.
Unknown Communication Methods and Reproduction Type
While some dinosaur species have been known to communicate through vocalizations, little is known about how the Bambiraptor communicated. Its lack of vocalization preserved in the fossil record leaves this aspect of its behavior a mystery. However, it is believed that they may have used visual cues and body language to communicate with each other.Similar to its communication methods, the reproduction type of the Bambiraptor is also unknown. However, based on its small size and lightweight bone structure, it is believed to have laid eggs, like most other non-avian dinosaurs.
Well-Preserved Fossils: Unlocking the Secrets of the Bambiraptor
The Bambiraptor was first discovered in 1993 by paleontologist David Burnham in Montana. Since then, several well-preserved fossils have been unearthed, giving scientists a clearer understanding of this remarkable dinosaur.A well-preserved fossil is a rare and precious find. It provides an accurate representation of the animal’s anatomy and behavior, offering scientists a unique opportunity to study and learn about the Bambiraptor's way of life.
The Top Predator in Its Environment
With its sharp claws, quick agility, and fierce hunting skills, the Bambiraptor was a top predator in its environment. Its lightweight bone structure and long legs allowed it to move swiftly, making it difficult for its prey to escape. Its hunting techniques were likely similar to those of modern birds of prey, swooping down on its prey with precision and speed.Being a top predator also meant that the Bambiraptor played a crucial role in the ecosystem. As a predator, it helped to regulate the population of its prey, maintaining a balanced and healthy environment.
But Wait, Why Is It Called the Bambiraptor?
You may be wondering: why was this fearsome predator named after a beloved Disney character? Well, it all started with the discovery of its fossils.When paleontologist David Burnham first came across the bones of the Bambiraptor, he noticed that they were very small, just like the Disney character Bambi. This led to the dinosaur being named after Bambi, but with the added suffix “raptor” to signify its predatory nature.
The Carnivorous Lifestyle of the Bambiraptor
As a carnivore, the Bambiraptor fed primarily on small vertebrates, such as lizards, birds, and mammals. Its sharp claws and teeth were perfectly adapted for tearing through flesh, making it a formidable hunter.Unlike later, larger raptors such as the Velociraptor, the Bambiraptor was not equipped to take down large prey. Instead, it focused on smaller animals, making it less of a threat to larger dinosaurs in its ecosystem.
Uncovering the Secrets of the Bambiraptor's Origins
The Bambiraptor is believed to have lived during the Late Cretaceous period, around 75 million years ago. During this time, the area that is now Montana was a humid, subtropical region with lush forests and diverse wildlife.Despite being a small and lightweight dinosaur, the Bambiraptor was a fierce and successful predator. Its swift and agile nature allowed it to thrive in its environment, leaving its mark in the rich history of the Earth.
In Conclusion
The Bambiraptor may have been small in size, but it was a mighty predator that played a vital role in its ecosystem. Thanks to well-preserved fossils, we have been able to uncover some of its secrets and learn more about this fascinating dinosaur.From its distinctive features to its ferocious hunting skills, the Bambiraptor has left a lasting impression on the field of paleontology. As scientists continue to study and unravel its mysteries, we can only imagine what other exciting discoveries await us in the world of dinosaurs.
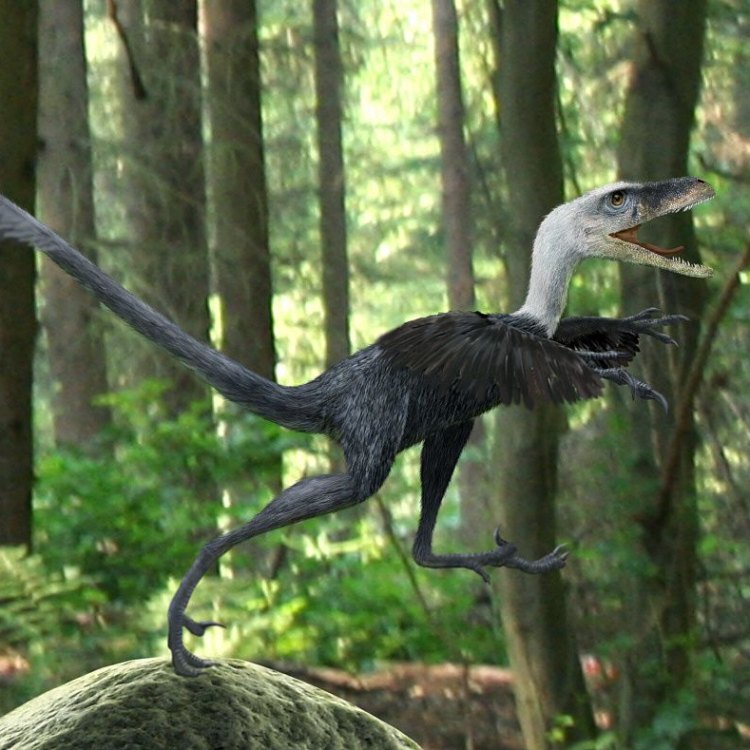

Bambiraptor: The Fierce, yet Adorable, Dinosaur from Late Cretaceous Period
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.