Hadrosaurids
Unknown
Hadrosaurs, also known as duck-billed dinosaurs were herbivorous creatures that roamed North America, Asia, and Europe during the late Cretaceous period. With a maximum speed of approximately 24 km/h, these dinosaurs were not the fastest, but their herd behavior and solid armor made them formidable prey. Despite their popularity, their skin color remains unknown, leaving their appearance up to our imagination.
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Hadrosaurids
Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
Feeding Behavior: Bulk feeders, grazers
The Magnificent Hadrosaurids: The Herbivorous Giants of the Late Cretaceous
The world of dinosaurs was full of fascinating creatures, each with their own unique features and behaviors. One of the most remarkable groups of dinosaurs from this era were the Hadrosaurids, also known by their scientific name, Hadrosauridae. These majestic creatures roamed the Earth during the Late Cretaceous period, and their legacy continues to enthrall us to this day.With their massive size and distinctive appearance, Hadrosaurids are a fascinating subject for paleontologists and dinosaur enthusiasts alike Hadrosaurids. In this article, we will take a closer look at the standout features of these incredible creatures and uncover what made them stand out among other dinosaurs.
The Basics: What Are Hadrosaurids?
Hadrosaurids were a family of herbivorous dinosaurs that lived during the Late Cretaceous period, which lasted from approximately 100 to 66 million years ago. They were a diverse group, with over 30 different species identified so far.Their name comes from the Greek words "hadros" meaning "bulky" and "sauros" meaning "lizard." This is a fitting name for these dinosaurs, as they were indeed bulky and one of the largest land animals of their time.
Physical Characteristics
The most striking physical feature of Hadrosaurids was their size. They could reach lengths of up to 15 meters, making them one of the longest known dinosaurs. Standing on all four legs, they could reach heights of 3 to 4.5 meters, making them taller than a modern-day elephant Hungarosaurus.Despite their massive size, Hadrosaurids were relatively lightweight. Their weight ranged from 2 to 4 tons, which is significantly less than other large dinosaurs like Tyrannosaurus rex.
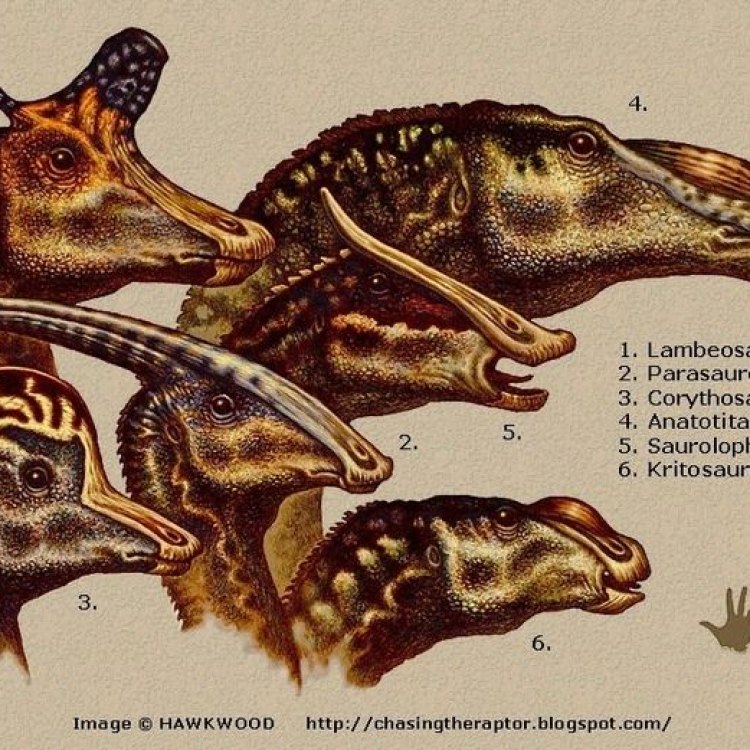
Their bodies were designed for life on land, with robust legs and sturdy bones to support their weight. They had a thick tail for balance, and some species even had a bony crest on their heads. The shape of this crest varied among species, and scientists believe it may have been used for display purposes or to amplify their calls.
Diet and Feeding Behavior
Hadrosaurids were herbivorous, meaning they only ate plants. They were bulk feeders, meaning they consumed large amounts of vegetation at once. They had hundreds of tightly packed teeth in their dental batteries, which they used to continuously crop and grind vegetation.Their teeth were designed for a specific purpose. The front teeth were used for cropping vegetation, while the back teeth were used for grinding it down. This allowed them to consume tough plant material that was difficult to digest.
Their feeding behavior was primarily grazing, where they would move through their habitat, feeding on low-lying vegetation. Some scientists also believe that they may have been able to stand on their hind legs to reach higher vegetation, similar to how modern-day giraffes feed.
Habitat and Geographical Distribution
Hadrosaurids were widespread and could be found in forests, swamps, and riversides. They preferred living near a water source, as it provided them with a constant supply of vegetation, and they were also good swimmers.Their fossils have been found in North America, Asia, and Europe, indicating they were widespread among the continents during the Late Cretaceous period.
Behavior and Social Structure
Hadrosaurids are believed to have lived in herds, consisting of a mix of adults and juveniles. This social structure allowed them to better protect themselves from predators, such as Tyrannosaurus rex.They were non-predatory dinosaurs, meaning they did not hunt or kill other creatures for food. However, they were not defenseless, and some species had bony plates or spikes on their bodies that may have served as a defense against predators.
Preferred Temperature and Adaptations
Hadrosaurids were prevalent in temperate to subtropical climates, where temperatures ranged from cool to warm. They were well-adapted to these environments, with features like their thick skin protecting them from the elements.The specific adaptations of Hadrosaurids are still being researched, but it is believed that their dental batteries were a significant advantage in their ability to consume a variety of plant material in their habitats.
Movement and Speed
Despite their size, Hadrosaurids were relatively agile and could move quickly when needed. They could reach maximum speeds of approximately 24 km/h, making them one of the fastest dinosaurs of their time.Their legs were adapted for running, with longer hind legs than front legs, providing a powerful propulsion to help them move quickly. Along with their sturdy bones, this allowed them to flee from predators when necessary.
The Mystery of Skin Color
One aspect that is still a mystery among Hadrosaurids is their skin color. Fossil evidence does not provide any clues to the color of their skin, leaving scientists to speculate based on other factors.Some believe that their skin may have been a light color, similar to modern-day elephants or rhinos, to help them stay cool in hot climates. Others believe they may have had a mottled or striped pattern to blend in with their surroundings and avoid being seen by predators.
The Legacy of Hadrosaurids
Hadrosaurids were a remarkable group of dinosaurs that played a crucial role in the ecosystem of the Late Cretaceous period. Their unique adaptations and behaviors made them successful in their environments, and their legacy lives on today through their fossil discoveries and our continued fascination with their world.Their importance goes beyond their physical characteristics, as they provide valuable insights into the evolution and diversity of life on Earth. Studying these magnificent creatures allows us to understand more about our planet's history and the fascinating creatures that once roamed it.
In Conclusion
Hadrosaurids were truly remarkable creatures that roamed the Earth millions of years ago. Their massive size, unique adaptations, and social behavior continue to fascinate us today. They are a testament to the diversity of life on our planet and remind us of the incredible creatures that once existed alongside us.As scientists continue to research these dinosaurs, we will undoubtedly uncover more about their lives and behaviors. But for now, the Hadrosaurids remain a star of the Late Cretaceous era and one of the most fascinating groups of dinosaurs in history.

Hadrosaurids
Dinosaur Details Hadrosaurids - Scientific Name: Hadrosauridae
- Category: Dinosaurs H
- Scientific Name: Hadrosauridae
- Common Name: Hadrosaurids
- Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
- Length: 9 to 15 meters
- Height: 3 to 4.5 meters
- Weight: 2 to 4 tons
- Diet: Herbivorous
- Feeding Behavior: Bulk feeders, grazers
- Predatory Behavior: Non-predatory
- Tooth Structure: Hundreds of tightly packed teeth in dental batteries
- Native Habitat: Forests, swamps, and riversides
- Geographical Distribution: North America, Asia, Europe
- Preferred Temperature: Temperate to subtropical
- Maximum Speed: Approximately 24 km/h
- Skin Color: Unknown
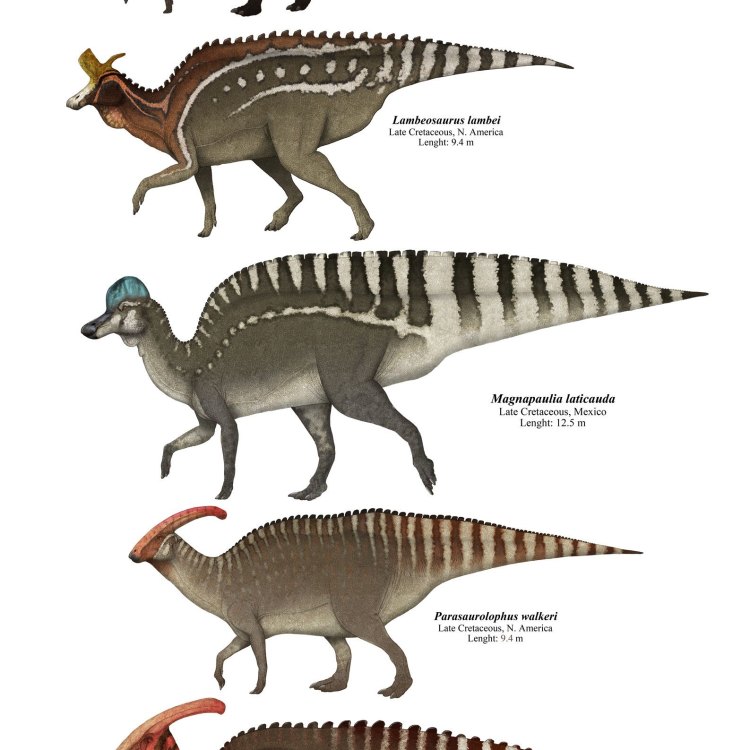

Hadrosaurids
- Bone Structure: Hollow bones with internal struts
- Reproduction Type: Egg-laying
- Activity Period: Diurnal
- Distinctive Features: Duck-billed snout, elaborate head crests
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Herding behavior, fast growth rate
- Largest Species: Shantungosaurus giganteus
- Smallest Species: Telmatosaurus transsylvanicus
- Fossil Characteristics: Well-preserved skeletons and skin impressions
- Role in Ecosystem: Ecological role as large herbivores
- Unique Facts: Had a complex social structure
- Predator Status: Prey
- Discovery Location: Various locations worldwide
- Discovery Year: 19th century
- Discoverer's Name: Sir Richard Owen
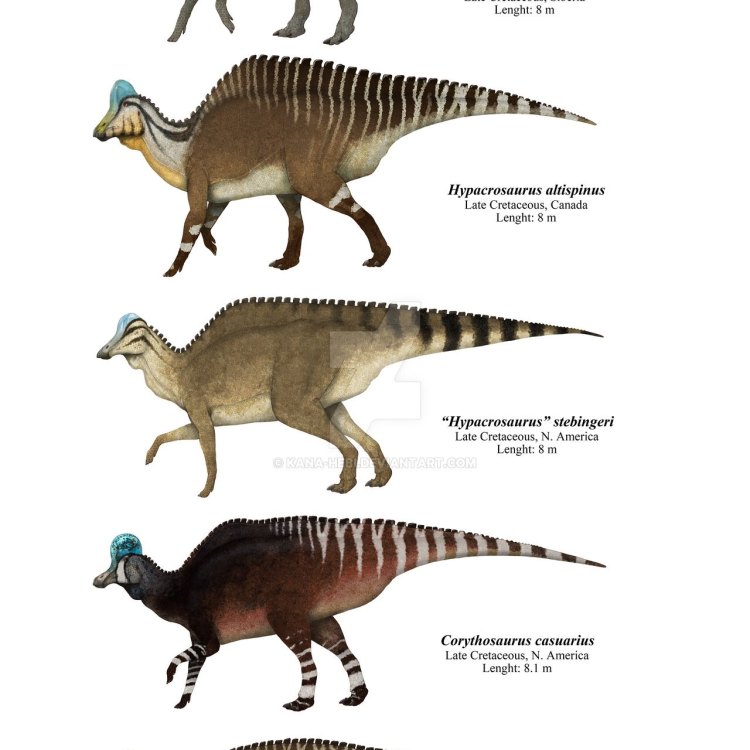
Hadrosauridae
The Fascinating World of Hadrosaurids: A Closer Look at the Duck-Billed Dinosaurs
Dinosaurs are a subject that has captivated people's imaginations for centuries. These ancient creatures, who roamed the earth for over 160 million years, have captured our fascination with their colossal size, unique features, and mysterious lifestyles. One particular group of dinosaurs, the Hadrosaurids, has gained popularity in recent years due to their distinct duck-billed snouts and elaborate head crests. These herbivorous dinosaurs, also known as "duck-billed dinosaurs," are one of the most diverse and successful groups of dinosaurs, with over 80 known species OnTimeAiraz.Com. Let's take a closer look at these fascinating creatures and uncover the secrets of the Hadrosaurids.The Bone Structure of Hadrosaurids
One of the most distinctive features of Hadrosaurids is their bone structure. These dinosaurs had large, hollow bones with internal struts, making them lightweight yet strong. This unique bone structure allowed them to move swiftly, despite their massive size. The internal struts also made their bones more resistant to stress and fractures, a necessary adaptation for their active lifestyle.
The Reproduction Type of Hadrosaurids
Hadrosaurids were egg-laying dinosaurs, also known as oviparous animals. Just like their modern-day reptile counterparts, these dinosaurs laid eggs, which later hatched into young ones. The eggs were often laid in a nest, and the parents would take turns incubating them, providing proper care until they hatched. This reproductive strategy was crucial for the survival of these dinosaurs, ensuring the continuity of their species Hypsibema.
The Activity Period of Hadrosaurids
Hadrosaurids were diurnal creatures, meaning that they were primarily active during the day and slept at night. These dinosaurs were adapted to the diurnal cycle of the earth, with eyesight and other sensory organs perfectly suited for the daylight activities. They would spend their days foraging for plants and socializing with other members of their species, while the nights were for resting and sleeping.
Distinctive Features of Hadrosaurids
Hadrosaurids were undoubtedly known for their distinctive duck-billed snout, giving them the nickname "duck-billed dinosaurs." This unique feature was initially thought to be used for filtering food from the water, similar to modern-day ducks. However, recent studies have shown that it was used for grinding and tearing through tough vegetation. Another notable feature of these dinosaurs was their elaborate head crests, which were likely used for display purposes, for communication within the herd, and possibly even as a defense mechanism against predators.
Communication Method of Hadrosaurids
While we know that Hadrosaurids had a complex social structure, the exact method of communication among these dinosaurs is still unknown. The elaborate head crests and other non-verbal cues were likely used to communicate within the herd, but the specifics of their communication remain a mystery. Researchers continue to study the fossil evidence and try to uncover more about how Hadrosaurids communicated with each other.
Survival Adaptations of Hadrosaurids
Herding behavior and fast growth rate were two key survival adaptations of Hadrosaurids. These dinosaurs lived in large herds, consisting of hundreds of individuals, providing safety in numbers against predators. Their fast growth rate allowed them to reach adulthood quickly and reproduce, ensuring the continuity of their species. These adaptations, along with their quick and agile movements, helped Hadrosaurids thrive in their ecosystem.
The Largest and Smallest Species of Hadrosaurids
Of the over 80 known species of Hadrosaurids, the largest was Shantungosaurus giganteus, with an estimated length of 16 meters (52 feet) and a weight of 16 tonnes (17.6 tons). On the other side of the spectrum, the smallest species was Telmatosaurus transsylvanicus, with an estimated length of 1.8 meters (6 feet) and a weight of 200 kilograms (440 pounds). These extreme differences in size within the same species show the incredible diversity and adaptation of Hadrosaurids.
Fossil Characteristics of Hadrosaurids
The fossils of Hadrosaurids have provided valuable insight into these creatures' lifestyles and behavior. Unlike other dinosaur fossils, Hadrosaurid fossils are often found in well-preserved conditions, with complete skeletons and even skin impressions. These discoveries have allowed researchers to study their anatomy, locomotion, diet, and even their skin texture, giving us a better understanding of these dinosaurs.
Ecological Role of Hadrosaurids
As large herbivores, Hadrosaurids played a crucial role in their ecosystem. They were essential for maintaining the balance of plant life in their environment, preventing overgrazing and preserving biodiversity. By feeding on a wide variety of plants, they also dispersed seeds, acting as vital seed dispersers, helping plant species to spread and thrive.
Unique Facts about Hadrosaurids
Apart from their distinctive features and lifestyle, researchers have uncovered some interesting and unique facts about Hadrosaurids. One fascinating discovery is their complex social structure, with evidence of different age groups and social hierarchy within the herds. This suggests that they were highly intelligent animals, capable of forming strong social bonds and working together for survival. Another unique fact is that Hadrosaurids were found in various locations worldwide, including North America, Europe, and Asia, indicating their widespread distribution and adaptability.
Predator Status of Hadrosaurids
Hadrosaurids were mostly prey animals, hunted by predators such as Tyrannosaurus rex, Albertosaurus, and Deinonychus. These predators posed a significant threat to Hadrosaurids, and their herding behavior and fast growth rate were essential for their survival. By living in large herds, these dinosaurs could defend against predators and protect their young, ensuring that their species survived.
Discovery of Hadrosaurids
The discovery of Hadrosaurids dates back to the 19th century when Sir Richard Owen, a British paleontologist, first described and named the dinosaur group in 1842. Since then, numerous discoveries have been made worldwide, providing a wealth of information about these fascinating creatures.
In Conclusion
Hadrosaurids, with their unique bone structure, distinct features, and complex social structure, have captured the fascination of people of all ages. These adaptable and intelligent creatures may have gone extinct millions of years ago, but their legacy continues to live on through the valuable discoveries made by paleontologists. As we continue to uncover more about these duck-billed dinosaurs, we gain a better understanding of our planet's past and the wondrous creatures that roamed it.
The Magnificent Hadrosaurids: The Herbivorous Giants of the Late Cretaceous
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.