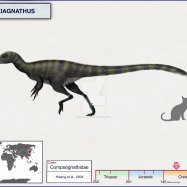
Pachyrhinosaurus
Unknown
Pachyrhinosaurus, a lesser-known herbivorous dinosaur, roamed the Alaskan, Canadian, and American regions. Its unique skin color remains a mystery, along with its maximum speed. Explore more about this fascinating 'P' dinosaur and unveil the secrets of the prehistoric world. #Pachyrhinosaurus #Dinosaurs #Alaska #Canada #UnitedStates #Herbivore #PrehistoricWorld
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Pachyrhinosaurus
Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
Feeding Behavior: Herbivorous
Pachyrhinosaurus: The Massive Herbivore of the Late Cretaceous
In the vast, prehistoric landscape of the Late Cretaceous period, a unique and extraordinary dinosaur roamed the land – the Pachyrhinosaurus. This magnificent creature, with its distinct features and massive size, has captured the fascination of many since its discovery in the early 20th century.The Pachyrhinosaurus, also known by its scientific name Pachyrhinosaurus, was a herbivorous dinosaur that lived approximately 70-69 million years ago. Its name derives from the Greek words “pachy” meaning thick and “rhinos” meaning nose, in reference to its thick, bony nasal, and cranial crest Pachyrhinosaurus. This crest, along with the dinosaur’s other distinctive features, makes it a standout among its prehistoric counterparts.
Discovering the Pachyrhinosaurus
First discovered in 1902 in Alberta, Canada by paleontologist Charles M. Sternberg, the Pachyrhinosaurus was initially thought to be a new species of the well-known dinosaur Triceratops. However, further studies and excavations in the following decades revealed that this unique creature belonged to its own genus.Since its discovery, various fossils of the Pachyrhinosaurus have been found in different parts of North America, including Alaska, Canada, and the United States. Its widespread distribution indicates that this dinosaur thrived in its native habitat of temperate to subtropical climates.
The Physical Appearance of the Pachyrhinosaurus
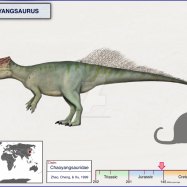
The Pachyrhinosaurus was a massive dinosaur, measuring around 7-8 meters in length, 4 meters in height, and weighing between 3-4 tonnes. Its large size and unique physical features made it a formidable presence in the Late Cretaceous ecosystem.One of the most remarkable features of the Pachyrhinosaurus was its thick, bony nasal crest that protruded from its snout Parksosaurus. This crest varied in size and shape among different species of the dinosaur, including a large, flattened crest on the Pachyrhinosaurus altispinus and a small, pointed crest on the Pachyrhinosaurus perotorum.
The dinosaur’s skull also featured rough, bumpy bosses that gave it a rough and rugged appearance. These bosses, along with its thick skin, may have served as protection against predators.
Feeding Behavior and Diet
As mentioned, the Pachyrhinosaurus was a herbivore, meaning it subsisted on a diet of plants. Being a large and bulky dinosaur, it required a significant amount of food to sustain itself. It is believed that the Pachyrhinosaurus fed on several types of vegetation, including ferns, horsetails, and cycads.Researchers have also found evidence of gastroliths, or stomach stones, in the remains of Pachyrhinosaurus fossils. These stones were likely used to aid in digestion, indicating that the dinosaur had a diet primarily consisting of tough, fibrous plant matter.
The Unique Tooth Structure of the Pachyrhinosaurus
One of the most intriguing aspects of the Pachyrhinosaurus is its dental structure. Its teeth were leaf-shaped with roughened enamel, a feature not seen in any other type of dinosaur.The dinosaur’s leaf-shaped teeth were designed specifically for grinding and crushing vegetation, making them well-suited to its herbivorous diet. Additionally, the rough enamel may have helped to grip and tear through tough plant matter, making feeding easier for these massive creatures.
The Pachyrhinosaurus' Native Habitat and Geographic Distribution
The Pachyrhinosaurus was primarily native to North America, with fossils discovered in Alberta, Canada, Alaska, and the United States. This region was a diverse and fertile ecosystem during the Late Cretaceous period, providing the perfect habitat for the Pachyrhinosaurus to thrive.Similar to other herbivorous dinosaurs, the Pachyrhinosaurus may have migrated to find food as the seasons changed. It is also possible that they lived in herds, as fossils of multiple individuals have been found in the same location.
The Behavior of the Pachyrhinosaurus
Despite its intimidating physical appearance, the Pachyrhinosaurus was non-predatory and had a peaceful disposition. Its thick skin, nasal crest, and bumpy bosses may have been used for display and communication among its kind.Although their behavioral patterns are not fully understood, it is believed that these dinosaurs lived in groups, possibly divided into different age groups. This may have served as a way to protect themselves from predators like the fearsome Tyrannosaurus Rex.
The Maximum Speed and Skin Color of the Pachyrhinosaurus
Unfortunately, due to the limited fossil evidence, the maximum speed and skin color of the Pachyrhinosaurus remain a mystery. However, using calculations based on its estimated weight and stride length, it is thought that the Pachyrhinosaurus could have reached a top speed of around 24-27 miles per hour.Similarly, the skin color of the Pachyrhinosaurus is also unknown, with researchers unable to determine its color from fossil remains. However, it is speculated that the dinosaur may have had a mottled color pattern for camouflage or a bright and vibrant color for display purposes.
The Legacy of the Pachyrhinosaurus
The Pachyrhinosaurus may have roamed the Earth millions of years ago, but its legacy continues to captivate us today. Its unique physical features and behavior have been a subject of interest for dinosaur enthusiasts and researchers alike.Additionally, the discovery of the Pachyrhinosaurus has given us valuable insights into the diverse and dynamic ecosystem of the Late Cretaceous period. Its fossils, along with those of other dinosaurs, have helped us piece together a better understanding of our planet's history and the evolution of life on Earth.
In Conclusion
The Pachyrhinosaurus may have been a lesser-known dinosaur compared to its more famous counterparts, but its distinctive features and remarkable existence make it a standout in the world of paleontology. From its massive size to its unusual cranial crest, this herbivorous dinosaur continues to fascinate and intrigue us.While much remains unknown about the Pachyrhinosaurus, the ongoing research and discoveries surrounding this remarkable creature will undoubtedly continue to shed light on its fascinating evolution and behavior. And it is these ongoing advancements in scientific knowledge that make us appreciate and learn more about the extraordinary creatures that once roamed our planet.
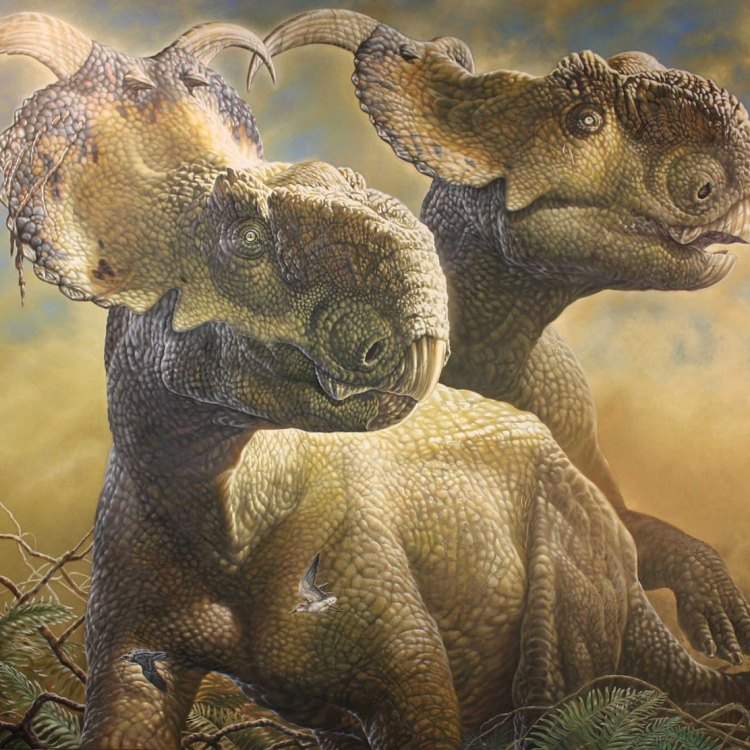

Pachyrhinosaurus
Dinosaur Details Pachyrhinosaurus - Scientific Name: Pachyrhinosaurus
- Category: Dinosaurs P
- Scientific Name: Pachyrhinosaurus
- Common Name: Pachyrhinosaurus
- Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
- Length: 7 - 8 meters
- Height: 4 meters
- Weight: 3 - 4 tonnes
- Diet: Herbivore
- Feeding Behavior: Herbivorous
- Predatory Behavior: Non-predatory
- Tooth Structure: Leaf-shaped with roughened enamel
- Native Habitat: North America
- Geographical Distribution: Alaska, Canada, and United States
- Preferred Temperature: Temperate to subtropical climates
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown
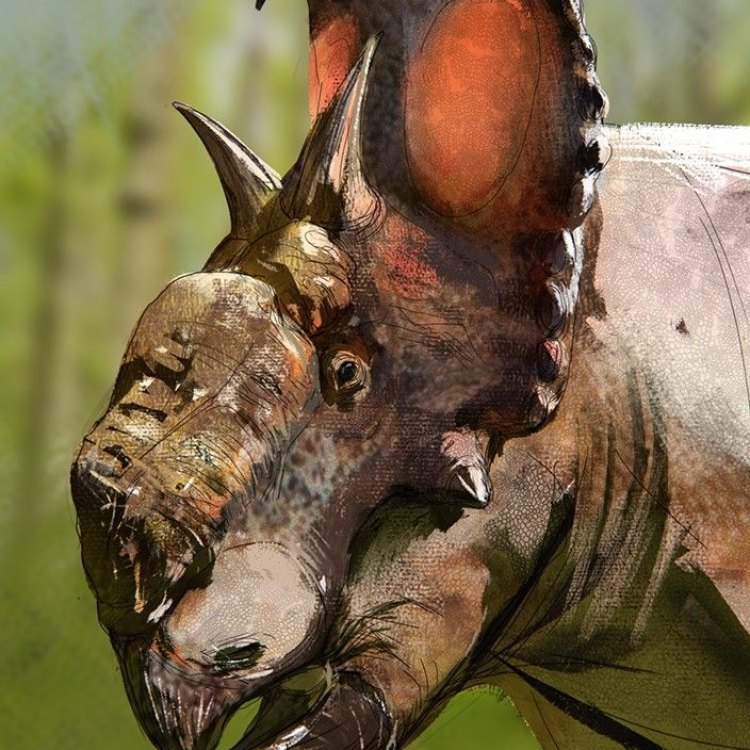

Pachyrhinosaurus
- Bone Structure: Large and robust
- Reproduction Type: Egg-laying
- Activity Period: Diurnal
- Distinctive Features: Large bony frill on its skull with several large horns
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Possibly used its frill for display or species recognition
- Largest Species: Pachyrhinosaurus canadensis
- Smallest Species: Pachyrhinosaurus lakustai
- Fossil Characteristics: Large skull with a tall frill and horn cores
- Role in Ecosystem: Herbivore and a potential prey for larger predators
- Unique Facts: One of the last known ceratopsians to have evolved
- Predator Status: Non-predatory
- Discovery Location: North America
- Discovery Year: 1946
- Discoverer's Name: Charles M. Sternberg
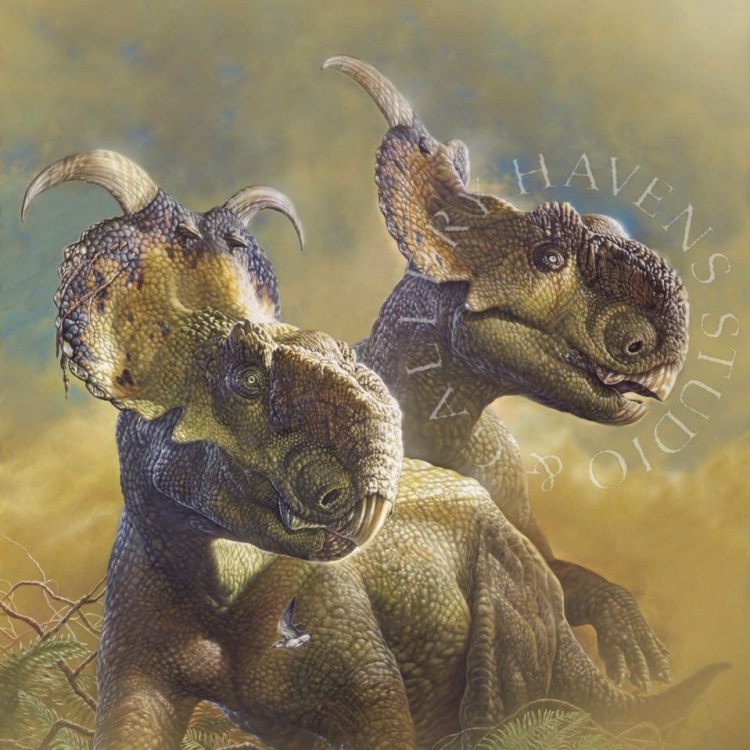

Pachyrhinosaurus
The Unique Features of Pachyrhinosaurus: A Fascinating Prehistoric Creature that Once Roamed North America
The world of dinosaurs is one filled with endless fascination and mystery. With new discoveries being made every day, we are constantly learning more about these prehistoric giants that once roamed the Earth. Among the many fascinating dinosaurs that have captured our imagination, one stands out for its distinct features and evolutionary significance – Pachyrhinosaurus.Pachyrhinosaurus was a large and robust dinosaur with a unique bone structure OnTimeAiraz.Com. Its name, which means "thick-nosed lizard", was given due to the unusual skull structure that gave the dinosaur its distinctive appearance. Let us delve deeper into this intriguing species and uncover its many unique features and characteristics.
Bone Structure: Large and Robust
Pachyrhinosaurus was a ceratopsian, a group of herbivorous dinosaurs that were characterized by their large skulls and distinctive frills. What set Pachyrhinosaurus apart from other ceratopsians was its particularly large and robust bone structure. It is estimated that Pachyrhinosaurus could grow up to 24 feet in length, making it one of the largest known ceratopsians.
Its most notable feature was the large bony frill that extended from the back of its skull. The frill was adorned with several large horns, giving Pachyrhinosaurus an impressive and intimidating appearance. This bony frill was unique to Pachyrhinosaurus and was a defining feature of the species.
Reproduction Type: Egg-Laying
As with most dinosaurs, Pachyrhinosaurus was a reptile and reproduced through egg-laying Pararhabdodon. The exact process of how they reproduced remains a mystery, but it is believed that Pachyrhinosaurus laid its eggs in a nest and then cared for them until they hatched. This suggests that the species may have been monogamous, as both parents would have been involved in the care of the eggs.
Activity Period: Diurnal
Pachyrhinosaurus was a diurnal species, meaning it was active during the day. This is quite different from many other dinosaurs that were thought to be nocturnal. Being active during the day would have allowed Pachyrhinosaurus to take advantage of the warm sun and the abundance of food sources available during daylight hours.
Distinctive Features: Large Bony Frill and Horns
Pachyrhinosaurus was easily recognizable due to its unique bony frill and prominent horns. The frill was made of bone and extended from the back of the skull, with several large horn cores protruding from it. The exact purpose of this frill and horns is still debated among scientists, but one theory suggests that they were used for display or species recognition. It is also possible that they may have had a role in regulating body temperature or providing protection.
Communication Method: Unknown
Despite its impressive frill and horns, the communication method of Pachyrhinosaurus remains a mystery. It is possible that the dinosaurs used visual displays, such as head movements or body postures, to communicate with each other. However, there is no concrete evidence to support this theory, and more research is needed to determine how Pachyrhinosaurus communicated.
Survival Adaptation: Possibly Used its Frill for Display or Species Recognition
One of the key survival adaptations of Pachyrhinosaurus was its distinct frill and horns. These features may have played a crucial role in helping the species survive and thrive in its environment. As mentioned earlier, they could have been used for display or species recognition, giving Pachyrhinosaurus a way to communicate and potentially attract mates or ward off competitors.
Additionally, this bony frill may have provided Pachyrhinosaurus with some protection against predators. It is believed that the frill may have been used to absorb the impact of attacks from other dinosaurs. This could have been a crucial survival adaptation for a species that lived alongside large carnivorous dinosaurs.
Largest Species: Pachyrhinosaurus Canadensis
There have been several species of Pachyrhinosaurus discovered, but the largest is Pachyrhinosaurus canadensis. This species was estimated to be up to 24 feet in length and weighed several tons. It is believed to have been the most common species of Pachyrhinosaurus and had the widest distribution, spanning from Alaska to southern Alberta, Canada.
Smallest Species: Pachyrhinosaurus Lakustai
On the other end of the spectrum is Pachyrhinosaurus lakustai, the smallest known species of Pachyrhinosaurus. This species was discovered in Alberta, Canada, and was noticeably smaller than its larger counterparts, measuring at only 12 feet in length. Despite its smaller size, Pachyrhinosaurus lakustai was still a formidable herbivore and an important part of the ecosystem.
Fossil Characteristics: Large Skull with a Tall Frill and Horn Cores
The fossils of Pachyrhinosaurus give us a better understanding of its physical appearance and unique features. One of the most prominent characteristics of Pachyrhinosaurus fossils is the large skull with its tall frill and prominent horn cores. These features were what made Pachyrhinosaurus stand out among other ceratopsians and have cemented its place in dinosaur history.
Role in Ecosystem: Herbivore and Potential Prey for Larger Predators
Pachyrhinosaurus was a herbivore, meaning it fed on plants and vegetation. Being a large and robust species, it is estimated that Pachyrhinosaurus would have needed a significant amount of plant material to sustain itself. This would have made it an important player in the ecosystem, helping to regulate plant growth and balance the food chain.
At the same time, Pachyrhinosaurus was also prey for larger predators, such as the infamous Tyrannosaurus Rex. This was a constant threat for Pachyrhinosaurus and may have played a role in shaping its evolutionary adaptations, such as its robust bone structure and bony frill.
Unique Facts: One of the Last Known Ceratopsians to Have Evolved
One of the most unique facts about Pachyrhinosaurus is that it was one of the last known ceratopsians to have evolved. The species lived during the Late Cretaceous period, approximately 75-70 million years ago, making it one of the most recent ceratopsians in the fossil record.
This evolutionary timing gives us a glimpse into the changing landscape and environment during the late Cretaceous period. It is believed that Pachyrhinosaurus evolved to adapt to a changing climate and environment, along with other species of dinosaurs that lived during this time.
Predator Status: Non-Predatory
Despite its intimidating appearance, Pachyrhinosaurus was a non-predatory species. Its diet consisted solely of plants and vegetation, and its robust bone structure was not suitable for hunting or attacking other animals. This makes Pachyrhinosaurus a unique and interesting species, as it relied on its physical features mainly for defense and survival in a dangerous world filled with predators.
Discovery Location: North America
Pachyrhinosaurus fossils have been discovered in North America, primarily in the United States and Canada. The first fossils of this species were found by renowned paleontologist Charles M. Sternberg in 1946 in Alberta, Canada. Since then, more discoveries have been made in other regions of North America, providing us with a better understanding of the species' distribution and evolution.
Discovery Year: 1946
Pachyrhinosaurus was first discovered in 1946 by Charles M. Sternberg in Alberta, Canada. This discovery was a significant moment in the field of paleontology, as it introduced scientists to a new and unique species of ceratopsian. Since then, more specimens have been discovered throughout North America, leading to a better understanding of Pachyrhinosaurus and its role in the prehistoric world.
Discoverer's Name: Charles M. Sternberg
Charles M. Sternberg was an American-Canadian paleontologist who made several significant discoveries in North America. He found the first fossils of Pachyrhinosaurus in Alberta, Canada, in 1946, along with many other dinosaur species. Sternberg's discoveries have played a crucial role in our understanding of ancient life on Earth and continue to fascinate and educate people to this day.
In conclusion, Pachyrhinosaurus is a unique and fascinating dinosaur that once roamed North America. From its robust bone structure and distinct frill and horns to its evolutionary significance and discovery by Charles M. Sternberg, Pachyrhinosaurus has left a significant mark on the world of dinosaurs and continues to captivate our imagination. As more discoveries are made and research is conducted, we can only hope to uncover more about this enigmatic species and its role in the prehistoric world.
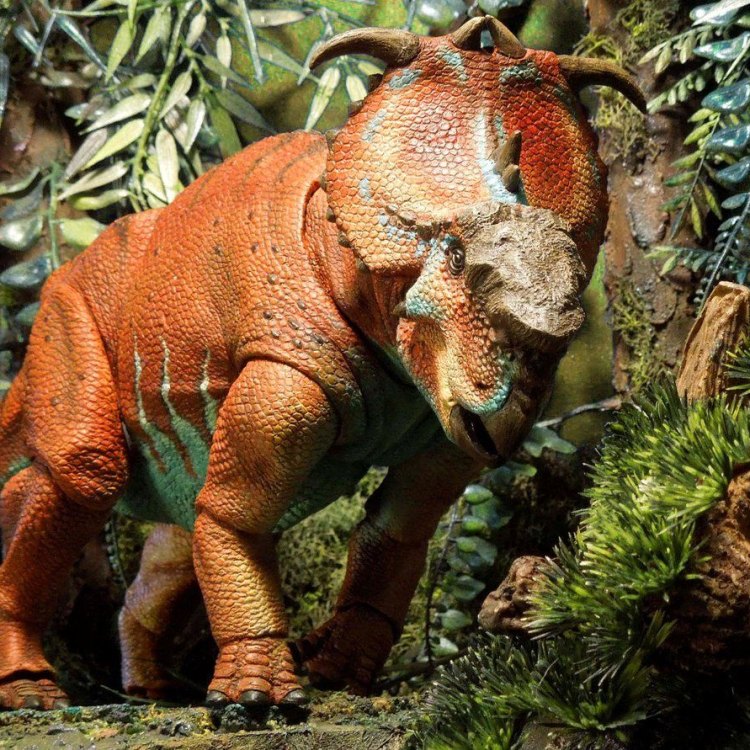

Pachyrhinosaurus: The Massive Herbivore of the Late Cretaceous
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.