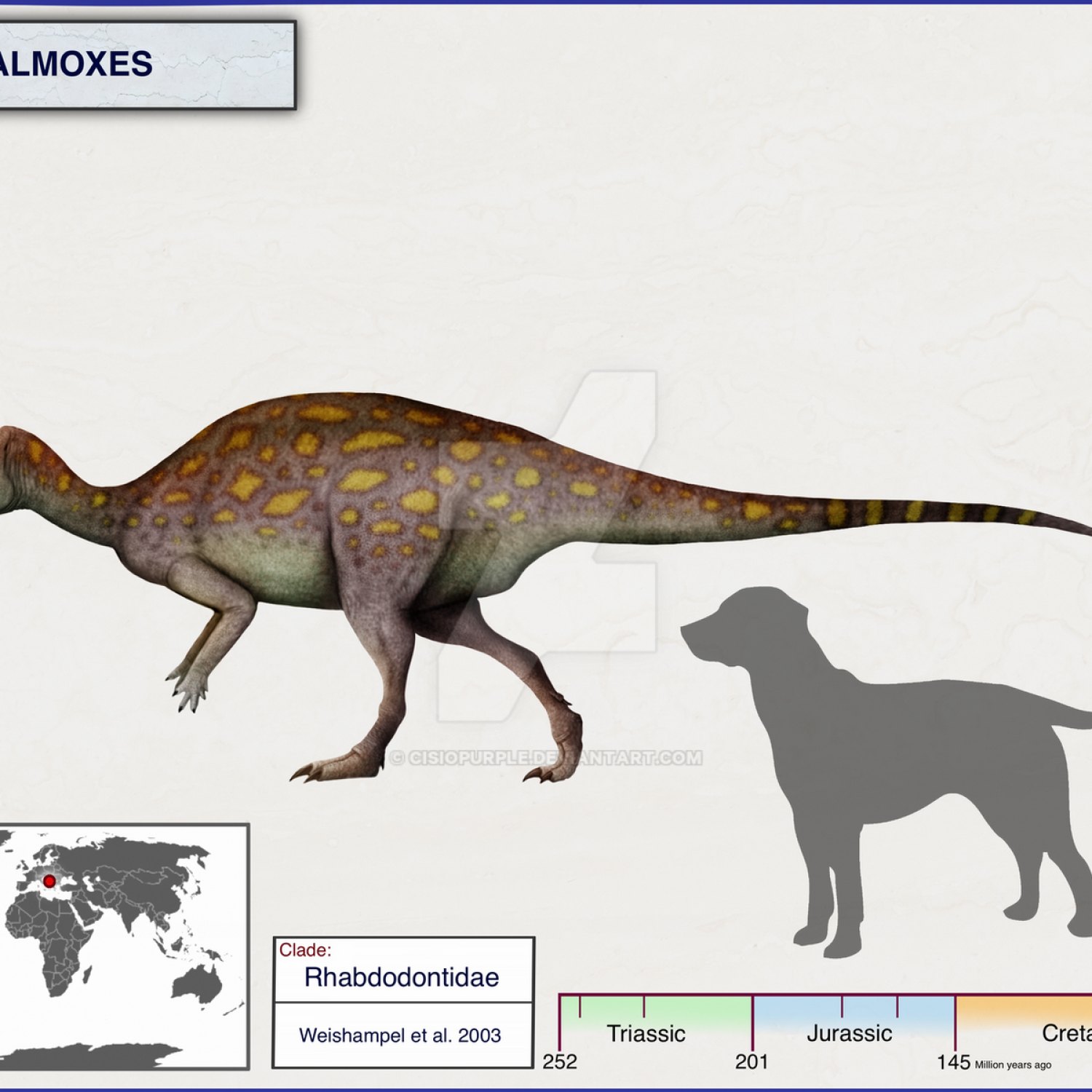
Zalmoxes
Unknown
Meet Zalmoxes, a lesser-known but fascinating dinosaur that roamed Eastern Europe millions of years ago. Although its skin color is a mystery, it is believed to have been a peaceful herbivore. With an unknown maximum speed, we can only imagine how graceful this dinosaur must have been. Let's delve deeper into the intriguing world of Zalmoxes! #dinosaur #Zalmoxes #herbivore #EasternEurope
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Zalmoxes
Geological Era: Early Cretaceous
Feeding Behavior: Browsing
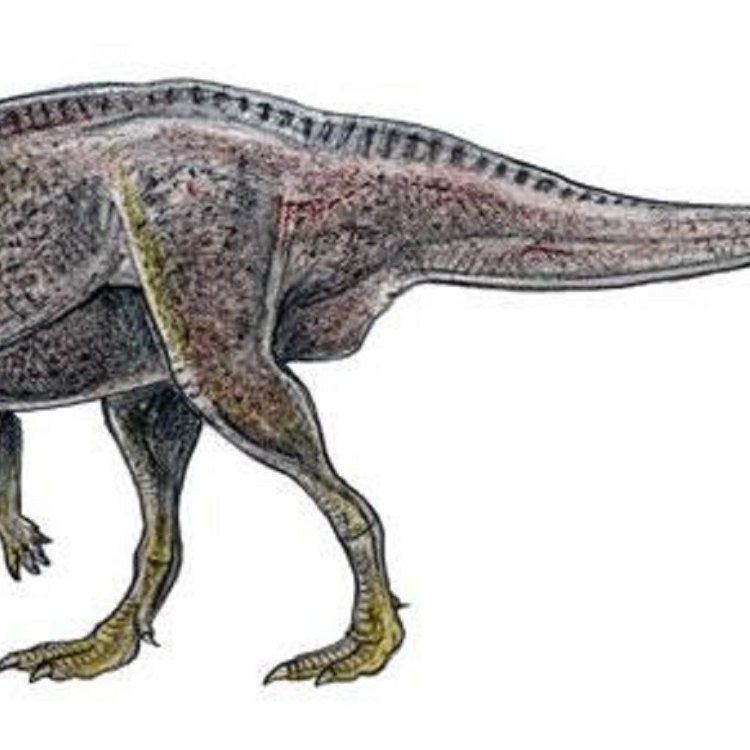
The Fascinating World of Zalmoxes: A Unique Dinosaur Species from Eastern Europe
From gigantic tyrannosaurs to armored stegosaurs, the world of dinosaurs is known for its diversity and sheer magnificence. Among the many remarkable species that ruled the Earth millions of years ago, one particular dinosaur stands out for its unique features and fascinating history – Zalmoxes.Found exclusively in Eastern Europe, Zalmoxes is a lesser-known but significant member of the dinosaur family. Its scientific name, Zalmoxes, is derived from the ancient Dacian god "Zalmoxis," reflecting the dinosaur's strong connection to the region's culture and heritage Zalmoxes. Let's delve deeper into this fascinating creature and discover all the intriguing details about it.
Identification and Discovery
Zalmoxes is a medium-sized dinosaur, measuring approximately 4 meters in length, 1.5 meters in height, and weighing around 400 kilograms. Its body structure was slim and agile, with long hind legs and a relatively short neck. Its front limbs were shorter than its hind limbs, which is a common trait among bipedal dinosaurs.This dinosaur was discovered in the year 1990 by the paleontologist Dan Grigorescu in Romania, in the Haţeg Basin region. The fossils were found in the Sânpetru Formation, which dates back to the Early Cretaceous period, approximately 110 million years ago. Initially, the discovery was believed to be of a small therizinosaur. However, further analysis revealed that it was a completely new species, belonging to the family of ornithopod dinosaurs Zhuchengcerato.
Diet and Feeding Behavior
Zalmoxes was a herbivorous dinosaur, meaning it fed on plants exclusively. Its name, "Zalmoxes," translates to "Zalmoxis' ox," emphasizing its vegetarian diet. The shape and structure of its teeth were well-adapted for browsing and shredding off vegetation. It had leaf-shaped teeth, ideal for cutting through tough plant material. Its jaws also had a peculiar structure, which enabled it to clip off foliage efficiently.Based on the available evidence, it is believed that Zalmoxes was a generalist feeder, which means it could feed on a wide variety of plant species. As per paleontologists, this dinosaur specialized in feeding on low-lying bushes, ferns, and small trees, which would be found in its native habitat.
Habitat and Distribution
Zalmoxes inhabited island environments, which were abundant in the Haţeg Basin during the Early Cretaceous period. These islands were a result of a geographical phenomenon known as "island dwarfism," where certain animals evolved to be smaller in size due to limited resources and space. It is believed that Zalmoxes was a direct descendant of larger mainland dinosaurs, and it evolved to be smaller in size over time.Zalmoxes fossils have been found in various locations in Eastern Europe, such as Romania, Bulgaria, and Hungary. Its wide distribution indicates that this dinosaur was adapted to surviving in different climates and terrains.
Predatory Behavior and Defense Mechanisms
Despite its fearsome appearance, Zalmoxes was a non-predatory dinosaur, meaning it did not hunt or feed on other animals. Its small size and herbivorous diet would have made it vulnerable to larger predators, such as raptors and theropods. However, it had a unique defense mechanism that allowed it to escape from potential predators – its agility.With its long hind legs and lightweight body, Zalmoxes could quickly evade danger by running and jumping through the dense vegetation in its native habitat. It is estimated that this dinosaur could reach a maximum speed of 30 kilometers per hour, which is quite impressive for its size.
Climate Preferences and Adaptations
Zalmoxes preferred moderate temperatures, similar to the climate prevalent in Eastern Europe during the Early Cretaceous period. Its island habitat was known for its warm climate, with mild fluctuations in temperature, making it an ideal environment for this dinosaur species.Being a medium-sized dinosaur, Zalmoxes was well-adapted to its environment. Its slim and agile body structure allowed it to navigate through narrow spaces, while its optimized respiratory system allowed it to make efficient use of oxygen. These adaptations enabled this dinosaur to thrive in its native habitat.
Significance in Evolutionary History
Zalmoxes was a significant link in the evolutionary history of dinosaurs. By studying this dinosaur, paleontologists discovered that there was a parallel evolution of smaller-sized dinosaurs in the Haţeg Basin, similar to the concept of island dwarfism seen in modern animals. This discovery helped scientists understand the process of island adaptation and its impact on the evolution of species.Moreover, Zalmoxes is also significant because it is one of the few ornithopod dinosaurs that have been found in Eastern Europe. This discovery, along with others, have led to the conclusion that this region was a biodiversity hotspot during the Early Cretaceous period, with a variety of dinosaur species coexisting and evolving together.
The Mystery of Skin Color
One of the most intriguing aspects of Zalmoxes is its skin color. Due to the lack of complete fossil evidence, scientists have not been able to determine the exact color of this dinosaur's skin. However, based on its probable habitat and the coloration of modern-day lizards and crocodiles living in similar environments, it is speculated that Zalmoxes may have had a light brown or olive green skin color with darker stripes or patches.Conclusion
Zalmoxes may be a lesser-known dinosaur species, but it is undoubtedly a fascinating one with a unique story to tell. Its adaptations and behavior provide valuable insights into the evolutionary process and the impact of island environments on species. This dinosaur serves as a reminder of the sheer diversity of the prehistoric world and the miraculous ways in which species adapted to survive in their respective habitats. Hopefully, further discoveries and research will unravel more mysteries about this remarkable creature, and we will continue to learn more about the captivating world of dinosaurs.
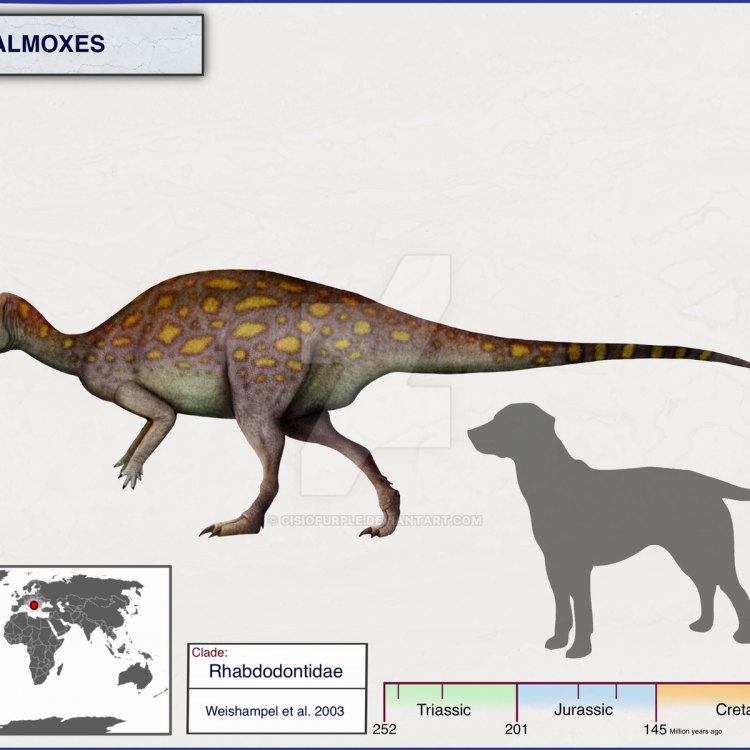
Zalmoxes
Dinosaur Details Zalmoxes - Scientific Name: Zalmoxes
- Category: Dinosaurs Z
- Scientific Name: Zalmoxes
- Common Name: Zalmoxes
- Geological Era: Early Cretaceous
- Length: 4 meters
- Height: 1.5 meters
- Weight: 400 kilograms
- Diet: Herbivore
- Feeding Behavior: Browsing
- Predatory Behavior: Non-predatory
- Tooth Structure: Leaf-shaped teeth
- Native Habitat: Island environments
- Geographical Distribution: Eastern Europe
- Preferred Temperature: Moderate temperatures
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown

Zalmoxes
- Bone Structure: Lightweight and hollow bones
- Reproduction Type: Egg-laying (Oviparous)
- Activity Period: Unknown
- Distinctive Features: Long, low skull and a beak-like snout
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Adapted to island environments
- Largest Species: Unknown
- Smallest Species: Unknown
- Fossil Characteristics: Well-preserved skeletal remains
- Role in Ecosystem: Herbivorous browser
- Unique Facts: One of the few dinosaurs known from the island of Haţeg
- Predator Status: Non-predatory
- Discovery Location: Romania
- Discovery Year: 1994
- Discoverer's Name: Nicolae Atudorei

Zalmoxes
The Fascinating Zalmoxes: A Lightweight Herbivorous Dinosaur Adapted to Island Environments
The world of dinosaurs was filled with a variety of species, with some being fierce predators, while others were gentle herbivores. Among these lesser-known yet intriguing creatures is Zalmoxes, a lightweight, egg-laying dinosaur that inhabited the island of Haţeg in Romania.Zalmoxes was first discovered in 1994 by Romanian paleontologist Nicolae Atudorei. Its name comes from a combination of the Dacian god Zalmoxis and the Greek word 'mex' meaning ‘long’ OnTimeAiraz.Com. Zalmoxes belongs to the family of ornithopod dinosaurs, which were known for their beaked snouts and herbivorous diet. However, what sets Zalmoxes apart are its unique features and adaptations.
Let's explore the fascinating world of Zalmoxes and discover what makes this dinosaur species so special.
Bone Structure: Lightweight and Hollow Bones
One of the most distinctive features of Zalmoxes is its lightweight and hollow bones. This unique adaptation is similar to modern-day birds and is known as pneumaticity. The air cavities in the bones not only make them lightweight but also increase their strength and stiffness, making Zalmoxes agile and swift.The hollow bones also had another important benefit for Zalmoxes. As it lived on an island, resources were scarce, and food was limited. Therefore, the lighter bones allowed for efficient movement, saving energy that could be used for finding food Zuniceratops.
Reproduction Type: Egg-Laying (Oviparous)
Similar to other ornithopod dinosaurs, Zalmoxes was oviparous, meaning it laid eggs to reproduce. The eggs were laid in nests, and the hatchlings were cared for by their parents until they were old enough to fend for themselves.The exact number or size of Zalmoxes' eggs is unknown, but researchers speculate that they would have been similar to other herbivorous dinosaurs, such as Hadrosaurs, which laid dozens of eggs at a time in communal nests.
Activity Period: Unknown
Unfortunately, due to the limited fossils and information available, the exact activity period of Zalmoxes remains unknown. However, based on its herbivorous diet, it can be assumed that it was most active during daylight hours, like other dinosaurs.However, some researchers suggest that Zalmoxes could have been crepuscular, meaning it was most active at dawn and dusk. This adaptation would have allowed it to avoid the hot daylight hours, where resources were scarce, and predators were more active.
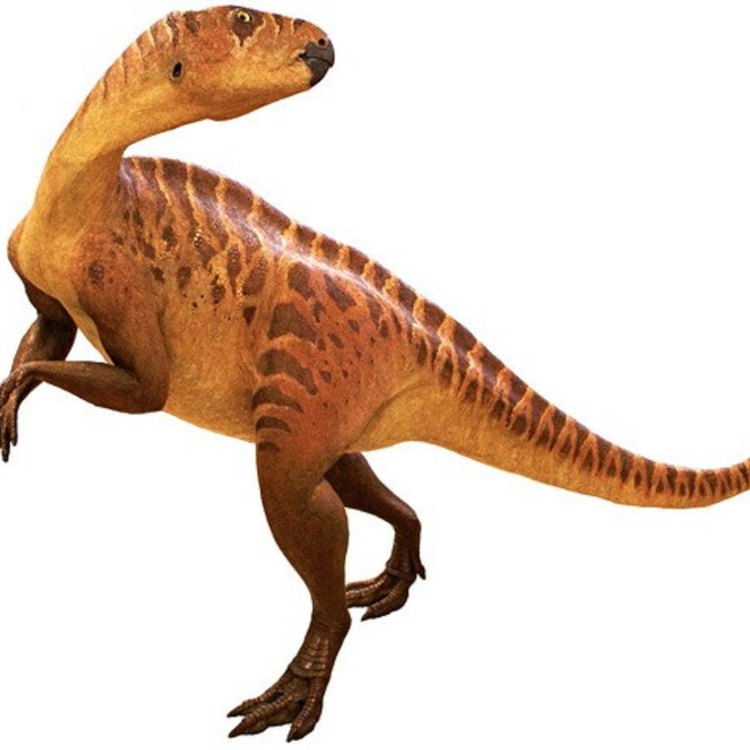
Distinctive Features: Long, Low Skull and a Beak-like Snout
One of the most striking physical characteristics of Zalmoxes was its elongated, low skull and beak-like snout. This adaptation was perfect for its herbivorous diet, allowing it to pluck vegetation from the ground with ease.The low skull also suggests that Zalmoxes likely had a more horizontal posture, with its head closer to the ground. This would have allowed it to graze on low-lying plants, making the most of its island environment.
Communication Method: Unknown
As with many other lesser-known dinosaurs, Zalmoxes' communication method remains a mystery. However, based on its beaked snout and lack of horns or crests, it is unlikely that it used vocalizations to communicate.It is possible that Zalmoxes used other methods of communication, such as body language and displays, to interact with its own kind or other dinosaurs.
Survival Adaptation: Adapted to Island Environments
Living on a small island, Zalmoxes had to face unique challenges that its mainland counterparts did not. Limited land and resources meant that competition for food and territory was high. Therefore, Zalmoxes had to adapt to its surroundings to survive.With its lightweight bones and low skull, Zalmoxes was well-suited to move quickly and efficiently on the island. Its herbivorous diet also allowed it to coexist with other herbivorous dinosaurs without direct competition.
Largest Species: Unknown, Smallest Species: Unknown
Due to the limited fossils of Zalmoxes, it is not possible to determine the largest or smallest species. However, based on the size of the island of Haţeg and comparisons with other ornithopod dinosaurs, it is estimated that Zalmoxes would have been a medium-sized dinosaur, measuring around 6-7 feet tall and 20-25 feet in length.Fossil Characteristics: Well-Preserved Skeletal Remains
One of the most significant contributions of Zalmoxes to the scientific community is its well-preserved skeletal remains. Unlike other dinosaur fossils, which are usually fragmented and incomplete, Zalmoxes' fossils were in excellent condition, providing valuable insights into the anatomy and behavior of this species.The pristine condition of the fossils also allowed for detailed studies of Zalmoxes, including its bone structure, growth patterns, and dietary preferences.
Role in Ecosystem: Herbivorous Browser
As a gentle herbivore, Zalmoxes played a crucial role in its ecosystem as a browser. Its diet would have included various plants, such as ferns, conifers, and cycads, shaping the vegetation and contributing to a diverse ecosystem.Zalmoxes also likely interacted with other herbivorous dinosaurs, such as the dwarf sauropod Magyarosaurus and the iguanodontian Telmatosaurus, further enriching the island's ecosystem.
Unique Facts: One of the Few Dinosaurs Known from the Island of Haţeg
One of the most exceptional and intriguing facts about Zalmoxes is that it is one of the few dinosaurs known to have inhabited the island of Haţeg. This island, also known as the ‘Island of Giants,’ was home to various dwarf dinosaurs, such as dwarf sauropods and theropods.The isolation of the island resulted in unique evolutionary paths for these dinosaurs, leading to their miniaturized size. Zalmoxes' fossils provide evidence of the incredible diversity and adaptation that existed on this island.
Predator Status: Non-Predatory
With its herbivorous diet and lack of formidable physical traits, it is unlikely that Zalmoxes was a predatory species. Instead, it likely coexisted with other carnivorous dinosaurs on the island, such as the giant dromaeosaur Balaur.Zalmoxes' location, size, and diet would have likely put it lower on the food chain, making it less of a threat to other dinosaurs.
Discovery Location: Romania, Discovery Year: 1994, Discoverer's Name: Nicolae Atudorei
Zalmoxes was discovered in the Haţeg Basin of Romania in 1994 by Romanian paleontologist Nicolae Atudorei. Its fossils were found in the village of Sânpetru, located in the southwestern Transylvanian Basin.Atudorei's discovery of Zalmoxes added to the already rich paleontological history of Romania and provided valuable insights into the lives of dinosaurs on the island of Haţeg.
The Legacy of Zalmoxes
Although relatively lesser-known compared to other famous dinosaurs, Zalmoxes has left an important legacy in the scientific community. Its unique adaptations and adaptations to island life have provided valuable insights into the lives of dinosaurs in specialized environments.Additionally, its discovery has shed light on the diversity of dinosaurs on the island of Haţeg and the incredible evolutionary paths that they followed.
As researchers continue to unearth new fossils and gather more information, we can only imagine the untold stories and mysteries that Zalmoxes holds. But one thing is for sure; this lightweight herbivore has earned its place in the fascinating world of dinosaurs.
The Fascinating World of Zalmoxes: A Unique Dinosaur Species from Eastern Europe
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.