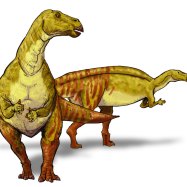
Heterodontosaurus
Unknown
Meet the Heterodontosaurus, a unique dinosaur with unknown skin color and maximum speed. These herbivores once roamed the Southern African region, making them a fascinating addition to the world of dinosaurs. Discover more about this mysterious creature and its distinguishing features. #Heterodontosaurus #Dinosaurs #SouthernAfrica
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Heterodontosaurus
Geological Era: Jurassic
Feeding Behavior: Herbivorous
The Fascinating Heterodontosaurus: Unraveling the Mysteries of This Unique Jurassic Herbivore
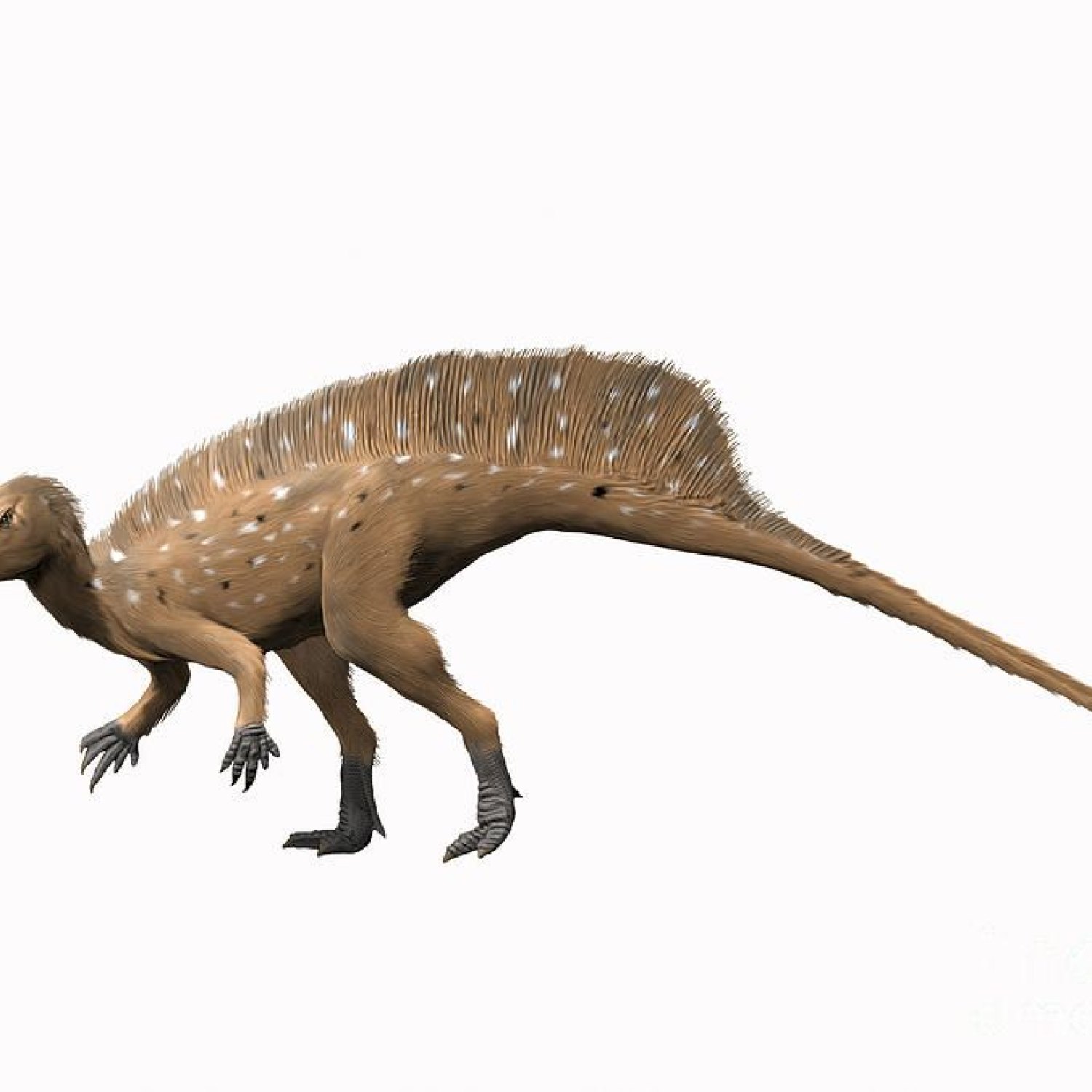
The Jurassic period is known for its diverse and magnificent creatures, from the mighty T-Rex to the swift Velociraptors. Among these giants, there existed a lesser-known, but equally fascinating, dinosaur - the Heterodontosaurus. With its unusual name and distinct features, this dinosaur has piqued the interest of paleontologists and dinosaur enthusiasts alike.Heterodontosaurus, which means "different-toothed lizard," is a small herbivorous dinosaur that lived during the early Jurassic period, approximately 200 million years ago Heterodontosaurus. It is classified under the family Heterodontosauridae, a group of primitive, ornithischian dinosaurs that were characterized by their distinctive teeth. Let's delve deeper into the world of this unique dinosaur and discover its remarkable features.
Size and Appearance
Standing at a mere 30 centimeters tall and measuring 1 meter in length, the Heterodontosaurus was one of the smallest dinosaurs of its time. Despite its size, it had a stocky build and was well adapted to its environment. Its hind legs were longer than its front legs, which suggests that it was probably a fast runner.But what makes the Heterodontosaurus truly stand out is its unique dentition. Unlike most dinosaurs, which had a uniform set of teeth, this herbivore had a varied tooth structure, with different teeth adapted for different functions. Its front teeth were sharp and pointed, while its back teeth were flatter and designed for grinding food. These different tooth shapes, known as heterodonty, are what gave this dinosaur its name Hypselosaurus.
Diet and Feeding Behavior
As a herbivore, the Heterodontosaurus primarily fed on plants, such as ferns, roots, and other vegetation found in its native habitat - woodlands. Its heterodonty allowed it to have a varied diet, as it could effectively chew and grind different types of plant matter.But how did this small dinosaur defend itself against potential predators? Despite its sharp front teeth, the Heterodontosaurus was a non-predatory dinosaur and did not have any means of self-defense. Instead, it relied on its speed and agility to evade predators, and to further protect itself, it may have lived in groups, providing safety in numbers.
Geographical Distribution and Habitat
Fossils of the Heterodontosaurus have only been found in Southern Africa, specifically in South Africa and Lesotho. This suggests that it had a limited geographical distribution and was possibly endemic to this region. It is believed that this dinosaur inhabited woodlands, a habitat filled with a variety of plants suitable for its herbivorous diet.The Timeline of Discovery
The first fossils of the Heterodontosaurus were discovered in the early 1960s by a team of paleontologists led by Alfred Crompton and Alan Charig. They unearthed multiple skeletons in South Africa, and after a thorough analysis, the researchers concluded that these fossils belonged to a previously unknown dinosaur species.Further excavations in the following decades revealed more fossils, including juvenile specimens, shedding light on the growth and development of this small dinosaur. As more fossils were discovered, new interpretations and theories about the Heterodontosaurus emerged, making it a subject of ongoing research and study.
The Mysteries That Remain
While we have learned a great deal about the Heterodontosaurus, there are still many unanswered questions surrounding this unique creature. For instance, its preferred temperature and skin color remain a mystery, as the fossil record does not provide any clues. Paleontologists continue to study these dinosaurs, hoping to uncover more information about their appearance and biology.Another unanswered question relates to the maximum speed of this dinosaur. Due to its small size, it was undoubtedly swift and agile, but the exact extent of its speed is still unknown. With advances in technology and new discoveries, we may one day have a more accurate understanding of the Heterodontosaurus's capabilities.
The Impact of the Heterodontosaurus
The Heterodontosaurus may not be as well-known as other dinosaurs, but its discovery has contributed greatly to our understanding of the diverse world of dinosaurs. Its unique dentition and small size have challenged previous notions about dinosaur evolution and have opened up new avenues for research.Moreover, the Heterodontosaurus has become an important species in the study of ornithischian dinosaurs, providing valuable insights into the group's behavior, ecology, and adaptation. Its fascinating characteristics continue to intrigue scientists and inspire further study.
Concluding Thoughts
The Heterodontosaurus may have been small in size, but it has certainly made a big impact in the world of paleontology. Its unusual tooth structure, coupled with its herbivorous and non-predatory behaviors, make it a standout among its dinosaur counterparts. With ongoing research, we can hope to unravel more mysteries surrounding this captivating creature and uncover more fascinating facts about the Heterodontosaurus.
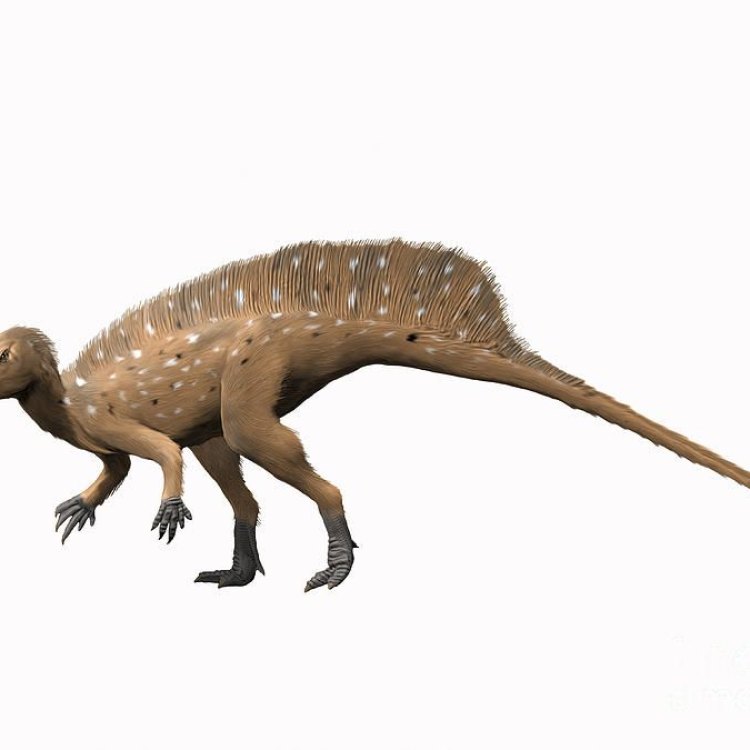
Heterodontosaurus
Dinosaur Details Heterodontosaurus - Scientific Name: Heterodontosaurus
- Category: Dinosaurs H
- Scientific Name: Heterodontosaurus
- Common Name: Heterodontosaurus
- Geological Era: Jurassic
- Length: 1 meter
- Height: 30 centimeters
- Weight: 5 kilograms
- Diet: Herbivore
- Feeding Behavior: Herbivorous
- Predatory Behavior: Non-predatory
- Tooth Structure: Heterodont
- Native Habitat: Woodlands
- Geographical Distribution: Southern Africa
- Preferred Temperature: Unknown
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown
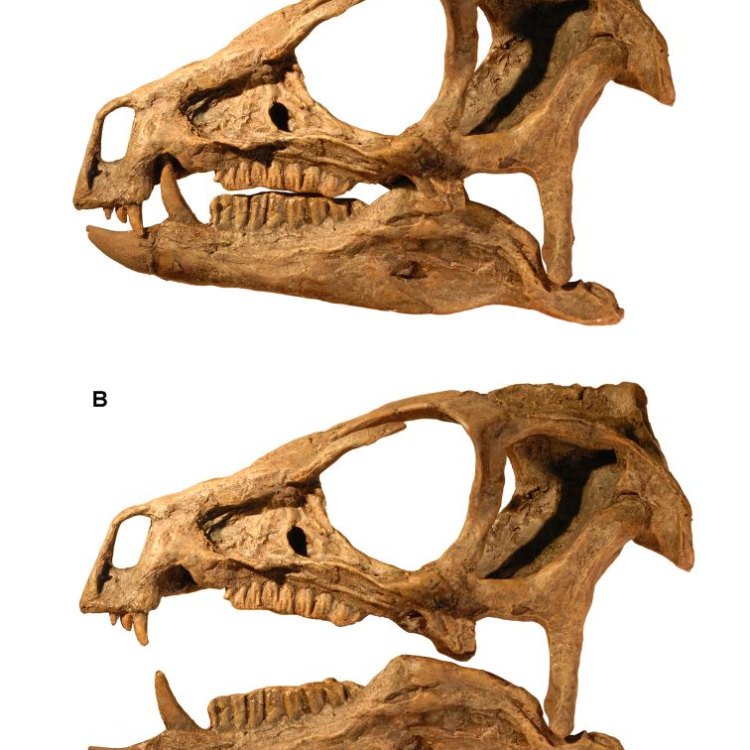
Heterodontosaurus
- Bone Structure: Unknown
- Reproduction Type: Unknown
- Activity Period: Unknown
- Distinctive Features: Long canine-like front teeth
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Unknown
- Largest Species: Heterodontosaurus tucki
- Smallest Species: Heterodontosaurus planus
- Fossil Characteristics: Partial skeletons
- Role in Ecosystem: Unknown
- Unique Facts: One of the earliest known herbivorous dinosaurs
- Predator Status: Non-predatory
- Discovery Location: South Africa
- Discovery Year: 1962
- Discoverer's Name: Richard Thulborn
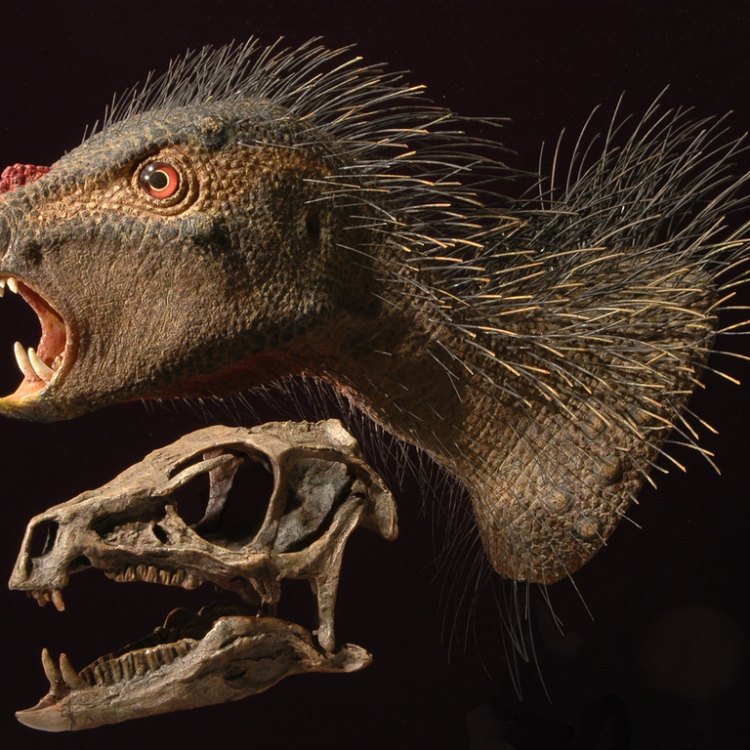

Heterodontosaurus
The Mysterious Heterodontosaurus: A Peek into the Early Days of Dinosaurs
Once upon a time, long before the T-Rex and the Brontosaurus roamed the Earth, there was a small herbivorous dinosaur with long canine-like front teeth, known as the Heterodontosaurus. It may not be a household name like its larger and more popular dinosaur cousins, but this small creature has captivated the attention of paleontologists and dinosaur enthusiasts alike with its elusive nature and unique features.Unlike other dinosaurs, there is much that is unknown about the Heterodontosaurus. Its bone structure, reproductive type, and activity period are all still a mystery OnTimeAiraz.Com. However, what we do know is that this dinosaur provides us with a valuable glimpse into the early days of dinosaurs. Let's delve deeper and uncover the fascinating characteristics and facts of this enigmatic creature.
A Snapshot of the Heterodontosaurus
The name Heterodontosaurus comes from the Greek words "heteros" meaning different and "odons" meaning teeth. This is a fitting name, considering the distinctive feature of this dinosaur is its long, canine-like front teeth. It is believed that these teeth were used for shredding and breaking down tough plant material, making the Heterodontosaurus one of the earliest known herbivorous dinosaurs.It is estimated that the Heterodontosaurus lived during the Early Jurassic period, approximately 200 million years ago. The largest and most well-known species of this dinosaur is the Heterodontosaurus tucki, standing at about 3 feet tall and 7 feet long. On the other end of the spectrum is the Heterodontosaurus planus, the smallest species, measuring only about 14 inches in length. Both species were discovered in South Africa, the only known location where Heterodontosaurus fossils have been found Huaxiagnathus.
The Mystery of Heterodontosaurus's Bone Structure and Reproduction
One of the most puzzling aspects of the Heterodontosaurus is its bone structure. There is no complete skeleton of this dinosaur, so its bone structure is still largely a mystery. However, partially preserved skeletons and skull fragments have been discovered, giving paleontologists some insight into the structure of this elusive dinosaur. These fossils have revealed that the Heterodontosaurus was bipedal, meaning it walked on two legs, with its front limbs being shorter than its hind limbs.Unfortunately, the reproductive type of the Heterodontosaurus also remains a mystery. This is due to the lack of fossil evidence and the fact that no eggshells or nests have been found. Without this crucial information, it is difficult for scientists to determine how this dinosaur reproduced.
A Look into the Activity Period and Communication Method of Heterodontosaurus
As we continue to unravel the mysteries of the Heterodontosaurus, we come across two more unknowns - its activity period and communication method. Since we do not know the reproductive type of this dinosaur, it is difficult to determine its activity period. However, based on the fossils found, it is believed that the Heterodontosaurus was active during daylight hours.The communication method of this dinosaur is also unknown. While most dinosaurs are known to communicate with a combination of vocalizations and body language, it is impossible to determine how the Heterodontosaurus communicated without any fossil evidence.
The Puzzle of Heterodontosaurus's Survival Adaptations
Another area of mystery in the Heterodontosaurus's life is its survival adaptations. How did this small dinosaur survive and thrive in an environment filled with much larger and potentially threatening predators? Without any fossil evidence or complete skeletons, it is difficult to determine the specific survival adaptations of the Heterodontosaurus.However, based on its long, sharp front teeth, it is believed that this dinosaur may have used its teeth as a defense mechanism against predators. It is also possible that this agile and quick-footed dinosaur was able to evade predators with its speed and agility.
A Unique Role in the Ecosystem
While we may not know much about its bone structure, reproduction, activity period, communication method, survival adaptations, or even its role in the ecosystem, there is one thing we do know - the Heterodontosaurus played a crucial role in the early days of the dinosaur ecosystem.The Heterodontosaurus was one of the earliest known herbivorous dinosaurs, filling the vital role of a plant eater in a world dominated by carnivorous dinosaurs. Its unique teeth allowed it to consume a variety of plant material, which helped shape the ecosystem and create a balance between plant and animal life.
The Legacy of Heterodontosaurus
For such a mysterious and elusive creature, the Heterodontosaurus has left behind a remarkable legacy. Its discovery in 1962 by paleontologist Richard Thulborn in South Africa has provided us with valuable insights into the early days of dinosaurs. The fossils of this dinosaur have also played a key role in understanding the evolution and diversification of dinosaurs throughout history.As paleontologists continue to dig deeper and uncover more fossils of this intriguing creature, we may eventually solve the puzzle of its elusive bone structure, reproductive type, activity period, communication method, survival adaptations, and role in the ecosystem. Until then, the Heterodontosaurus will continue to captivate our imaginations and remind us of the mysteries waiting to be unraveled in our prehistoric past.

The Fascinating Heterodontosaurus: Unraveling the Mysteries of This Unique Jurassic Herbivore
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.