Dacentrurus
Unknown
Dacentrurus, a lesser-known dinosaur from Europe, was a herbivore with an unknown top speed. Its skin color remains a mystery, making it an elusive creature. Although not as famous as its Jurassic cousins, Dacentrurus was a fascinating dinosaur that roamed the lands millions of years ago. #Dacentrurus #Herbivore #Europe #Unknown #JurassicCousins
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Dacentrurus
Geological Era: Late Jurassic
Feeding Behavior: Large, low browsing dinosaur
The Mighty Dacentrurus: Uncovering the Secrets of the Late Jurassic Herbivore
The Late Jurassic period was a time of immense diversity in the world of dinosaurs. From gigantic sauropods to raptors, the era was home to a wide array of creatures that roamed the Earth. Among these fascinating creatures was the Dacentrurus, a lesser-known but equally intriguing herbivorous dinosaur.Also known by its scientific name Dacentrurus armatus, this dinosaur lived in the late Jurassic period around 155 million years ago Dacentrurus. Its name is derived from the Greek words "daktylos" meaning finger and "kentrion" meaning spur due to the unique feature of spines on its vertebrae.
Native to the woodlands of Europe, the Dacentrurus is believed to have been an essential member of its ecosystem. Let's take a closer look at this intriguing dinosaur and uncover its standout features.
The Anatomy of Dacentrurus
The Dacentrurus was a large dinosaur, measuring around 9-10 meters in length and standing at a height of 3.5 meters. It weighed in at a whopping 2-3 tons, making it a force to be reckoned with in its environment.One of the most intriguing features of this dinosaur was its unique spiny armor. Its body was covered in bony plates that acted as a natural defense against predators. These spines were also present on its vertebrae, giving it a unique appearance Deltadromeus.
Unlike other herbivorous dinosaurs, the Dacentrurus had a distinctive stance, with its front legs longer than its hind legs. This adaptation allowed it to comfortably browse on low-lying vegetation, making it a significant contributor to the woodland ecosystem.
Diet and Feeding Behavior
The Dacentrurus was a herbivore, meaning it fed only on plants. Its diet primarily consisted of low-lying vegetation, such as bushes and ferns, which it could easily access with its unique posture.The shape of its teeth and jaw structure were perfectly suited for tearing through these plants. Its teeth were broad and leaf-shaped, with sharp edges that could efficiently cut through tough vegetation. This adaptation allowed it to consume a significant amount of food, making it a crucial factor in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem.
Non-Predatory Behavior
Unlike many other dinosaurs of the era, the Dacentrurus was not a predator. It relied solely on its armor and unique posture to protect itself from predators. But that doesn't mean it was entirely defenseless.In addition to its spiny armor, the Dacentrurus also had a muscular tail that it could use as a weapon when faced with danger. Its tail was thick and sturdy, with a club-like end that could deliver a powerful blow to any potential predator.
The Mystic Color of Dacentrurus
One of the most intriguing mysteries surrounding this dinosaur is its skin color. Unfortunately, due to the lack of well-preserved fossil evidence, scientists have been unable to determine the exact color of its skin. However, based on the environmental factors of its native habitat, it is believed that the Dacentrurus may have had a predominantly brown or green color to blend in with its surroundings.Habitat and Distribution
The Dacentrurus was native to the woodlands of Europe, specifically in countries such as France, England, and Portugal. The lush green forests in this region provided the ideal habitat for this large, low browsing dinosaur.Its geographical distribution was relatively limited, with fossils being found primarily in Europe. However, it is possible that the Dacentrurus had a more extensive range, but due to the lack of fossil evidence, this cannot be confirmed.
The Preferred Climate of Dacentrurus
The Dacentrurus was well adapted to moderate temperatures. It is believed that its preferred climate was humid and temperate, similar to the climate of Europe during the late Jurassic period. This was the perfect environment for lush vegetation to thrive, providing an abundant food source for the Dacentrurus.The Mysterious Speed of Dacentrurus
One aspect of this dinosaur that remains a mystery is its maximum speed. Unlike other dinosaurs of the era, such as the Velociraptor, the Dacentrurus was not built for speed. Its large body and unique posture may have hindered its ability to run, making it more of a slow-moving creature.However, this does not mean the Dacentrurus was entirely immobile. Its strong legs and muscular tail could have propelled it to a moderate speed if needed. Unfortunately, due to a lack of fossil evidence, its maximum speed remains unknown.
The Extinction of Dacentrurus
The exact reason for the extinction of the Dacentrurus is still a subject of debate among scientists. It is believed that changing environmental conditions and competition from other herbivorous dinosaurs may have played a significant role in its demise.Around the same time as the Dacentrurus, the giant sauropods and armored stegosaurs were also roaming the Earth. With a limited food supply, these larger dinosaurs may have outcompeted the Dacentrurus, eventually leading to its extinction.
In Conclusion
The Dacentrurus may not be as well-known as some of its counterparts from the late Jurassic period, but it was undoubtedly an essential part of its ecosystem. Its unique features, such as its spiny armor and leaf-shaped teeth, make it a fascinating subject for researchers to study.Despite its relatively short existence on this planet, the Dacentrurus has left a lasting impact on the world of paleontology. With continued research and study, perhaps more secrets of this mighty herbivore will be uncovered, shedding light on its role in the intricate web of life during the late Jurassic era.

Dacentrurus
Dinosaur Details Dacentrurus - Scientific Name: Dacentrurus armatus
- Category: Dinosaurs D
- Scientific Name: Dacentrurus armatus
- Common Name: Dacentrurus
- Geological Era: Late Jurassic
- Length: 9-10 meters
- Height: 3.5 meters
- Weight: 2-3 tons
- Diet: Herbivorous
- Feeding Behavior: Large, low browsing dinosaur
- Predatory Behavior: Non-predatory
- Tooth Structure: Leaf-shaped teeth for eating vegetation
- Native Habitat: Woodlands
- Geographical Distribution: Europe
- Preferred Temperature: Moderate temperatures
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown
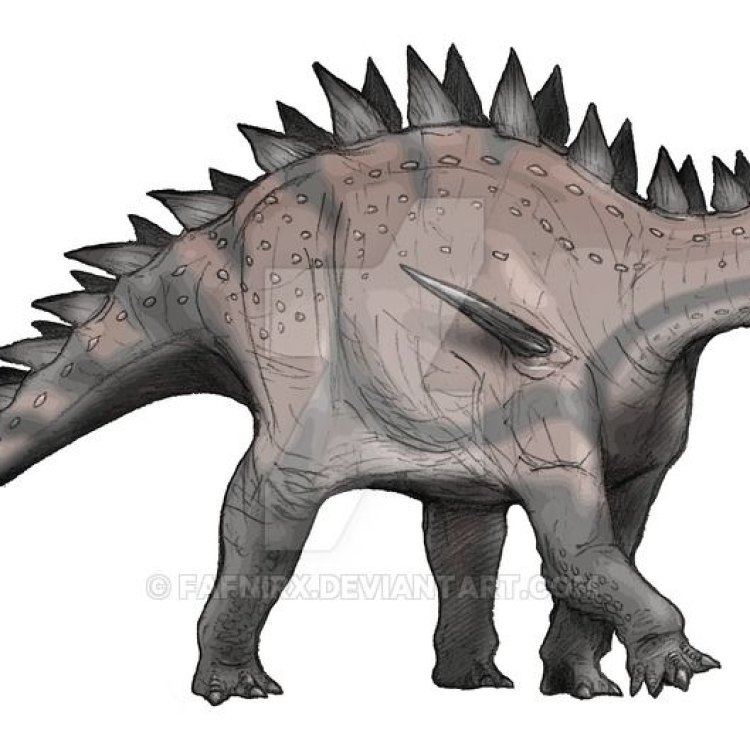
Dacentrurus
- Bone Structure: Robust and sturdy bones
- Reproduction Type: Egg-laying
- Activity Period: Diurnal or day-active
- Distinctive Features: Long spikes on its tail and shoulder
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Large size and defensive spikes
- Largest Species: Dacentrurus armatus
- Smallest Species: Unknown
- Fossil Characteristics: Fragmentary skeletal remains
- Role in Ecosystem: Herbivorous grazer
- Unique Facts: One of the largest stegosaurians
- Predator Status: Non-predatory
- Discovery Location: England
- Discovery Year: 1875
- Discoverer's Name: John Hulke
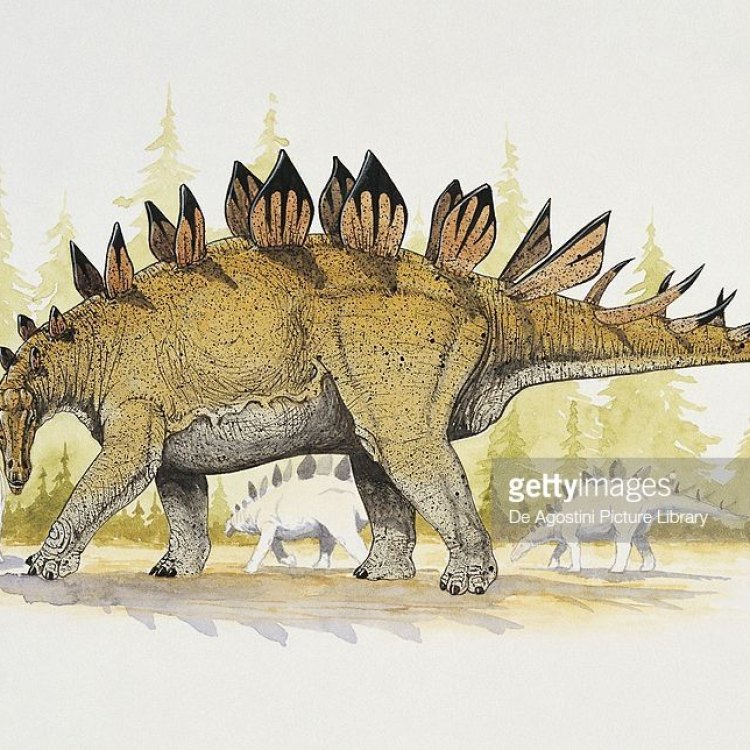

Dacentrurus armatus
The Mighty Dacentrurus: A Large and Robust Herbivore from the English Countryside
Deep in the heart of the English countryside, an ancient giant once roamed the earth. This remarkable creature, known as Dacentrurus, was a prominent member of the stegosaurian family and one of the largest known species to exist. With its distinctive bone structure, defensive spikes, and impressive size, Dacentrurus was a force to be reckoned with in its ecosystem. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of Dacentrurus, exploring its unique features, its role in the environment, and the story of its discovery OnTimeAiraz.Com.Anatomy and Physical Features
The name Dacentrurus is derived from Greek, meaning "tail full of points." This name is fitting, as one of the most distinctive physical features of this species is its long tail adorned with sharp spikes. The spikes on its tail were likely used for defense against predators or for display during mating rituals. In addition to these tail spikes, Dacentrurus also had long spikes on its shoulders, adding an extra layer of protection.Aside from its spikes, Dacentrurus also had a robust and sturdy bone structure. This is a common characteristic of stegosaurians, as they were known for their massive size and weight. Dacentrurus, in particular, was estimated to be around 9 meters long and weigh up to 5 tons, making it one of the largest members of its family. Its strong bones and big size were crucial for its survival in a world filled with predators.
Reproductive Strategies
Like most dinosaurs, Dacentrurus was an egg-laying species Diamantinasaurus. This means that it reproduced by laying eggs rather than giving birth to live young. The exact details of its reproductive strategies are still unknown, but it is believed that females would lay their eggs in nests on the ground, similar to modern-day birds.Activity and Behavior
Another intriguing aspect of Dacentrurus is its activity pattern. Fossil evidence suggests that it was a diurnal or day-active species. This means that it was awake and active during the day and likely took shelter at night. This behavior is not uncommon among herbivorous dinosaurs, as it allowed them to take advantage of the abundance of vegetation during the day while avoiding predators at night.As for communication methods, not much is known about how Dacentrurus communicated. They were likely vocal creatures, but without any soft tissue preserved in the fossil record, it is challenging to determine their exact vocalization methods. However, it is believed that they may have used a combination of visual displays and low-frequency calls to communicate with one another.
Survival Adaptations
As mentioned earlier, one of the most critical survival adaptations of Dacentrurus was its large size and defensive spikes. These features made it a formidable opponent for any predator that dared to challenge it. Its spikes acted as a defense mechanism against smaller predators, while its size alone was enough to intimidate most larger predators. These adaptations, along with its sturdy bones, allowed Dacentrurus to thrive in its ecosystem and survive for millions of years.Discovery and Fossil Record
The first remains attributed to Dacentrurus were discovered in 1875 in England by physician and paleontologist, John Hulke. The fossil remains consisted of fragments of bones, including pieces of the skull, vertebrae, and limb bones. Additional fossils have since been found in different parts of England, making it the primary location for Dacentrurus discoveries.Due to the fragmented nature of its fossil record, scientists have speculated that Dacentrurus may have roamed in herds. This theory is supported by the fact that many fossil remains have been found in close proximity to one another.
Role in the Ecosystem
Dacentrurus was an herbivorous grazer, meaning that it primarily fed on plants. Its diet would have consisted of a variety of vegetation, including ferns, cycads, and conifers. As a large and dominant species, it is likely that Dacentrurus played a crucial role in controlling the growth of plants in its ecosystem, ultimately shaping the landscape.Unique Facts and Legacy
Despite its massive size and impressive features, Dacentrurus is not as well-known as some of its dinosaur cousins, such as the famous Stegosaurus. However, it remains one of the largest stegosaurians and a remarkable species in its own right. With its distinctive spikes and robust anatomy, Dacentrurus has captivated the minds of scientists and the public alike.In Conclusion
In summary, Dacentrurus was a remarkable creature that roamed the earth millions of years ago. With its robust bone structure, long spikes, and large size, this herbivorous grazer was a force to be reckoned with in its environment. However, despite all its defensive adaptations, Dacentrurus was a non-predatory species, subsisting on a diet of plants.Thanks to the dedicated work of paleontologists like John Hulke, we now have a better understanding of this magnificent species and its role in the ecosystem. Dacentrurus may have gone extinct long ago, but its legacy lives on, providing us with a glimpse into the fascinating world of dinosaurs.
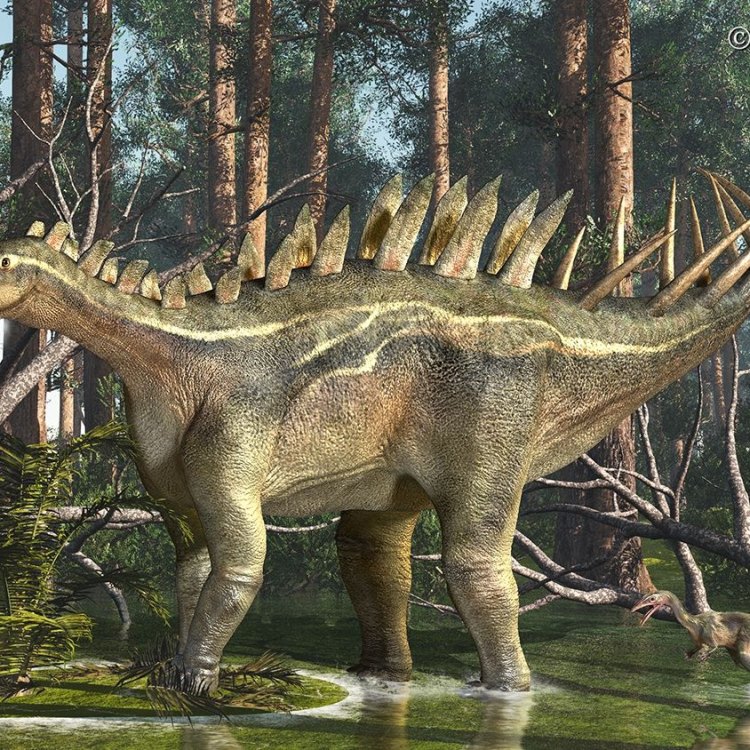

The Mighty Dacentrurus: Uncovering the Secrets of the Late Jurassic Herbivore
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.