Qianzhousaurus
Unknown
Get to know the Qianzhousaurus, a carnivorous dinosaur from Asia, with unknown skin color and speed. Discovered in China, it's part of the Q category of dinosaurs. Learn about this fascinating creature and its potential role in the ecosystem. Keep exploring the world of dinosaurs and uncover more marvels from the past. #Qianzhousaurus #carnivore #China #dinosaur #ecosystem #discovery
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Qianzhousaurus
Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
Feeding Behavior: Active predator
A Closer Look at Qianzhousaurus - The Fierce Carnivore of Late Cretaceous Asia
It's a name that may not be as well-known as T-Rex or Velociraptor, but Qianzhousaurus was one of the fiercest predators of the Late Cretaceous era. This dinosaur, with its razor-sharp teeth and group-hunting behavior, roamed the lands of Asia, particularly in what is now known as China. In this article, we will take a closer look at this fascinating creature, exploring its physical characteristics, behavior, and place in ancient history.The Discovery of Qianzhousaurus
In 2014, a team of paleontologists discovered the fossils of the Qianzhousaurus in the Ganzhou region of China Qianzhousaurus. It was named after the city of Qianzhou in the Ganzhou region and the Latin word "saurus" which means lizard. The species name "sinensis" refers to its origin in China.The discovery of Qianzhousaurus was significant because it was the first tyrannosaurid dinosaur found with a nearly complete skull. This allowed scientists to examine its physical features in detail and gain a better understanding of this unique species.
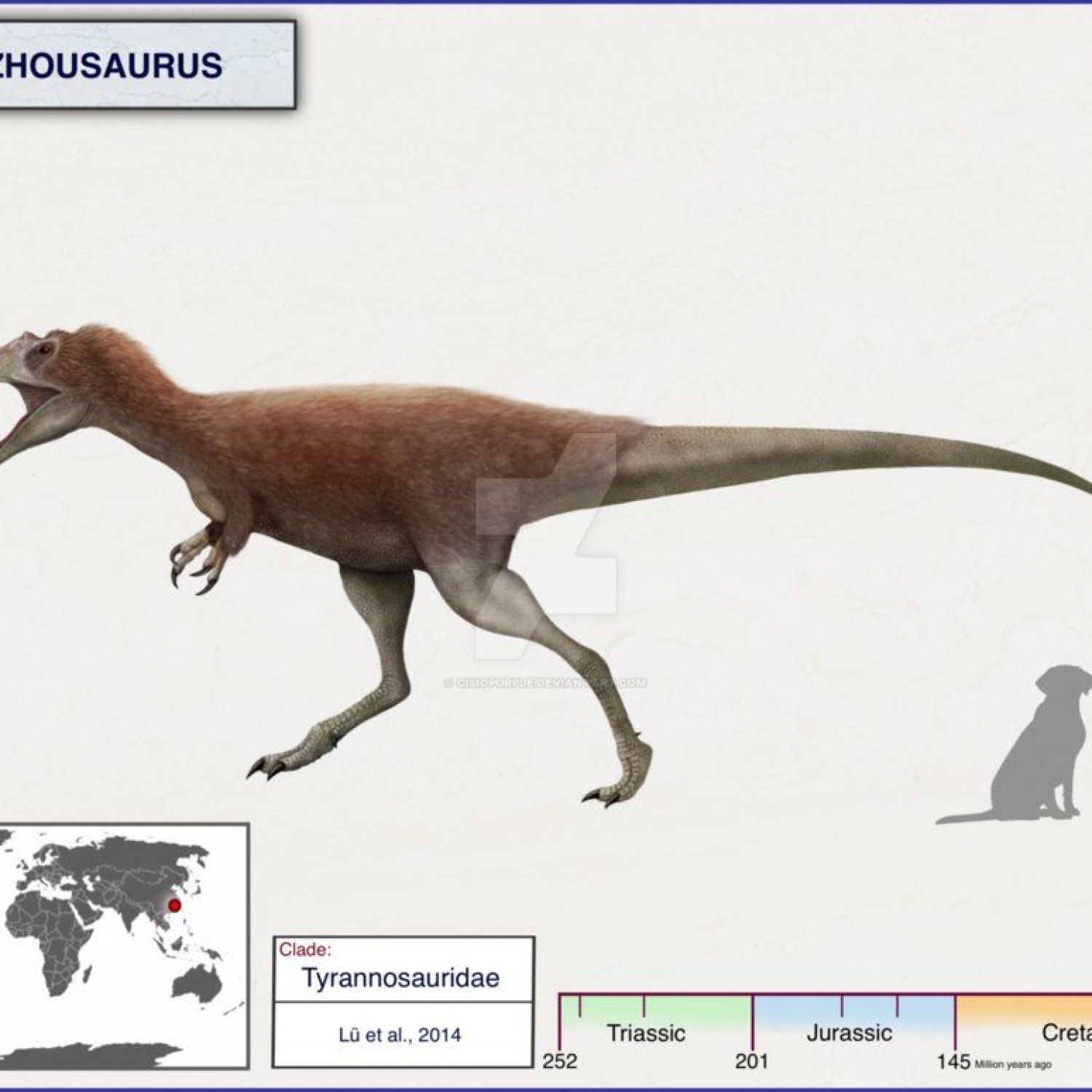
The Physical Characteristics of Qianzhousaurus
Like other tyrannosaurs, Qianzhousaurus was a large and intimidating dinosaur. It was estimated to be around 9 meters in length, 2.5 meters in height, and weighed around 2 tons. Its long and powerful legs enabled it to run at high speeds, making it a formidable predator.One of the most distinctive features of Qianzhousaurus was its skull, which was long and narrow compared to other tyrannosaurs Quetecsaurus. This gave it a more streamlined appearance, making it a highly efficient hunter. Its teeth were also unique, with blade-like edges that were designed to tear through flesh and crush bones. This tooth structure made Qianzhousaurus one of the most efficient predators of its time.
Feeding and Predatory Behavior
Qianzhousaurus was a carnivorous dinosaur, meaning that it fed exclusively on meat. Its sharp teeth and powerful jaw muscles were perfect for hunting and killing prey. It is believed that Qianzhousaurus was an active predator, meaning that it actively chased and hunted down its prey rather than scavenging for food.What's fascinating about Qianzhousaurus is that it had a group-hunting behavior, similar to modern-day wolves or lions. This means that they worked together in packs to take down larger and more formidable prey. This behavior was highly beneficial for the survival of the species as it allowed them to hunt more efficiently and ensure a steady food supply for the group.
Habitat and Geographical Distribution
Qianzhousaurus was a land-dwelling dinosaur, belonging to the Late Cretaceous period, which lasted from 100.5 to 66 million years ago. During this time, the Earth's continents were arranged differently, and what is now known as China was a part of the supercontinent, Laurasia.Qianzhousaurus was primarily found in the Ganzhou region of China, and it is believed that it inhabited warm to temperate areas. This means that it could survive in a range of temperatures, making it adaptable to different climates.
The Legacy of Qianzhousaurus
The discovery of Qianzhousaurus has shed new light on the evolution of tyrannosaurs, particularly in the Asian region. It has also helped scientists gain a better understanding of the diversity of dinosaurs in this region during the Late Cretaceous period.One of the most significant findings from studying Qianzhousaurus is that it provides evidence of group-hunting behavior in tyrannosaurs. This behavior was previously only attributed to smaller predatory dinosaurs, but Qianzhousaurus has shown that even large and powerful predators like the tyrannosaur could benefit from hunting in groups.
In Conclusion
Qianzhousaurus may not be as well-known as some other dinosaurs, but its unique physical characteristics and predatory behavior have made it a remarkable and fascinating discovery. Its razor-sharp teeth, efficient hunting behavior, and group-hunting techniques have solidified its place as one of the top predators of the Late Cretaceous period. The discovery of Qianzhousaurus has not only provided valuable insights into the ancient world, but it has also sparked new questions and theories about the evolution of dinosaurs. As scientists continue to unearth more fossils and study this remarkable species, we can only imagine what else we will learn about the fierce Qianzhousaurus.
Qianzhousaurus
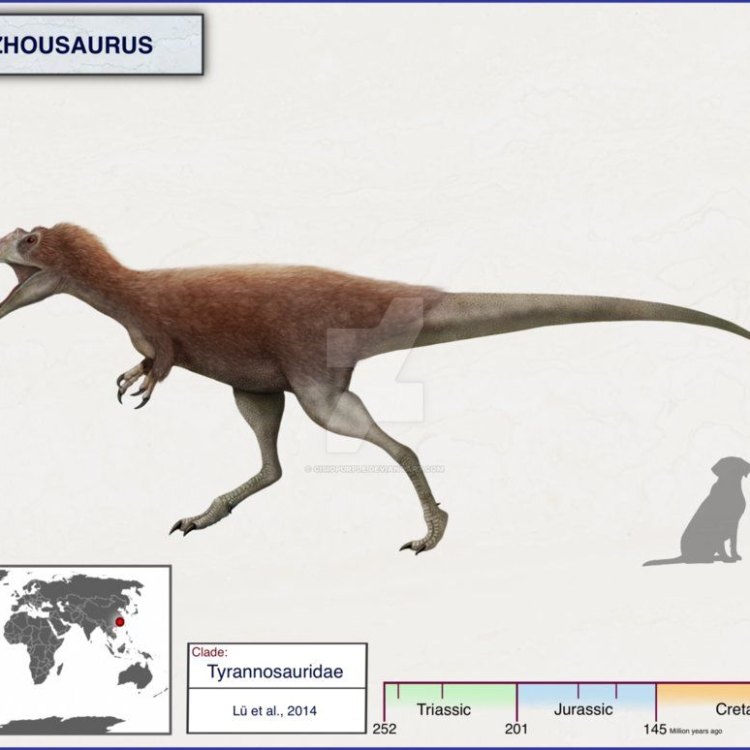
Dinosaur Details Qianzhousaurus - Scientific Name: Qianzhousaurus sinensis
- Category: Dinosaurs Q
- Scientific Name: Qianzhousaurus sinensis
- Common Name: Qianzhousaurus
- Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
- Length: 9 meters
- Height: 2.5 meters
- Weight: 2 tons
- Diet: Carnivorous
- Feeding Behavior: Active predator
- Predatory Behavior: Hunting in groups
- Tooth Structure: Blade-like and sharp teeth
- Native Habitat: Land
- Geographical Distribution: Asia (China)
- Preferred Temperature: Warm to temperate
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown
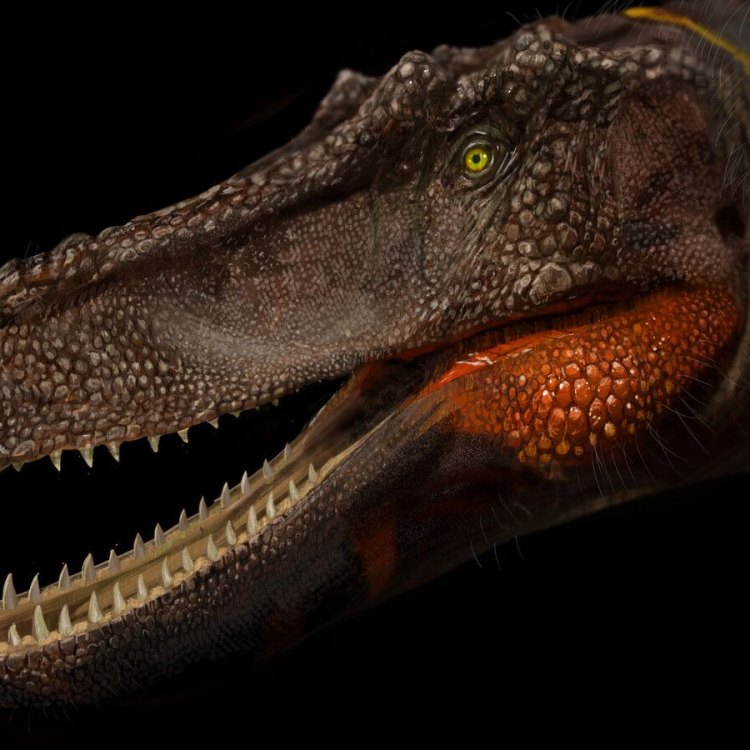

Qianzhousaurus
- Bone Structure: skeletal structure similar to other theropod dinosaurs
- Reproduction Type: Egg-laying
- Activity Period: Diurnal
- Distinctive Features: Prominent 'horns' on its head
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Sharp and serrated teeth for tearing flesh
- Largest Species: Qianzhousaurus sinensis
- Smallest Species: Unknown
- Fossil Characteristics: Nearly complete skull with preserved soft tissues
- Role in Ecosystem: Top predator
- Unique Facts: One of the few dinosaurs with preserved facial features
- Predator Status: Extinct
- Discovery Location: China
- Discovery Year: 2014
- Discoverer's Name: Lü Junchang
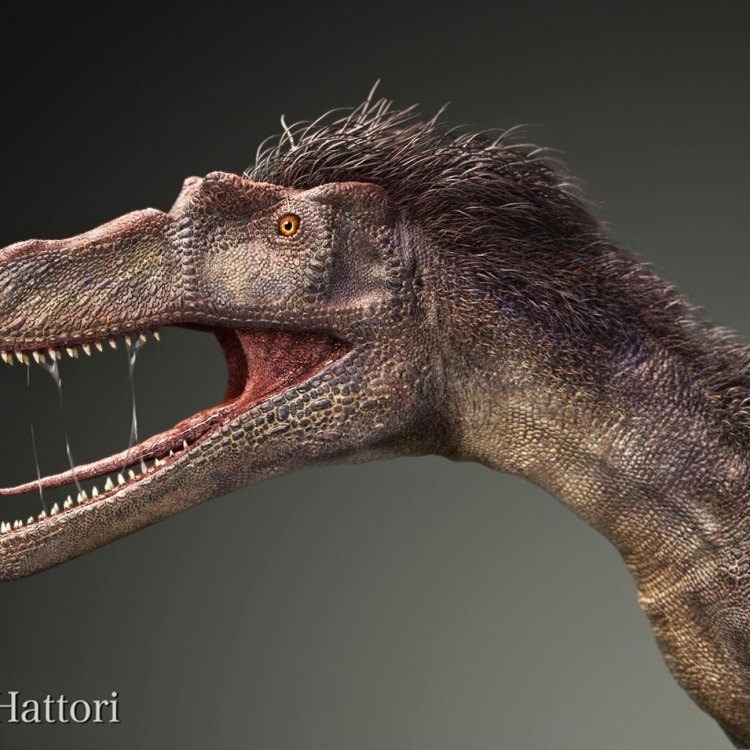
Qianzhousaurus sinensis
The Dangerous Predator of the Past: Discovering the Qianzhousaurus
When we think of dinosaurs, we often imagine massive creatures with long necks and sharp teeth. But not all dinosaurs fit this stereotype. In 2014, a new species of theropod dinosaur was discovered in southern China - the Qianzhousaurus.With its distinctive features and role as a top predator, the Qianzhousaurus quickly became a topic of interest among paleontologists and dinosaur enthusiasts OnTimeAiraz.Com. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of this ancient creature and learn more about its physical features, behavior, discovery, and unique place in the ecosystem.
Welcome to Qianzhousaurus
Named after the Qianzhou in Ganzhou, Jiangxi province, China, Qianzhousaurus sinensis was first discovered by a team of Chinese paleontologists led by Lü Junchang. It is believed to have lived during the late Cretaceous period, about 72 million years ago.The Qianzhousaurus was a theropod dinosaur, meaning that it belonged to the group of carnivorous dinosaurs that walked on two legs. Its skeletal structure was similar to other theropod dinosaurs, such as the Tyrannosaurus rex and Velociraptor. However, it had its unique features that set it apart from its relatives.
One of the most distinctive features of the Qianzhousaurus was the two prominent 'horns' protruding from its skull. These horns, measuring up to 30 centimeters in length, gave the dinosaur a fierce and intimidating appearance. Scientists believe that these horns may have been used for display purposes, attracting mates or intimidating rivals, rather than for actual combat Qiupalong.
With its sharp and serrated teeth, the Qianzhousaurus was well adapted for tearing flesh, making it a dangerous predator. Its teeth were also continuously replaced, ensuring a constant supply of sharp teeth for hunting and survival.
The Life of a Qianzhousaurus
Based on its skeletal structure, scientists believe that the Qianzhousaurus was a bipedal and swift runner. It is estimated to have been about 8 meters (26 feet) in length and weighing around 1.2 tonnes (2,600 pounds). This would have made it one of the largest theropod dinosaurs of its time, even larger than the famous T. rex.Qianzhousaurus was an egg-laying species, reproducing through laying eggs that would hatch into young dinosaurs. Researchers believe that it was a diurnal creature, meaning that it was most active during the day. Its sharp and keen eyesight would have helped it hunt for prey during daylight hours.
The communication method of the Qianzhousaurus is still unknown, as there is no evidence of vocal cords or other communication structures preserved in the fossils. However, it is possible that it used visual and body language to communicate with others of its kind.
Fascinating Fossils: Preserved Soft Tissue and Facial Features
One of the most fascinating aspects of the Qianzhousaurus is that it is one of the few dinosaurs with preserved facial features. The nearly complete skull of the dinosaur was discovered with soft tissues, such as skin and muscle, still intact. This is a rare occurrence, as soft tissues are often not preserved in fossils.The presence of soft tissue allowed scientists to study the dinosaur's facial features in detail, providing a glimpse into how the Qianzhousaurus may have looked during its time on Earth. From this, they were able to determine that it had a beak, much like modern-day birds, and its skin was scaly.
The discovery of soft tissues in the Qianzhousaurus fossils also shed light on the coloration of the dinosaur. Studies suggest that it had a dark, mottled coloration, possibly used as camouflage to blend in with its surroundings while hunting.
The Role of Qianzhousaurus in the Ecosystem
As a top predator, the Qianzhousaurus played a crucial role in the ecosystem of its time. Its prey likely consisted of smaller dinosaurs and other animals such as lizards and small mammals. By hunting and controlling the population of its prey, the Qianzhousaurus helped maintain a balanced ecosystem.But it wasn't just a predator. The Qianzhousaurus was also a source of food for other carnivorous dinosaurs, such as the infamous T. rex. Its presence in the food chain helped in the transfer of energy and nutrients, contributing to the overall health of the ecosystem.
Discovering the Qianzhousaurus
The first fossils of the Qianzhousaurus were discovered in 2014 in southern China. The area where the fossils were found is known for its rich deposits of dinosaurs, making it an ideal location for paleontologists to search for new species.The team of paleontologists, led by Lü Junchang, found a nearly complete skull with soft tissues preserved. Later, other parts of the skeleton, such as the foot, were also discovered, allowing for a more complete understanding of the dinosaur's physical features.
The discovery of the Qianzhousaurus was a significant moment in paleontology, as it provided valuable insights into the evolution and diversity of theropod dinosaurs. It also showcased the importance of preserving fossils and continuous research in the field of paleontology.
The Extinction of Qianzhousaurus
Unfortunately, like all dinosaurs, the Qianzhousaurus became extinct around 66 million years ago. The cause of its extinction is believed to be the same as that of the other dinosaurs - the asteroid impact that led to the mass extinction event known as the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction.This catastrophic event wiped out nearly 75% of all species on Earth, including the Qianzhousaurus. But thanks to the preserved fossils, we can still learn about these magnificent creatures and their place in our planet's history.
The Legacy of Qianzhousaurus
The discovery of the Qianzhousaurus has not only provided a better understanding of the past but also sparked curiosity and interest in the field of paleontology. This dangerous predator from the past continues to capture the imagination of people around the world, from scientists to children fascinated by dinosaurs.The Qianzhousaurus also serves as a reminder of how much we still have to learn about our planet's past. While we have made significant progress in understanding the existence and behaviors of dinosaurs, there are many more discoveries waiting to be made.
In Conclusion
The Qianzhousaurus was a remarkable and unique dinosaur that roamed the Earth more than 70 million years ago. With its distinctive features, role as a top predator, and rare preservation of soft tissue, it has captivated the interest of both scientists and the general public.From its discovery in China to its extinction in the mass extinction event, the Qianzhousaurus has left a lasting legacy and continues to intrigue us today. As we continue to unearth more about this ancient creature and the countless other species that once roamed our planet, we gain a better understanding of our planet's history and the incredible diversity of life that has existed.
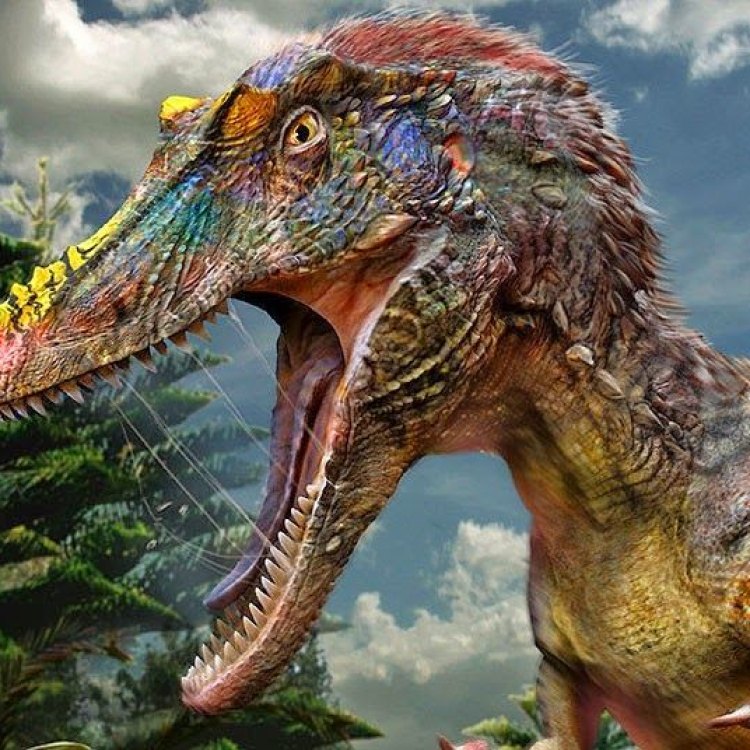

A Closer Look at Qianzhousaurus - The Fierce Carnivore of Late Cretaceous Asia
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.