Efraasia
Unknown
Efraasia is a lesser-known dinosaur that roamed across Europe, specifically Germany and Switzerland, millions of years ago. Believed to be an herbivore, this dinosaur's skin color is still a mystery. Its maximum speed is also unknown, adding to the intrigue of this unique creature. Keep an eye out for more information on Efraasia as scientists continue to uncover its prehistoric secrets. #Efraasia #dinosaurs #paleontology #Europe #prehistoriclife
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Efraasia
Geological Era: Late Triassic
Feeding Behavior: Grazing
Unraveling the Mysteries of Efraasia: The Herbivorous Giant of Europe's Triassic Era
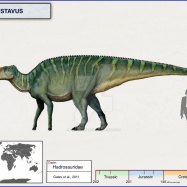
In the world of dinosaurs, carnivores like the fearsome T-Rex and velociraptors often steal the spotlight. But hidden in the shadows of these notorious predators lies a lesser-known, yet equally fascinating creature - Efraasia.Named after the German paleontologist Friedrich von Huene, who first discovered its fossils in 1904, Efraasia lived during the Late Triassic period, approximately 210 million years ago. Its remains have been found in Germany and Switzerland, making it a prominent resident of Europe during that time Efraasia.
Standing at about 3 meters in length and 1 meter in height, Efraasia was a medium-sized dinosaur. Although its weight is estimated to be around 100 kilograms, its diet was not one of meat or bones - unlike many of its fellow dinosaurs. Efraasia was a gentle herbivore, existing on a diet of plants and leaves with its grazing feeding behavior.
But what truly sets Efraasia apart from other herbivorous dinosaurs is its unique tooth structure. While most herbivores have broad, flat teeth for grinding and chewing plants, Efraasia had specialized leaf-shaped teeth - a characteristic typically seen in dinosaurs that feed on conifer plants. This adaptation allowed Efraasia to efficiently consume tough and fibrous plant material, making it a successful herbivore.
But don't let its seemingly harmless diet fool you - Efraasia was not completely defenseless. It sported sharp, small claws on its feet and hands, which it used for protecting itself and foraging for food.
Despite its size, Efraasia was not a predator and did not engage in any predatory behavior Epidexipteryx. Its non-aggressive behavior and peaceful nature were a stark contrast to the larger and more aggressive dinosaurs of the Triassic era.
Due to the limited fossil remains of Efraasia, not much is known about its physical features, such as skin color or maximum speed. But scientists have speculated that it had a warm-colored skin, suitable for the warm and humid climate of the Triassic period.
Efraasia's native habitat was on land, and it is believed to have roamed the rich forests and plains of Europe. During the Late Triassic period, Europe was a lush landmass, with a warm and humid climate, creating the perfect environment for a herbivore like Efraasia to thrive.
While many dinosaurs from this era were exceptional runners, Efraasia's ability to move quickly is unknown. It is hypothesized that due to its size and herbivorous diet, Efraasia may not have been a particularly fast dinosaur. However, its small, strong legs and agile movements made it a nimble and efficient forager.
It is also interesting to note that Efraasia lived during the time of the first dinosaurs, known as the Triassic-period dinosaurs - a group that diversified and evolved into some of the most iconic dinosaurs we know today.
The Triassic period was a crucial time for the evolution of dinosaurs, and Efraasia played a significant role in this process. Its herbivorous nature and unique teeth structure provided scientists with invaluable information about the dietary habits and adaptations of early dinosaurs.
But despite its contributions to the study of dinosaurs, Efraasia remains relatively unknown compared to its contemporaries. This is mainly due to the limited fossil remains of this remarkable creature and the fact that it lived during a time when the Earth's continents were still connected in a supercontinent called Pangaea.
As continental drift occurred, and the continents began to separate, Efraasia, along with many other dinosaur species, became isolated and ultimately extinct. As the Earth's landscape changed, so did the habitats and food sources for these dinosaurs, leading to their eventual demise.
Today, the fossils of Efraasia continue to be a source of fascination and intrigue for paleontologists, allowing them to piece together the story of this remarkable herbivore. Its unique tooth structure and peaceful nature have left an indelible mark in the world of dinosaurs, showcasing the diverse and complex creatures that once inhabited our planet.
In conclusion, although Efraasia may not have been as well-known as some of its dinosaur counterparts, it remains a crucial part of the puzzle in understanding the evolution and diversity of dinosaurs. Its gentle nature and importance in the Triassic period make it a standout creature in the rich history of dinosaurs, cementing its place as a beloved and respected part of the prehistoric world.

Efraasia
Dinosaur Details Efraasia - Scientific Name: Efraasia
- Category: Dinosaurs E
- Scientific Name: Efraasia
- Common Name: Efraasia
- Geological Era: Late Triassic
- Length: 3 meters
- Height: 1 meter
- Weight: around 100 kilograms
- Diet: Herbivorous
- Feeding Behavior: Grazing
- Predatory Behavior: Non-predatory
- Tooth Structure: Herbivorous (leaf-shaped teeth)
- Native Habitat: Land
- Geographical Distribution: Europe (Germany and Switzerland)
- Preferred Temperature: Warm climate
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown

Efraasia
- Bone Structure: Unknown
- Reproduction Type: Unknown
- Activity Period: Unknown
- Distinctive Features: Small size, long neck, long tail
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Unknown
- Largest Species: Efraasia minor
- Smallest Species: Efraasia major
- Fossil Characteristics: Partial skeleton
- Role in Ecosystem: Herbivore in Late Triassic ecosystems
- Unique Facts: One of the oldest known dinosaurs from Europe
- Predator Status: Non-predator
- Discovery Location: Germany and Switzerland
- Discovery Year: 1910
- Discoverer's Name: Eberhard Fraas

Efraasia
The Enigmatic Efraasia: Untold Tales of One of the Oldest Dinosaurs from Europe
When we think of dinosaurs, we often picture ferocious creatures like the Tyrannosaurus rex or the Velociraptor. However, not all dinosaurs were massive and terrifying. Some were small, gentle herbivores that roamed the earth over 200 million years ago. One such dinosaur was Efraasia, whose name means "ruler of Eberhard Fraas," the German paleontologist who discovered it in 1910 OnTimeAiraz.Com. Efraasia may not have the fame and recognition of other dinosaurs, but it has a fascinating story to tell.Efraasia is a genus of dinosaur belonging to the group of early ornithischians, characterized by a small size, long neck, and long tail. Unfortunately, not much is known about its bone structure, reproduction, or activity period, as no complete fossils have been found. However, what scientists do know is that Efraasia belongs to the Late Triassic period, making it one of the oldest known dinosaurs from Europe.
Efraasia was a relatively small dinosaur, with the largest species, Efraasia minor, measuring around ten feet in length. Its smallest species, Efraasia major, is estimated to have been about six feet long. While these may not seem like impressive sizes compared to other dinosaurs, it was the norm for early dinosaurs during that time.
One of the most distinctive features of Efraasia is its long neck and tail. Its long neck would have allowed it to reach high vegetation and graze on plants, while its long tail helped it maintain balance and navigate its surroundings Erlikosaurus. These unique features were essential for the survival of this small, herbivorous dinosaur.
Speaking of survival, Efraasia's specific survival adaptations remain unknown. However, scientists speculate that its small size and herbivorous diet may have helped it avoid predators. Apart from being prey to larger carnivorous dinosaurs, Efraasia was not a predator itself.
Efraasia had a significant role to play in the Late Triassic ecosystem, where it lived alongside other dinosaurs like Plateosaurus and Coelophysis. As an herbivore, Efraasia would have played a vital role in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem by controlling plant growth. Its long neck would have allowed it to eat a wide variety of plants, making it a crucial player in the food chain.
Fossils of Efraasia have been discovered in Germany and Switzerland, which were once part of the ancient landmass known as Pangaea. Pangaea was a supercontinent that existed during the early Mesozoic Era, and its breakup eventually led to the separation of continents as we know them today. The discovery of Efraasia in both Germany and Switzerland suggests that it was widespread and had a relatively large range during its time.
The fossil characteristics of Efraasia remain limited to a partial skeleton, making it challenging for scientists to fully understand this dinosaur. The fossils discovered include a fragment of the lower jaw, a few vertebrae, and a collar bone or clavicle. From these remains, scientists have been able to classify Efraasia as an early ornithischian dinosaur and place it in the same group as other herbivorous dinosaurs like Stegosaurus and Triceratops.
Efraasia's discovery by Eberhard Fraas in 1910 was a significant milestone in the study and understanding of dinosaurs. Fraas was a renowned German paleontologist and geologist, known for his many discoveries of prehistoric creatures. He is also credited with the discovery of other notable dinosaurs like the Prosauropod Plateosaurus and the pterosaur Rhamphorhynchus. Fraas's impact on the field of paleontology has been immense, and Efraasia is just one of his many accolades.
Despite being one of the oldest known dinosaurs from Europe, Efraasia is not as well-known as other dinosaurs from that time, like the aforementioned Plateosaurus. However, its significance cannot be understated. It provides valuable insights into the evolution and diversity of dinosaurs during the Late Triassic period, a crucial time in the history of life on earth.
While we may never know much about Efraasia's communication methods or specific survival adaptations, its unique features, and role in the ecosystem make it a fascinating dinosaur to study. It was a gentle giant of its time, peacefully grazing on plants and contributing to the balance of its environment.
In conclusion, Efraasia may not have been as famous or impressive as other dinosaurs, but its role in the story of life on earth is just as crucial. Its discovery opened up a window to the past, providing us with a glimpse of the diverse and fascinating world of dinosaurs during the Late Triassic period. And with ongoing research and discoveries, who knows what more we may learn about Efraasia in the future.
Unraveling the Mysteries of Efraasia: The Herbivorous Giant of Europe's Triassic Era
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.