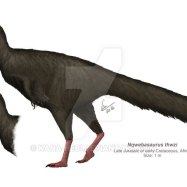
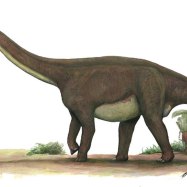
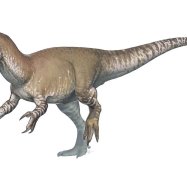
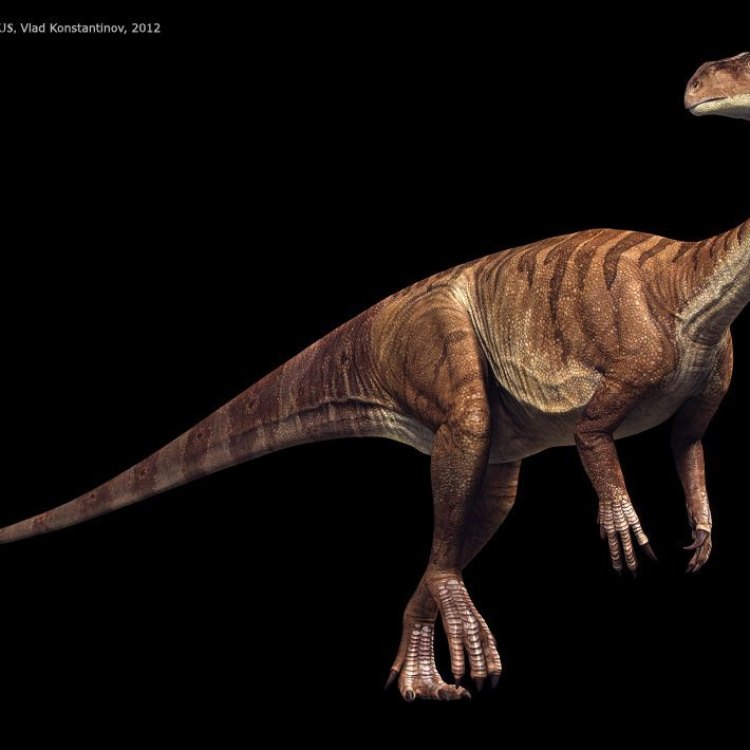
Plateosaurus
Unknown
Plateosaurus, a herbivorous dinosaur, roamed the Earth during the late Triassic period. With its unknown skin color and maximum speed, this creature dominated the European continent. Despite its large size, this dinosaur was a peaceful plant-eater, making it a fascinating addition to the world of dinosaurs. #Plateosaurus #herbivore #EuropeanDinosaurs #TriassicPeriod
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Plateosaurus
Geological Era: Late Triassic
Feeding Behavior: Grazing
Uncovering the Secrets of the Plateosaurus: A Fascinating Herbivore From the Late Triassic Era
The Earth is home to a diverse range of creatures, both past and present, that have roamed the planet for millions of years. Among them are the mighty dinosaurs, which have always captured the imagination of people of all ages. From massive predators like the T-rex to gentle herbivores like the Diplodocus, dinosaurs have been the subject of fascination and research for decades.However, there is one dinosaur that often goes unnoticed – the Plateosaurus Plateosaurus. Despite being one of the first and most abundant dinosaurs, the Plateosaurus has remained in the shadows, overshadowed by its more famous counterparts. But this gentle giant has a rich history and many interesting features that make it worth exploring. In this article, we will delve deep into the world of the Plateosaurus and uncover its secrets.
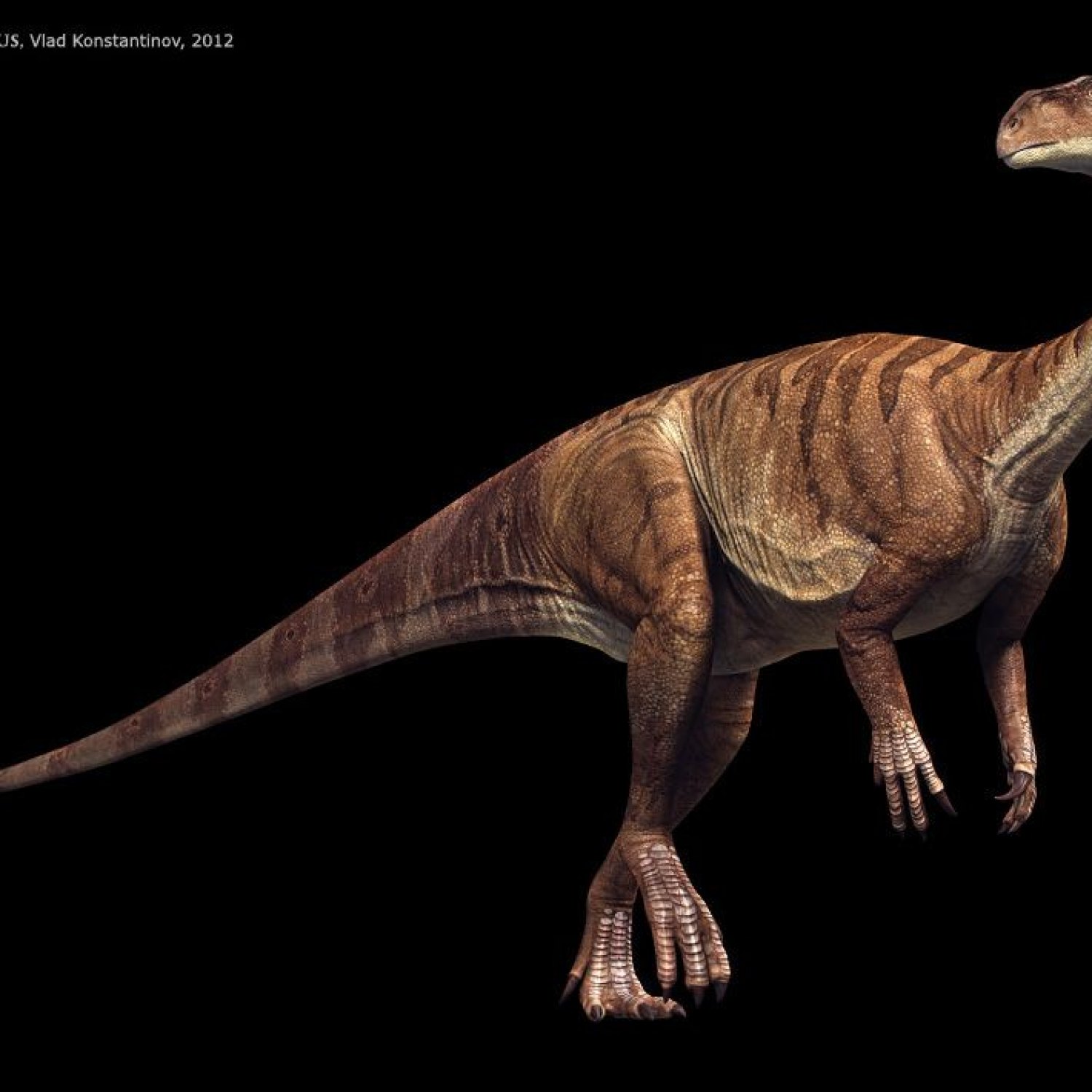
First discovered in 1834 by Johann Georg Wagler, the Plateosaurus belongs to the Superorder Dinosauria and the Order Saurischia. Its scientific name, Plateosaurus, means "flat lizard," which refers to the shape of its bones. Its remains, including fossils and footprints, have been found in Europe, specifically in countries like Germany and Switzerland. It is estimated to have lived around 214-204 million years ago, during the Late Triassic period, making it one of the oldest dinosaurs to have ever existed.
Physical Characteristics
The Plateosaurus was a large dinosaur, measuring 8-10 meters in length, 2-3 meters in height, and weighing around 1-2 tons. These measurements may vary given the differences in the specimens found, but one thing is for sure – this dinosaur was massive Paralititan. It had a long neck and a small head; its body was built for efficiency rather than speed. Its front limbs were shorter than its hind limbs, which were powerful and muscular, allowing it to stand up on its hind legs and reach for leaves on trees.Despite its massive size, the Plateosaurus was a herbivore, which means it only fed on plants. Its diet mainly consisted of conifers, cycads, and ferns, which were commonly found in its native habitat. Its feeding behavior was that of a grazer – it would move through the forests, plucking leaves and branches from trees with its beak-like mouth. Its teeth were leaf-shaped, perfect for grinding and crushing the tough plants it fed on. It is also believed that the Plateosaurus had a specialized stomach that could digest tough plant material, making it a highly efficient herbivore.
Natural Habitat and Distribution
The Plateosaurus was a terrestrial dinosaur, meaning it lived on land, unlike some other dinosaurs that lived in the water or could fly. Its native habitat was in Europe, and its fossils have been found in countries like Germany, Switzerland, and France. During its time, Europe was not a unified landmass but was divided into smaller continents, so the Plateosaurus existed in different areas within its geographical range.Being a herbivore, the Plateosaurus preferred a moderate climate, making its home in temperate regions. The temperate climate would have provided it with ample vegetation, essential for its survival. Its remains have also been found in areas that were once riverbanks, suggesting that the Plateosaurus may have spent some time near water sources, possibly to feed and quench its thirst.
Behavior and Social Structure
The Plateosaurus was a solitary animal, which means it preferred to roam and feed alone. It is believed that these dinosaurs lived in small herds, with one dominant individual leading the group. As mentioned earlier, its body was built more for efficiency than speed, so the Plateosaurus was not a predator. It had no natural enemies since it was too large to be preyed upon by other dinosaurs.However, research has shown that the Plateosaurus may have exhibited herding behavior as a defense mechanism. When a predator approached, the herd would stick close together, making it difficult for the predator to single out one of them. This strategy was essential for the survival of the species, as it ensured that more individuals reached adulthood and reproduced.
Uncovering the Plateosaurus Through Fossils
Since its discovery in the 19th century, many fossilized remains of the Plateosaurus have been found. These fossils have helped paleontologists uncover a wealth of information about this dinosaur, from its physical characteristics to its behaviors. One of the most notable findings was the discovery of a large bone bed in Germany, containing over 1,000 Plateosaurus fossils.These findings have allowed scientists to study and compare specimens, leading to the discovery of different species of Plateosaurus. It is believed that there were four distinct species, with slight variations in size and skeletal structure. This finding has helped shed light on the diversity within the Plateosaurus population and how these dinosaurs evolved over time.
Conclusion
Despite being overshadowed by its more famous counterparts, the Plateosaurus is a fascinating dinosaur with a rich history. From its massive size and herbivorous diet to its social behavior and discovery through fossils, this dinosaur has left a mark on the scientific community. Its presence in the Late Triassic period is a testament to its adaptability and survival skills, making it a crucial link in the evolutionary chain of dinosaurs.Although much remains unknown about the Plateosaurus, its story continues to unfold as paleontologists make new discoveries and advancements in technology. The Plateosaurus may have gone extinct millions of years ago, but its legacy continues to live on through the fossils it left behind. As we uncover more of its secrets, we continue to appreciate and understand the complexity of life on Earth and the diverse creatures that once roamed it.

Plateosaurus
Dinosaur Details Plateosaurus - Scientific Name: Plateosaurus
- Category: Dinosaurs P
- Scientific Name: Plateosaurus
- Common Name: Plateosaurus
- Geological Era: Late Triassic
- Length: 8-10 meters
- Height: 2-3 meters
- Weight: 1-2 tons
- Diet: Herbivore
- Feeding Behavior: Grazing
- Predatory Behavior: Non-predatory
- Tooth Structure: Leaf-shaped teeth
- Native Habitat: Terrestrial
- Geographical Distribution: Europe
- Preferred Temperature: Temperate
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown

Plateosaurus
- Bone Structure: Lightweight and hollow
- Reproduction Type: Sexual
- Activity Period: Diurnal (active during the day)
- Distinctive Features: Long neck and tail, bipedal stance
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Herbivorous diet and lightweight bones
- Largest Species: Plateosaurus engelhardti
- Smallest Species: Plateosaurus gracilis
- Fossil Characteristics: Well-preserved skeletal remains
- Role in Ecosystem: Herbivorous grazer
- Unique Facts: One of the first dinosaurs to be discovered and studied
- Predator Status: Non-predator
- Discovery Location: Germany
- Discovery Year: 1834
- Discoverer's Name: Heinrich von Meyer

Plateosaurus
The Fascinating Plateosaurus: A Lightweight Herbivorous Dinosaur with a Long History
The world of dinosaurs is a remarkable one, full of terrifying predators and colossal herbivores. But among these giants, there is a lesser-known dinosaur that stands out for its unique features and intriguing history – the Plateosaurus.Plateosaurus, the first of its kind to be discovered and studied, was a dinosaur that roamed the earth during the Late Triassic period, approximately 214 to 204 million years ago. Its name is derived from the Greek words "platys" meaning flat and "sauros" meaning lizard, due to its flat and broad pelvis OnTimeAiraz.Com. This extinct genus is believed to have lived in what is now known as Europe, specifically in present-day Germany.
So what makes Plateosaurus so special? Let's dive into its distinctive characteristics and explore the story of this fascinating dinosaur.
Bone Structure: Lightweight and Hollow for Efficient Movement
One of the most remarkable features of Plateosaurus is its bone structure. Its bones were lightweight and hollow, making it one of the earliest known dinosaurs to exhibit this adaptation. How did this adaptation benefit the Plateosaurus?Firstly, the lightweight bones made it easier for this dinosaur to move around, as it was believed to be quite agile and fast for its size. Plateosaurus had a relatively long and slender body, with a weight estimated to be between 1 to 2.3 tons and a height of about 9 meters. Its lightweight bones allowed for faster and more efficient movement, making it a formidable herbivore in its ecosystem.
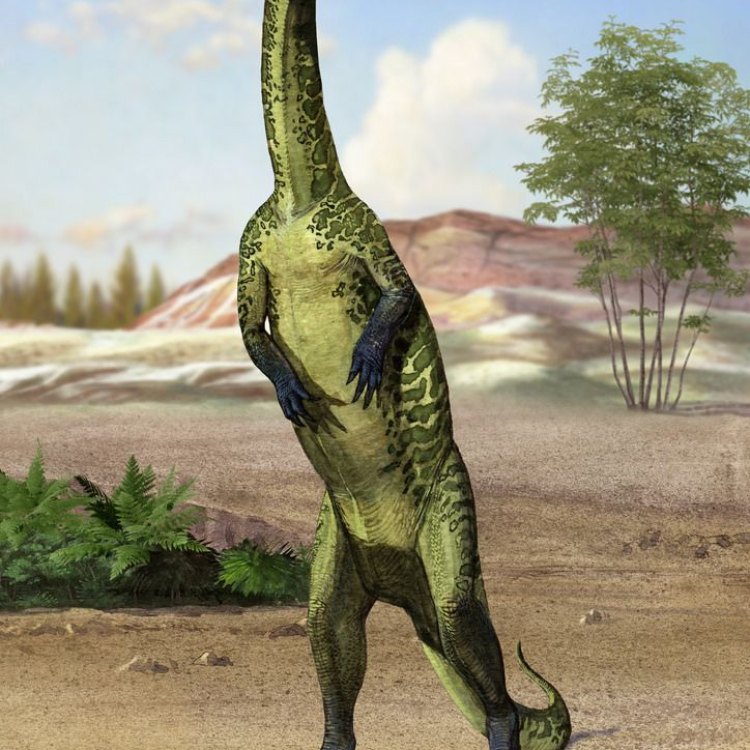
Another advantage of having lightweight bones was the ability to have a more upright posture Pegomastax. This helped Plateosaurus maintain a bipedal stance, meaning it walked on two legs. This was a distinguishing feature among early dinosaurs, as most of them walked on all fours.
Reproduction Type: Sexual and Unknown Communication Method
Like most dinosaurs, Plateosaurus reproduced sexually, with males and females coming together to mate and produce offspring. However, scientists are still unsure of how Plateosaurus communicated with one another. Since they lived in herds, it is possible that they had some form of communication, but it remains a mystery to this day.Distinctive Features: Long Neck and Tail, and a Bipedal Stance
Plateosaurus was a herbivore with a unique appearance, making it easily recognizable among other dinosaurs. It had a small head with a long slender neck that allowed it to reach leaves on trees, and a small mouth filled with sharp teeth to chomp on vegetation. Its most distinct feature was its long tail, which made up about half of its body length, and helped it maintain balance while walking and running.As a bipedal dinosaur, Plateosaurus stood on two legs, with shorter arms compared to its legs. These arms had sharp claws used for grasping vegetation and for defense against predators. Its long neck and tail, along with the bipedal stance, gave Plateosaurus a more bird-like appearance than other dinosaurs.
Survival Adaptation: Herbivorous Diet and Lightweight Bones
Plateosaurus was an herbivore, which meant it only ate plants and vegetation. However, during the Late Triassic period, most of the vegetation was made up of tough, fibrous plants, making it challenging for other herbivores to survive. This is where the lightweight bones of Plateosaurus came in handy.The strong but lightweight bones of this dinosaur allowed it to make quick movements and easily reach high branches for food. This gave Plateosaurus a competitive advantage in its ecosystem, allowing it to thrive and dominate as a herbivorous grazer.
Largest and Smallest Species
Scientists have discovered numerous species of Plateosaurus, with the largest being Plateosaurus engelhardti, and the smallest being Plateosaurus gracilis. The largest species could reach up to 9 meters in length, while the smallest was believed to be under 5 meters in length. Both species shared the same physical features, but the size difference suggests that Plateosaurus may have undergone some evolutionary changes over time.Fossil Characteristics: Well-Preserved Skeletal Remains
The skeletal remains of Plateosaurus are one of the most well-preserved among all dinosaurs. This is due to the fact that most of its fossils were found in a lake deposit in Germany, which acted as a natural preservation site. This has allowed us to study and learn more about this dinosaur in detail.Scientists have also found evidence of skin impressions and footprints, giving us an insight into what Plateosaurus may have looked like and how it moved.
Role in Ecosystem: Herbivorous Grazer
Plateosaurus played a vital role in its ecosystem as a herbivorous grazer. It was believed to have lived in large herds, constantly grazing on vegetation, and contributing to the balance of the environment. Its presence would have also attracted other herbivores, which served as prey for the predators in the ecosystem.As a non-predator, Plateosaurus likely had a significant influence on its environment, shaping the landscape and contributing to the diversity of plant life.
Unique Facts: One of the First Dinosaurs to be Discovered and Studied
Plateosaurus has a special place in the world of dinosaurs as one of the first to be discovered and studied. In 1834, a well-preserved skeletal remains of this dinosaur were found in Germany by a Swiss geologist and paleontologist, Heinrich von Meyer. This discovery marked a significant milestone in the study of dinosaurs, helping scientists understand the evolution and behavior of these prehistoric creatures.Today, Plateosaurus continues to fascinate and amaze scientists and dinosaur enthusiasts alike, with ongoing research and discoveries shedding more light on this remarkable creature.
Predator Status: Non-Predator
While Plateosaurus had a fierce appearance with its sharp teeth and claws, it was, in fact, a non-predator. Its diet and physical features were more suited for herbivorous behavior, and it was not equipped for hunting or defending itself against other predators.Plateosaurus lived in a time when dinosaurs were evolving and adapting to their environment, with some becoming ferocious predators, and others becoming docile herbivores like this remarkable dinosaur.
Discovery Location: Germany
The first fossils of Plateosaurus were found in Germany, mainly in the towns of Hechingen, Trossingen, and Halberstadt. However, this dinosaur has also been found in other European countries, such as Switzerland and France, suggesting that it may have roamed a larger area during its time.Discovery Year: 1834
Plateosaurus was first discovered in 1834 by Heinrich von Meyer, making it one of the earliest known dinosaurs to be studied. Since then, numerous fossils have been found, including an almost complete skeleton, giving us a better understanding of this prehistoric creature.The Fascinating History of Plateosaurus
Plateosaurus may not be as well-known as its larger dinosaur cousins, but it has a unique and fascinating history, from being one of the first dinosaurs to be discovered, to having distinct features and adaptations that allowed it to thrive in its environment.Its lightweight bones, long neck and tail, and bipedal stance, along with its role as a herbivorous grazer, make it a truly remarkable and unforgettable dinosaur. With ongoing research and discoveries, we continue to unlock the mysteries of this prehistoric creature and gain a deeper understanding of the world it once inhabited.

Uncovering the Secrets of the Plateosaurus: A Fascinating Herbivore From the Late Triassic Era
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.