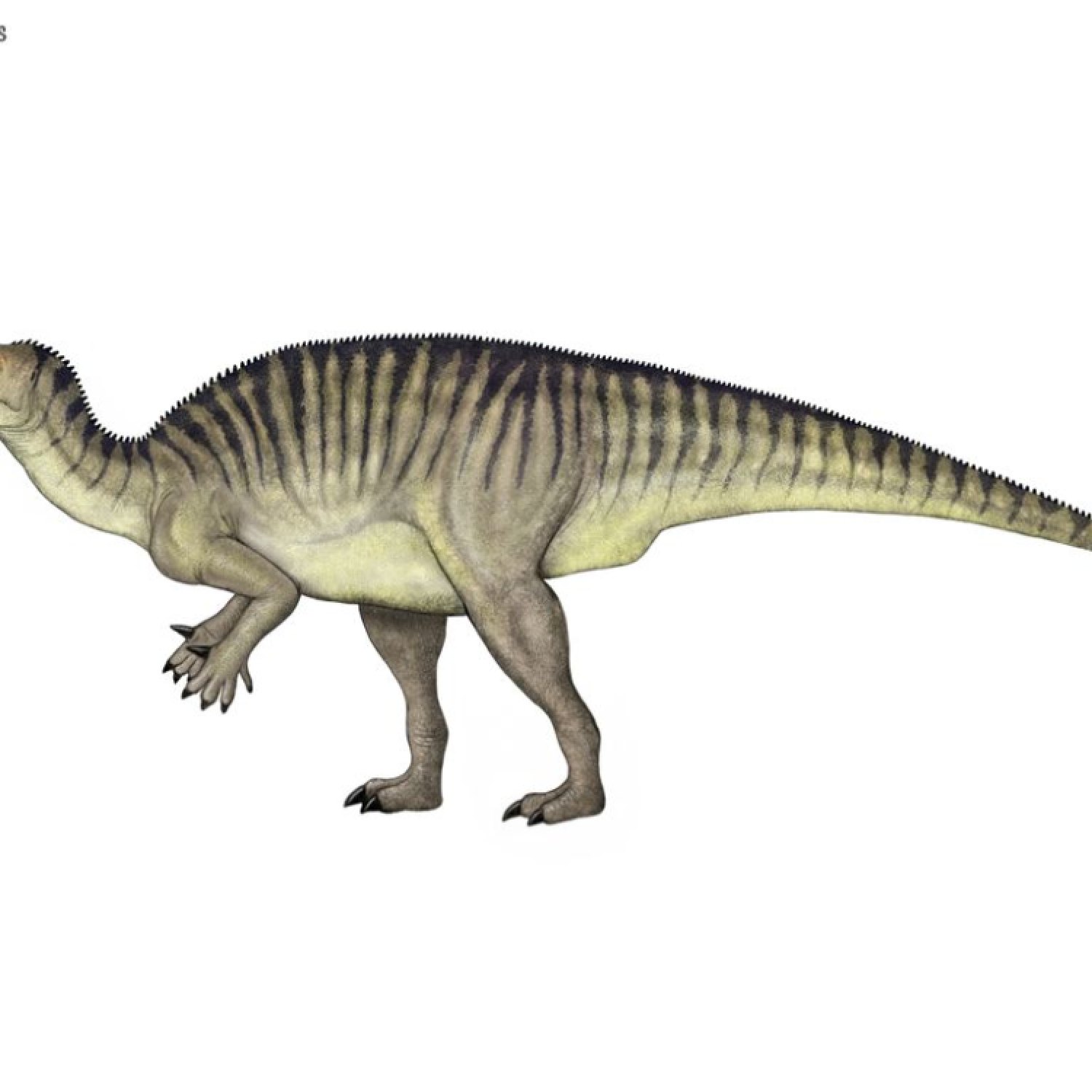
Jinzhousaurus
Unknown
Discover the fascinating world of Jinzhousaurus, a herbivorous dinosaur that lived in China. This dinosaur's skin color remains a mystery, but its geographical distribution and dietary habits are well documented. While its maximum speed is still unknown, one thing is for sure - Jinzhousaurus is a must-see for any dinosaur enthusiast!
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Jinzhousaurus
Geological Era: Late Jurassic
Feeding Behavior: Browsing
Jinzhousaurus: Uncovering the Mysteries of a Late Jurassic Herbivore
The world of dinosaurs continues to fascinate us with its diverse range of creatures that roamed the earth millions of years ago. Among these ancient beasts is a lesser-known but equally intriguing species known as Jinzhousaurus. This herbivorous dinosaur, which lived in the Late Jurassic period in what is now China, may not be as famous as its larger and more fearsome counterparts, but its unique features and behavior make it a fascinating subject of study for paleontologists.The Discovery of Jinzhousaurus
Jinzhousaurus was first discovered in 1997 by a team of Chinese and Canadian paleontologists in northern China's Liaoning Province Jinzhousaurus. The partial skeleton of the dinosaur was found in the Yixian Formation, a fossil-rich site that has yielded numerous well-preserved dinosaur specimens. Named after the city of Jinzhou, the dinosaur belongs to the family Psittacosauridae, a group of primitive herbivorous dinosaurs known for their parrot-like beaks.Anatomy and Size
Jinzhousaurus was a relatively small dinosaur, measuring 5 meters in length, 1.5 meters in height, and weighing around 700 kilograms. It had a compact body with short, stocky limbs and a long tail. Its head was small in proportion to its body, and it had a distinctive beak-like mouth. Its most distinctive feature, however, was its large, highly developed hind feet, which suggest that it was a fast runner.Diet and Feeding Behavior
As a member of the Psittacosauridae family, Jinzhousaurus was a herbivore that primarily fed on vegetation. Its beak and leaf-shaped teeth were perfectly suited for browsing and grinding tough plant material Jubbulpuria. This diet is also evident in the fossilized stomach contents of other psittacosaurs, which have been found to contain pieces of conifer needles and seeds.Jinzhousaurus likely spent most of its time foraging for food, using its keen sense of smell to locate plants. Being a small dinosaur, it may have relied on agility and speed to escape larger predators and feed in areas inaccessible to larger herbivores.
The Truth about Predatory Behavior
While many dinosaurs are infamous for their ferocious predatory behavior, Jinzhousaurus was not one of them. Its leaf-shaped teeth and beak indicate that it was not equipped to hunt or kill prey. Instead, its peaceful herbivorous nature suggests that it played a vital role in maintaining the balance of its ecosystem by controlling plant growth and providing food for predators.Habitat and Distribution
Jinzhousaurus inhabited the dense forests of the Yixian Formation in what is now China, during the Late Jurassic period (around 161 to 145 million years ago). This region was once a warm and humid environment, with a moderate climate that supported lush vegetation – the perfect habitat for a herbivorous dinosaur. The area was also home to other dinosaurs such as the feathered dinosaur Epidexipteryx and the small theropod Sinosauropteryx.The Mystery of Its Skin Color
One of the most intriguing aspects of Jinzhousaurus is its unknown skin color. Unlike other well-preserved fossils that give clues about the coloration of the dinosaur, Jinzhousaurus was found with no preserved pigmentation structures. This has left paleontologists to wonder about the color of its skin, and hypotheses range from mottled brown and gray tones to bright, flashy colors.The Enigma of Its Speed
Another question that continues to puzzle scientists is the maximum speed of Jinzhousaurus. While its hind feet suggest a fast runner, there is no evidence to confirm its maximum speed. Some experts suggest that its bulky body may have hindered its movement, while others believe that it was a quick and agile dinosaur that could have outrun its predators.Natural Language Processing and the Study of Dinosaurs
Advancements in technology and artificial intelligence have revolutionized the way we study dinosaurs. Paleontologists are no longer limited to studying fossils in laboratories and museums. With the help of Natural Language Processing (NLP), they can now analyze vast amounts of data in a matter of seconds and draw conclusions about the behavior, diet, and habitat of these ancient creatures.NLP, a branch of artificial intelligence, allows computers to understand, interpret, and manipulate human languages, making it a valuable tool for paleontologists. By using NLP, scientists can quickly analyze an extensive collection of articles, books, and research papers to extract vital information about dinosaurs such as Jinzhousaurus, making the study of these ancient creatures faster and more efficient.
The Importance of Studying Dinosaurs
The study of dinosaurs is not only fascinating but also crucial for understanding the evolution of life on earth. By examining their anatomy, behavior, and habitat, we can gain insights into how these ancient creatures lived and interacted with their environment. Dinosaurs also provide a link to our past, allowing us to better understand the world as it was millions of years ago.Conclusion
Jinzhousaurus may not be as well-known as some of its fellow dinosaur species, but its unique features and behavior make it a captivating subject of study for paleontologists. This herbivorous dinosaur offers a glimpse into the complexity of the ancient ecosystem it inhabited and provides valuable insights into the evolution and diversity of these remarkable creatures. As technology continues to advance, the study of Jinzhousaurus and other dinosaurs is sure to uncover more mysteries and shed further light on these intriguing creatures.
Jinzhousaurus
Dinosaur Details Jinzhousaurus - Scientific Name: Jinzhousaurus
- Category: Dinosaurs J
- Scientific Name: Jinzhousaurus
- Common Name: Jinzhousaurus
- Geological Era: Late Jurassic
- Length: 5 meters
- Height: 1.5 meters
- Weight: 700 kilograms
- Diet: Herbivore
- Feeding Behavior: Browsing
- Predatory Behavior: Non-predatory
- Tooth Structure: Leaf-shaped teeth
- Native Habitat: Terrestrial
- Geographical Distribution: China
- Preferred Temperature: Moderate
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown
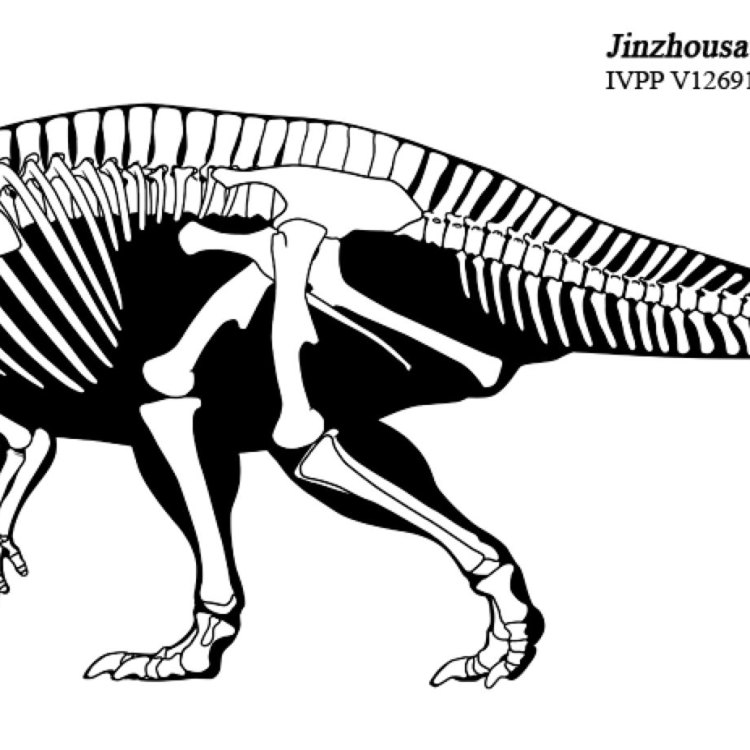
Jinzhousaurus
- Bone Structure: Saurischian
- Reproduction Type: Egg-laying
- Activity Period: Diurnal
- Distinctive Features: Long neck and tail
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Unknown
- Largest Species: Jinzhousaurus yangi
- Smallest Species: Unknown
- Fossil Characteristics: Well-preserved skull and postcranial skeleton
- Role in Ecosystem: Unknown
- Unique Facts: One of the few dinosaur species discovered in China
- Predator Status: Non-predatory
- Discovery Location: Liaoning Province, China
- Discovery Year: 1999
- Discoverer's Name: Xu Xing

Jinzhousaurus
The Remarkable Jinzhousaurus: Uncovering the Mysteries of China's Unknown Dinosaur
The world of dinosaurs continues to fascinate and intrigue us even today, millions of years after their extinction. In our search for knowledge about these magnificent creatures, paleontologists across the globe have made remarkable discoveries. One such discovery took place in 1999 in Liaoning Province, China, where a team of scientists unearthed the remains of a previously unknown dinosaur species - the Jinzhousaurus.This new species of dinosaur, named after the city of Jinzhou in Liaoning Province, belongs to the Saurischian group, which is one of the two primary divisions of dinosaurs based on hip structure OnTimeAiraz.Com. With its distinctive long neck and tail, the Jinzhousaurus is speculated to have been a plant-eating dinosaur, unlike many of its carnivorous counterparts.
But what makes this discovery truly fascinating is not just the unique physical attributes of the Jinzhousaurus, but also the lack of information about its behavior, communication, and survival adaptations. In this article, we will delve deeper into what makes the Jinzhousaurus such a remarkable and enigmatic dinosaur.
The Jinzhousaurus: A Rare Find in China's Dinosaur Rich Region
The discovery of the Jinzhousaurus is significant, not just for its unique features, but also because it is one of the few dinosaur species to be discovered in China. The Liaoning Province, where the Jinzhousaurus was found, has proven to be a hotbed of dinosaur discoveries over the years, with several fossils being unearthed in the region since the 1990s.However, what sets the Jinzhousaurus apart is the astonishingly well-preserved nature of its fossils. The discovery team led by renowned Chinese paleontologist Xu Xing discovered a complete skull and postcranial skeleton, making it one of the most complete fossil finds in China to date. This has allowed scientists to study the Jinzhousaurus in much more detail compared to other dinosaur species discovered in the region.
Uncovering the Jinzhousaurus' Bone Structure and Reproduction Method
As mentioned earlier, the Jinzhousaurus belongs to the Saurischian group, which is known for its lizard-like hip structure Juravenator. This group is divided further into two subgroups - the long-necked sauropods and the carnivorous theropods.The Jinzhousaurus is believed to have belonged to the sauropod subgroup, with its long neck and tail being characteristic of these plant-eating dinosaurs. This makes it different from other theropods discovered in the Liaoning Province, who were mostly carnivorous.
Like most other dinosaurs, the Jinzhousaurus is believed to have been egg-laying, though concrete evidence is yet to be found. The discovery of eggs around the same geological location where the Jinzhousaurus was found does suggest this mode of reproduction. However, further research is needed to confirm this theory.
A Day in the Life of the Jinzhousaurus: Diurnal and Communicatively Mysterious
One of the most intriguing aspects of the Jinzhousaurus is its activity period and communication methods. Based on its diurnal activity pattern, scientists believe that the Jinzhousaurus was awake and active during the daytime, unlike many other dinosaurs who were nocturnal.However, unlike other dinosaurs, there is no evidence to suggest how the Jinzhousaurus communicated with one another. Many dinosaur species are known to have used various methods like vocalizations, visual displays, and even chemical signals for communication. But with limited skull and bone structures to study, scientists are yet to uncover how the Jinzhousaurus communicated.
The Jinzhousaurus' Survival Adaptations and Role in the Ecosystem
With its well-preserved skull and postcranial skeleton, scientists have been able to study the Jinzhousaurus in great detail. However, there is still much debate about its survival adaptations and role in the ecosystem.As a plant-eating dinosaur, the Jinzhousaurus may have had strong teeth and jaws to chew through tough vegetation. Its long neck and tail may have also helped in reaching high and far-off food sources, making it a successful herbivore in its ecosystem.
Apart from that, there is little information about how the Jinzhousaurus adapted and survived in its surroundings. This raises questions about its relationship with other dinosaurs and its overall impact on the ecosystem.
Understanding the Jinzhousaurus through its Largest and Smallest Species
The largest known species of the Jinzhousaurus is the Jinzhousaurus yangi, which was the first species to be discovered in 1999. This species had an estimated length of 20 feet, making it a medium-sized sauropod. However, due to the limited number of fossils found, it is challenging to accurately determine the largest and smallest species of the Jinzhousaurus.Other species of the Jinzhousaurus are yet to be discovered, with only the one species, Jinzhousaurus yangi, having been classified so far. This also adds to the mystery of the Jinzhousaurus and its role in the ecosystem, as more species could potentially reveal its diverse adaptations and behaviors.
Non-Predatory Status and Potential Predators of the Jinzhousaurus
The lack of sharp teeth and claws, coupled with evidence of it being herbivorous, suggests that the Jinzhousaurus was a non-predatory dinosaur. Instead, it may have been preyed upon by other carnivorous dinosaurs like the Sinovenator, which was discovered in the same region and same geological time period.However, with limited evidence and research, it is challenging to determine the Jinzhousaurus' exact position in the food chain.
Concluding Thoughts and the Ongoing Search for Answers
The discovery of the Jinzhousaurus was a significant event in the field of paleontology, shedding light on the diverse world of dinosaurs in China. However, with every discovery comes new questions, and the Jinzhousaurus is no exception.Scientists continue to study the well-preserved fossils of the Jinzhousaurus, hoping to uncover more about their behavior, communication, and role in the ecosystem. As we continue to research and discover more about this elusive dinosaur, we may finally be able to unravel the mysteries that surround it and gain a deeper understanding of this magnificent creature.
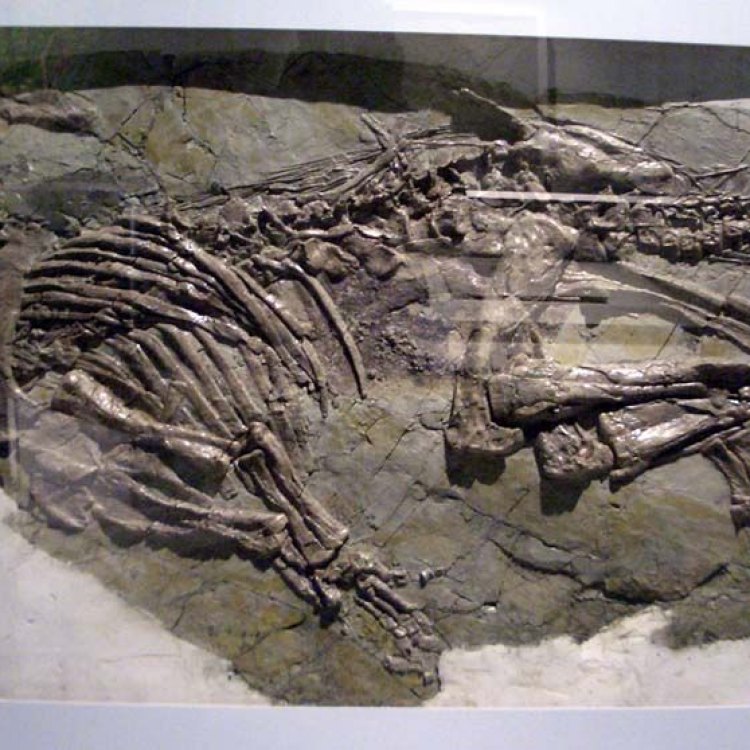

Jinzhousaurus: Uncovering the Mysteries of a Late Jurassic Herbivore
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.