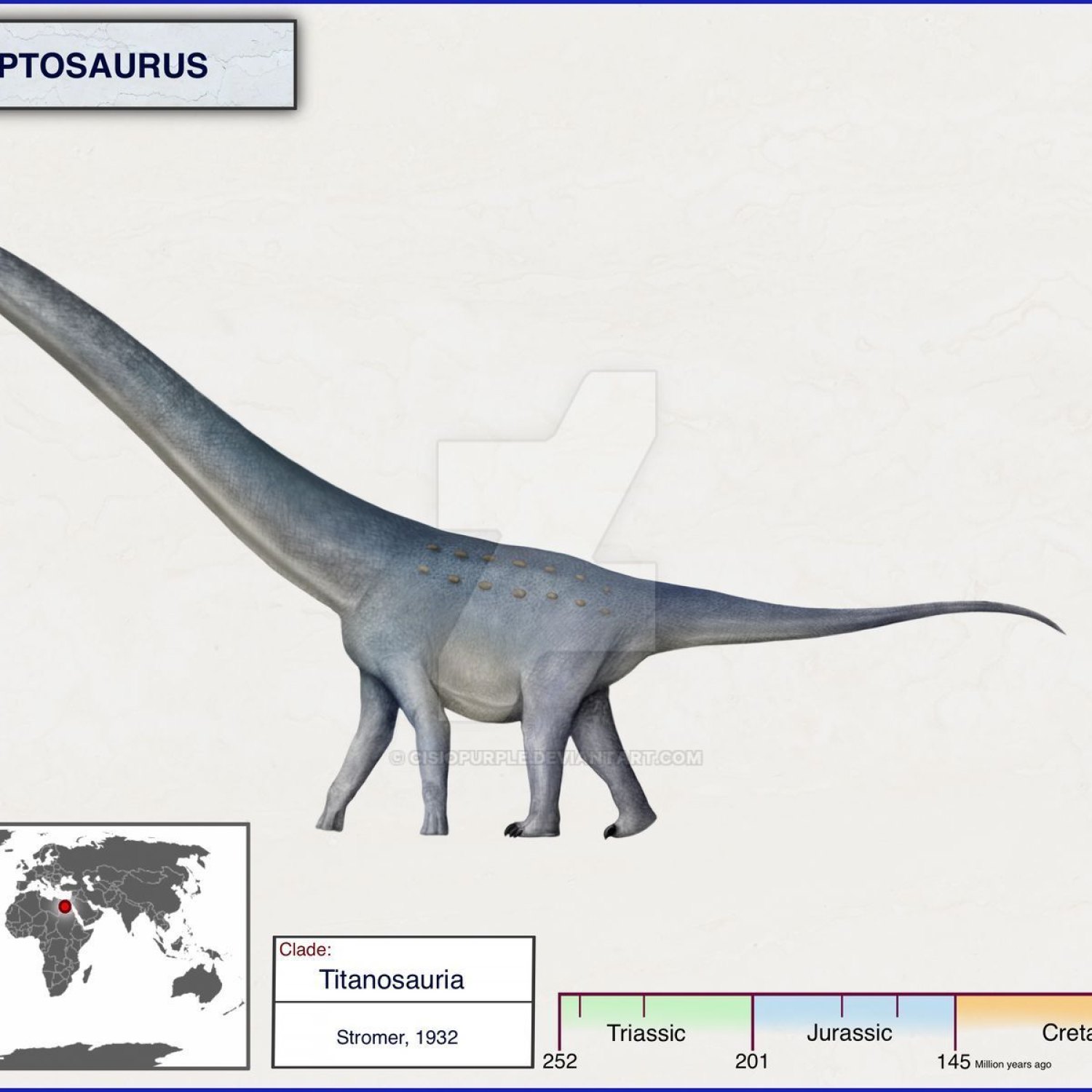
Aegyptosaurus
Unknown
Meet the Aegyptosaurus, a long-necked herbivore that roamed the land of Northern Africa millions of years ago. Its skin color remains a mystery, but one thing is for sure, this dinosaur could reach impressive speeds despite its large size. Read on to learn more about this mysterious creature from the Age of Dinosaurs. #Aegyptosaurus #Herbivore #NorthernAfrica #DinosaurFacts
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Aegyptosaurus
Geological Era: Early Cretaceous
Feeding Behavior: Browsing
The Mighty Aegyptosaurus: Exploring the Enigmatic Dinosaur of Northern Africa
Deep in the northern deserts of Africa, lies a creature that has captured the imagination of paleontologists and dinosaur enthusiasts for decades. With its large size, unique features, and mysterious behavior, the Aegyptosaurus has long been a subject of fascination and speculation.Scientifically known as Aegyptosaurus, this herbivorous dinosaur inhabited the Earth during the Early Cretaceous period, around 112 to 99 million years ago. Despite being discovered in the late 19th century, much about this dinosaur still remains a mystery, making it a prime subject for further study and research Aegyptosaurus.
In this article, we will dive deep into the world of Aegyptosaurus and uncover the fascinating facts and features of this enigmatic creature.
The Basics: What is Aegyptosaurus?
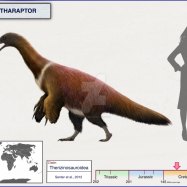
Aegyptosaurus is a genus of sauropod dinosaur that belonged to the family Titanosauridae. It roamed the Earth during the early Cretaceous period, the heyday of the dinosaurs. This massive herbivore was believed to be around 14 meters long and reach a towering height of 4 meters. With an estimated weight of 10 to 15 tons, the Aegyptosaurus was a true giant of its time.The name Aegyptosaurus is derived from the Greek word "Aegypto" meaning Egypt and "sauros" meaning lizard, referencing the discovery of this dinosaur in Northern Africa. It was first described in 1890 by German paleontologist Ernst Stromer, who unearthed its fossils from the Bahariya Formation in Egypt.
The Unique Features of Aegyptosaurus
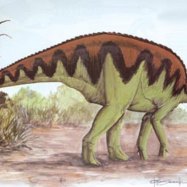
One of the most striking features of Aegyptosaurus was its appearance. While most of its Titanosaur relatives had long necks and tails, the Aegyptosaurus had a relatively shorter neck and tail Achelousaurus. This adaptation was likely due to the dry and arid climate of the region it inhabited. With a shorter neck and tail, the Aegyptosaurus could conserve water and energy more efficiently, allowing it to thrive in its harsh environment.Another standout feature of the Aegyptosaurus was its tooth structure. Unlike other sauropods that had peg-like and spoon-shaped teeth, the Aegyptosaurus had wider and more blade-like teeth, suggesting that its diet may have been quite different from its herbivorous counterparts. Researchers believe that the Aegyptosaurus was a browser, feeding on low-lying vegetation rather than the higher foliage that other sauropods favored.
The Enigmatic Behavior of Aegyptosaurus
Unlike some other predatory dinosaurs that have captured the public's imagination, Aegyptosaurus was believed to be a peaceful, non-predatory creature. Its large size and herbivorous diet suggest that it may not have had any natural predators during its time. This behavior is further supported by the fact that no fossil evidence of Aegyptosaurus being attacked or hunted by other dinosaurs has been found.However, some experts have speculated that the Aegyptosaurus may have engaged in intraspecific combat, meaning it may have battled with members of its own species for territory or resources. This theory is largely based on the remains of multiple specimens found in close proximity to each other, indicating group living and potential competition among individuals.
The Native Habitat and Geographical Distribution of Aegyptosaurus
Aegyptosaurus was a terrestrial creature, meaning it lived and thrived on land. Its fossils have been found in the Bahariya Formation in Egypt, which was once a lush and fertile floodplain, teeming with plant and animal life. It is believed that this region was covered in extensive forests and rivers during the early Cretaceous period, making it an ideal habitat for the Aegyptosaurus to flourish.While the Aegyptosaurus is believed to have originated in Northern Africa, it is possible that it may have also roamed in other parts of the continent. Fossil remains of similar Titanosaur species have been found in regions such as Niger and Morocco, suggesting a more extensive geographical distribution of these creatures during their time on Earth.
The Mysteries Surrounding Aegyptosaurus
Despite extensive research and study, there are still many mysteries surrounding the Aegyptosaurus. One of the most significant questions is its preferred temperature. As a creature that inhabited the arid regions of Africa, it is unclear how the Aegyptosaurus regulated its body temperature and survived in such extreme conditions.Another mystery is its skin color. While some scientists believe that the Aegyptosaurus may have had a scaly and reptilian-like skin, others argue that it may have had a covering of feathers or filaments. However, without any fossil evidence of skin impressions, its true appearance and color remain a topic of speculation and debate.
The Legacy of Aegyptosaurus
Despite being discovered over a century ago, Aegyptosaurus continues to captivate the minds of researchers and the general public alike. Its unique features and mysterious behavior have inspired countless theories and studies, shedding new light on the evolution and diversity of the dinosaur kingdom.The discovery of Aegyptosaurus also opened up new avenues for paleontologists to explore and uncover more about the world of dinosaurs. Its remains continue to provide valuable insights into the ancient ecosystem, shedding light on the complex interactions between different species and their environment.
Conclusion
Aegyptosaurus may have roamed the Earth millions of years ago, but its legacy lives on to this day. With its massive size, unique features, and enigmatic behavior, it continues to fascinate and intrigue us, giving us a glimpse into a world that existed long before humans.Through dedicated research and innovative technologies, we are gradually uncovering more about the Aegyptosaurus and its ancient world, helping us piece together the puzzle of the past. As we continue to explore and delve into the mysteries of this amazing creature, one thing is certain - the Aegyptosaurus will forever remain an iconic and enigmatic member of the dinosaur family.
Aegyptosaurus
Dinosaur Details Aegyptosaurus - Scientific Name: Aegyptosaurus
- Category: Dinosaurs A
- Scientific Name: Aegyptosaurus
- Common Name: Aegyptosaurus
- Geological Era: Early Cretaceous
- Length: Around 14 meters
- Height: Around 4 meters
- Weight: Around 10-15 tons
- Diet: Herbivorous
- Feeding Behavior: Browsing
- Predatory Behavior: Non-predatory
- Tooth Structure: Peg-like and spoon-shaped teeth
- Native Habitat: Terrestrial
- Geographical Distribution: Northern Africa
- Preferred Temperature: Unknown
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown

Aegyptosaurus
- Bone Structure: Large and sturdy
- Reproduction Type: Egg-laying
- Activity Period: Diurnal
- Distinctive Features: Long neck and tail, robust body
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Unknown
- Largest Species: Unknown
- Smallest Species: Unknown
- Fossil Characteristics: Fragmentary remains
- Role in Ecosystem: Unknown
- Unique Facts: The exact appearance and lifestyle of Aegyptosaurus is uncertain due to incomplete fossil evidence.
- Predator Status: Not a predator
- Discovery Location: Egypt
- Discovery Year: 1932
- Discoverer's Name: Stromer

Aegyptosaurus
The Mysterious Aegyptosaurus: A Closer Look at the Enigmatic Dinosaur
Dinosaurs have always captured the imagination of humans. These prehistoric creatures, which once roamed the Earth millions of years ago, still fascinate us today. From the towering Tyrannosaurus Rex to the massive Brachiosaurus, each dinosaur species has its own unique characteristics that make them stand out. However, there are some dinosaurs that remain shrouded in mystery, with little known about them OnTimeAiraz.Com. One such dinosaur is the Aegyptosaurus.
Aegyptosaurus was a sauropod, a type of herbivorous dinosaur known for their large size and long necks. It lived during the Late Cretaceous period, about 95-70 million years ago, in what is now modern-day Egypt. It is one of the lesser-known sauropod dinosaurs, with only fragmentary remains discovered so far. Due to the lack of complete fossil evidence, the true appearance and lifestyle of Aegyptosaurus remain a mystery.
The History of Aegyptosaurus Discovery
The first-known remains of Aegyptosaurus were discovered in 1932 by German paleontologist Ernst Stromer. Stromer was part of a series of expeditions to Egypt in the early 20th century, where he uncovered various dinosaur fossils. In 1932, Stromer excavated fragmentary remains of Aegyptosaurus in the Bahariya Formation, a geological formation known for its rich fossil deposits. These remains included some vertebrae and limb bones, which were later identified as belonging to a new sauropod species Animantarx.
Stromer named the newly discovered dinosaur Aegyptosaurus, which means "Egyptian lizard." However, due to the fragmentary nature of the fossils, the exact appearance and features of Aegyptosaurus were uncertain. Stromer initially thought it was a type of brachiosaur, a sauropod known for its long front legs and relatively shorter back legs. It wasn't until later discoveries and advancements in technology that scientists began to unravel the mystery surrounding Aegyptosaurus.
Bone Structure and Distinctive Features
From the limited fossil evidence, scientists have been able to piece together some information about the bone structure and distinctive features of Aegyptosaurus. As a sauropod, it is believed to have had a large and robust body, estimated to be around 15-20 meters long. Its neck was also long, similar to other sauropods, to reach food sources in tall trees. Its tail was also comparatively long, likely used as a balance while walking or to defend against predators.
One of the distinctive features of Aegyptosaurus is its robust body, which may have been an adaptation for survival. As a large herbivore, it would have needed a sturdy body to support its massive weight and to withstand the rigors of daily life. However, without complete fossil evidence, it is uncertain if there were any other unique physical characteristics that set Aegyptosaurus apart from other sauropods.
Communication Method and Reproduction
One of the mysteries surrounding Aegyptosaurus is its communication method. As with most dinosaurs, there is no evidence to suggest how they communicated with each other. Some scientists speculate that sauropods may have used vocalizations or body language to communicate, while others believe they may have had limited social interactions. Without any conclusive evidence, it remains unknown how Aegyptosaurus communicated with its kind.
Another aspect that is widely unknown is the reproductive behavior of Aegyptosaurus. Like other dinosaurs, Aegyptosaurus is believed to have laid eggs, as there have been no fossil evidence of live births. However, there is no way to confirm this as no Aegyptosaurus egg fossils have been found to date. This is another aspect of their life history that remains a mystery.
The Activity Period and Survival Adaptation of Aegyptosaurus
Based on the fossil evidence, scientists estimate that Aegyptosaurus was diurnal, which means it was active during the day. This is a common activity period for large herbivorous dinosaurs as it allows them to forage for food and avoid potential predators. As for its survival adaptation, this remains uncertain as well. However, as with most sauropod dinosaurs, Aegyptosaurus may have developed adaptations to help it survive in its environment, such as a sturdy body and long neck for reaching food sources.
Role in the Ecosystem and Predator Status
The role of Aegyptosaurus in its ecosystem is another aspect that remains unclear. As a large herbivore, it likely played a crucial role in maintaining the balance of its environment by grazing on plants and contributing to nutrient cycling. However, without a complete understanding of its behavior and ecological niche, its precise role is unknown.
One thing that is certain is that Aegyptosaurus was not a predator. Its large size, herbivorous diet, and lack of known predatory adaptations suggest that it was not a hunter. Instead, it likely relied on its size and strength to defend against potential predators, such as theropods like Spinosaurus, which were known to inhabit the same region during the same time period.
Other Unique Facts About Aegyptosaurus
Aside from its uncertain appearance and lifestyle, there are several other unique facts about Aegyptosaurus that make it an intriguing dinosaur species. For example, no one knows exactly how many species of Aegyptosaurus existed. The fossil evidence discovered so far is limited to fragmentary remains, making it challenging to determine if all the fossils belong to the same species or multiple species.
Another interesting fact is that the only known skeletons of Aegyptosaurus were destroyed during World War II. The fossils were stored at the Munich Museum and were unfortunately bombed and destroyed during the war. This adds to the mystery surrounding this elusive dinosaur, as we may never know if the complete skeletons could have provided more answers about its appearance and lifestyle.
In Conclusion
Aegyptosaurus is undoubtedly one of the most fascinating and elusive dinosaurs. For decades, scientists have been trying to unravel the mystery surrounding this enigmatic species. With limited fossil evidence, it is challenging to determine its exact appearance, lifestyle, and role in its ecosystem. However, recent discoveries and advancements in technology have shed some light on this mysterious dinosaur, giving us a glimpse into its world. The ongoing research and exploration into the Bahariya Formation in Egypt may bring us closer to solving the puzzle of Aegyptosaurus. Until then, this enigmatic dinosaur will continue to captivate our imagination and spark our curiosity.
Dinosaurs have always captured the imagination of humans. These prehistoric creatures, which once roamed the Earth millions of years ago, still fascinate us today. From the towering Tyrannosaurus Rex to the massive Brachiosaurus, each dinosaur species has its own unique characteristics that make them stand out. However, there are some dinosaurs that remain shrouded in mystery, with little known about them OnTimeAiraz.Com. One such dinosaur is the Aegyptosaurus.
Aegyptosaurus was a sauropod, a type of herbivorous dinosaur known for their large size and long necks. It lived during the Late Cretaceous period, about 95-70 million years ago, in what is now modern-day Egypt. It is one of the lesser-known sauropod dinosaurs, with only fragmentary remains discovered so far. Due to the lack of complete fossil evidence, the true appearance and lifestyle of Aegyptosaurus remain a mystery.
The History of Aegyptosaurus Discovery
The first-known remains of Aegyptosaurus were discovered in 1932 by German paleontologist Ernst Stromer. Stromer was part of a series of expeditions to Egypt in the early 20th century, where he uncovered various dinosaur fossils. In 1932, Stromer excavated fragmentary remains of Aegyptosaurus in the Bahariya Formation, a geological formation known for its rich fossil deposits. These remains included some vertebrae and limb bones, which were later identified as belonging to a new sauropod species Animantarx.Stromer named the newly discovered dinosaur Aegyptosaurus, which means "Egyptian lizard." However, due to the fragmentary nature of the fossils, the exact appearance and features of Aegyptosaurus were uncertain. Stromer initially thought it was a type of brachiosaur, a sauropod known for its long front legs and relatively shorter back legs. It wasn't until later discoveries and advancements in technology that scientists began to unravel the mystery surrounding Aegyptosaurus.
Bone Structure and Distinctive Features
From the limited fossil evidence, scientists have been able to piece together some information about the bone structure and distinctive features of Aegyptosaurus. As a sauropod, it is believed to have had a large and robust body, estimated to be around 15-20 meters long. Its neck was also long, similar to other sauropods, to reach food sources in tall trees. Its tail was also comparatively long, likely used as a balance while walking or to defend against predators.One of the distinctive features of Aegyptosaurus is its robust body, which may have been an adaptation for survival. As a large herbivore, it would have needed a sturdy body to support its massive weight and to withstand the rigors of daily life. However, without complete fossil evidence, it is uncertain if there were any other unique physical characteristics that set Aegyptosaurus apart from other sauropods.
Communication Method and Reproduction
One of the mysteries surrounding Aegyptosaurus is its communication method. As with most dinosaurs, there is no evidence to suggest how they communicated with each other. Some scientists speculate that sauropods may have used vocalizations or body language to communicate, while others believe they may have had limited social interactions. Without any conclusive evidence, it remains unknown how Aegyptosaurus communicated with its kind.Another aspect that is widely unknown is the reproductive behavior of Aegyptosaurus. Like other dinosaurs, Aegyptosaurus is believed to have laid eggs, as there have been no fossil evidence of live births. However, there is no way to confirm this as no Aegyptosaurus egg fossils have been found to date. This is another aspect of their life history that remains a mystery.
The Activity Period and Survival Adaptation of Aegyptosaurus
Based on the fossil evidence, scientists estimate that Aegyptosaurus was diurnal, which means it was active during the day. This is a common activity period for large herbivorous dinosaurs as it allows them to forage for food and avoid potential predators. As for its survival adaptation, this remains uncertain as well. However, as with most sauropod dinosaurs, Aegyptosaurus may have developed adaptations to help it survive in its environment, such as a sturdy body and long neck for reaching food sources.Role in the Ecosystem and Predator Status
The role of Aegyptosaurus in its ecosystem is another aspect that remains unclear. As a large herbivore, it likely played a crucial role in maintaining the balance of its environment by grazing on plants and contributing to nutrient cycling. However, without a complete understanding of its behavior and ecological niche, its precise role is unknown.One thing that is certain is that Aegyptosaurus was not a predator. Its large size, herbivorous diet, and lack of known predatory adaptations suggest that it was not a hunter. Instead, it likely relied on its size and strength to defend against potential predators, such as theropods like Spinosaurus, which were known to inhabit the same region during the same time period.
Other Unique Facts About Aegyptosaurus
Aside from its uncertain appearance and lifestyle, there are several other unique facts about Aegyptosaurus that make it an intriguing dinosaur species. For example, no one knows exactly how many species of Aegyptosaurus existed. The fossil evidence discovered so far is limited to fragmentary remains, making it challenging to determine if all the fossils belong to the same species or multiple species.Another interesting fact is that the only known skeletons of Aegyptosaurus were destroyed during World War II. The fossils were stored at the Munich Museum and were unfortunately bombed and destroyed during the war. This adds to the mystery surrounding this elusive dinosaur, as we may never know if the complete skeletons could have provided more answers about its appearance and lifestyle.
In Conclusion
Aegyptosaurus is undoubtedly one of the most fascinating and elusive dinosaurs. For decades, scientists have been trying to unravel the mystery surrounding this enigmatic species. With limited fossil evidence, it is challenging to determine its exact appearance, lifestyle, and role in its ecosystem. However, recent discoveries and advancements in technology have shed some light on this mysterious dinosaur, giving us a glimpse into its world. The ongoing research and exploration into the Bahariya Formation in Egypt may bring us closer to solving the puzzle of Aegyptosaurus. Until then, this enigmatic dinosaur will continue to captivate our imagination and spark our curiosity.

The Mighty Aegyptosaurus: Exploring the Enigmatic Dinosaur of Northern Africa
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.