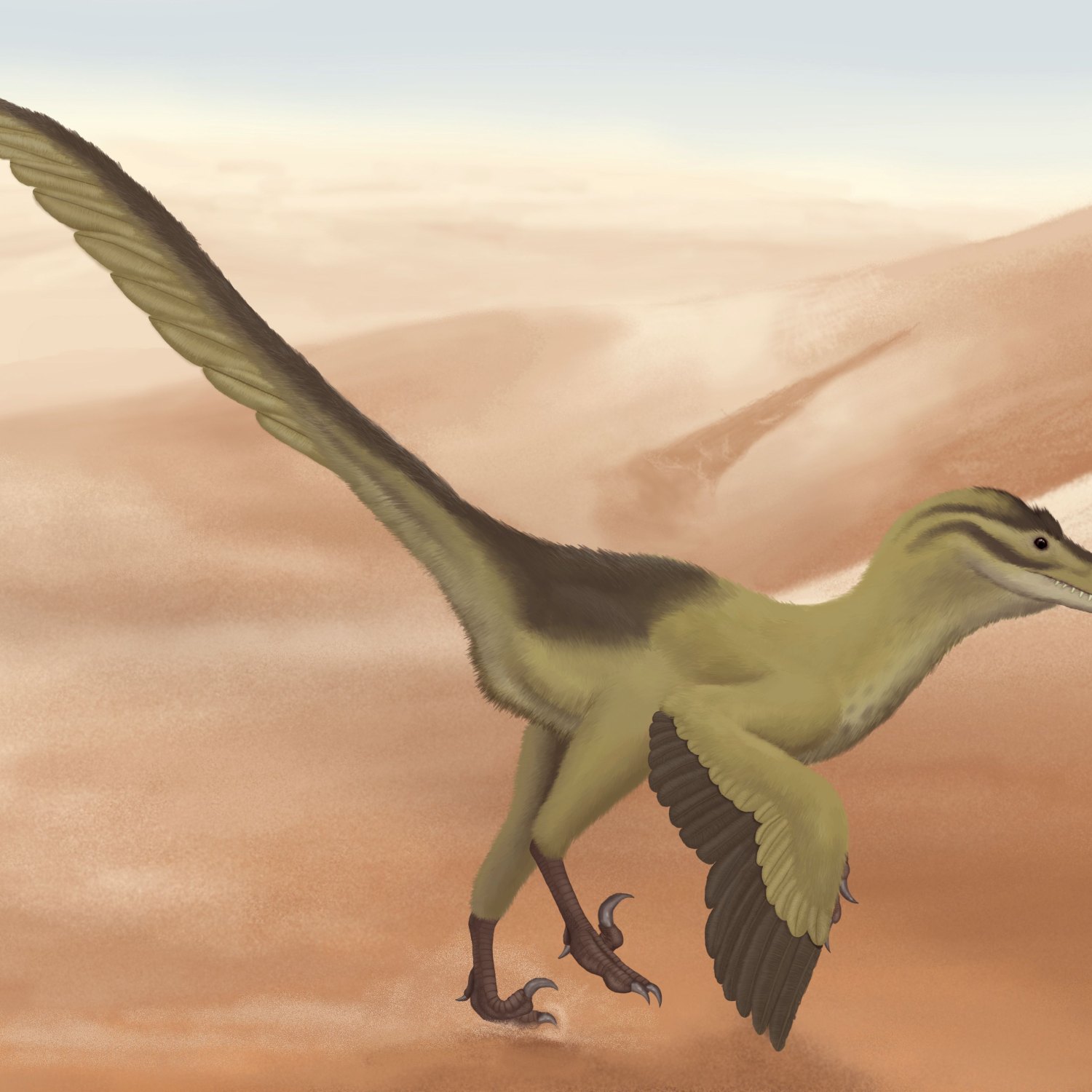
Linheraptor
Unknown
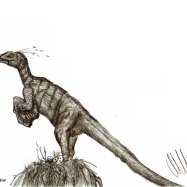
Linheraptor, a vicious raptor from Mongolia known for its speed and carnivorous diet. Its skin color remains a mystery, but its sharp claws and quick movements make it a formidable predator. Learn more about this fascinating dinosaur and its role in the prehistoric world. #Linheraptor #Mongolia #Carnivore #Dinosaurs.
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Linheraptor
Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
Feeding Behavior: Carnivorous
The Fierce Hunter of the Late Cretaceous: Linheraptor
When we think of the Late Cretaceous period, images of large, ferocious predators like T. Rex and Velociraptor often come to mind. However, there was another lesser-known but equally formidable hunter that roamed the open plains of Mongolia during this time - Linheraptor.Linheraptor, whose scientific name is derived from the Chinese term "Linhe" meaning "river", was a medium-sized theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 75 million years ago Linheraptor. Its name is also a nod to the Linhe region of Inner Mongolia, where the first fossilized remains of this species were discovered in 2008.
While Linheraptor may not be as well-known as some of its more famous relatives, this dinosaur has a fascinating story and notable characteristics that make it a standout predator of the Late Cretaceous era.
Appearance and Size
Linheraptor was a formidable predator, measuring about 3 meters in length and standing at 1 meter tall at the hips. Its exact weight is unknown, but it was estimated to be around 45-90 kilograms based on comparisons with other similar theropod dinosaurs like its close relative, Velociraptor.
Like many theropods, Linheraptor has a long, slender tail and thin, hollow bones that made it lightweight and agile. Its long legs and sharp claws were perfect for quick bursts of speed and deadly strikes. And although its arms may seem small in comparison to its body, they were still strong and dexterous, equipped with sharp, recurved claws.
Diet and Feeding Behavior
Linheraptor was a fierce carnivore with a diet consisting mainly of meat. Its serrated and razor-sharp teeth were typical of theropods, making them well-suited for tearing apart flesh Latirhinus. And while it may have been smaller than other predators of its time, Linheraptor was a skilled and active hunter.
Like its more famous relative, Velociraptor, Linheraptor is believed to have hunted in groups, making it a formidable and efficient predator. Its speed, agility, and sharp claws would have made it an excellent pack hunter, able to take down larger prey such as the herbivorous Protoceratops.
Native Habitat and Geographic Distribution
Linheraptor lived in the open plains of what is now the Gobi Desert in Mongolia during the Late Cretaceous period. Its native habitat would have been a vast, semi-arid landscape with sparse vegetation and a warm, dry climate, similar to the modern-day Mongolian steppe.
The Linhe region, where the first fossilized remains of this dinosaur were discovered, was once a river delta that was rich in diverse plant and animal life. This would have made it an ideal hunting ground for Linheraptor and its pack.
Predatory Behavior
As an active hunter, Linheraptor would have relied on its speed and agility to take down prey. It is believed that it may have used a combination of speed and stealth to catch its meals. However, this dinosaur was also equipped with strong jaws and sharp teeth, making it a deadly and efficient killer.
Some studies suggest that Linheraptor may have used its long claws to pin down prey while delivering fatal bites to vulnerable parts of the body, such as the neck or underbelly. And with its sharp, serrated teeth, it would have been able to rip through tough skin and bones with ease.
Discoveries and Importance
The first fossilized remains of Linheraptor were discovered in 2008 by a joint Chinese-American team in the Wulansuhai Formation of Inner Mongolia. The initial discovery consisted of a well-preserved skeleton, including almost-complete limbs, shoulder and sternum bones, and some vertebrae.
Further excavations and discoveries in the same region have yielded more fossilized remains, including skull fragments, teeth, and a partial articulated skeleton of a juvenile Linheraptor. These discoveries have helped paleontologists gain a better understanding of this dinosaur's anatomy, behavior, and evolutionary history.
Linheraptor's unique features, such as its slender build, long legs, and sharp claws, have also provided valuable insight into its predatory behavior and the evolution of similar theropod dinosaurs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Linheraptor may not be as well-known as some of its more famous dinosaur relatives, but it certainly holds its own in terms of its predatory prowess and importance in paleontology. This medium-sized theropod dinosaur may have been smaller in size, but it was a ferocious predator with sharp teeth, strong claws, and a killer instinct.
Its discoveries have provided valuable information about its physical characteristics, behavior, and habitat, giving us a glimpse into the fascinating world of the Late Cretaceous period. And with ongoing excavations and new discoveries, there is still much to learn about this fierce hunter of the ancient Gobi Desert.
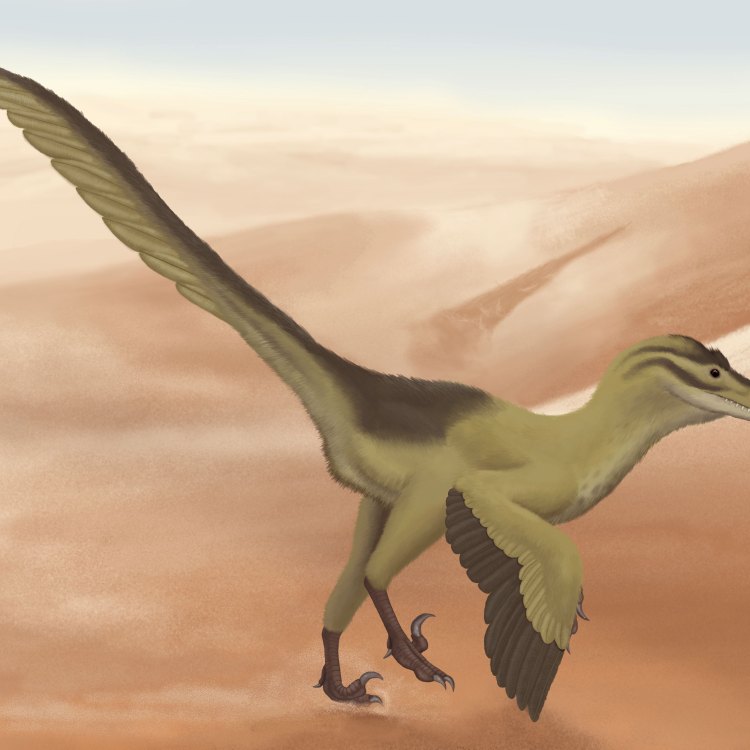

Linheraptor
Dinosaur Details Linheraptor - Scientific Name: Linheraptor
- Category: Dinosaurs L
- Scientific Name: Linheraptor
- Common Name: Linheraptor
- Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
- Length: 3 meters
- Height: 1 meter
- Weight: Unknown
- Diet: Meat
- Feeding Behavior: Carnivorous
- Predatory Behavior: Active hunter
- Tooth Structure: Sharp and serrated
- Native Habitat: Open plains
- Geographical Distribution: Mongolia
- Preferred Temperature: Unknown
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown
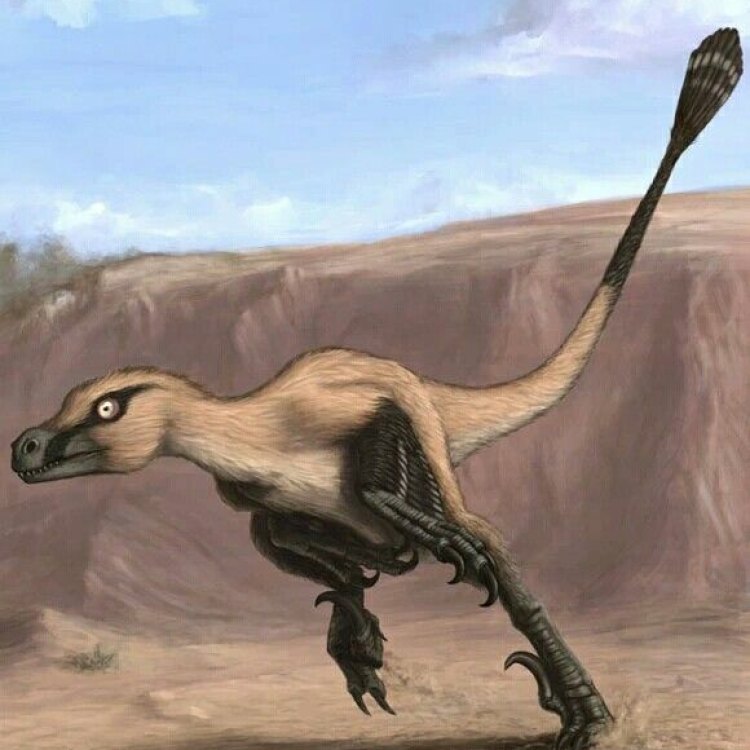

Linheraptor
- Bone Structure: Unknown
- Reproduction Type: Unknown
- Activity Period: Unknown
- Distinctive Features: Large curved claws on hands and feet
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Unknown
- Largest Species: Unknown
- Smallest Species: Unknown
- Fossil Characteristics: Partial skeletons and isolated bones
- Role in Ecosystem: Apex predator
- Unique Facts: Linheraptor had large, curved claws on its hands and feet, which were likely used for catching and holding onto prey.
- Predator Status: Extinct
- Discovery Location: Inner Mongolia, China
- Discovery Year: 2008
- Discoverer's Name: Xu Xing

Linheraptor
The Fascinating World of Linheraptor: The Apex Predator of Inner Mongolia
Deep in the heart of Inner Mongolia, an ancient predator once roamed the land, leaving behind a legacy of fierce and devastating power. This predator is none other than Linheraptor, a formidable carnivore that ruled the region millions of years ago.The name Linheraptor comes from the combination of two words – "Linhe" which means "plains" in Chinese and "raptor" which means "thief" in Latin. This name is fitting for this fierce predator, as it is believed that Linheraptor was an apex predator, at the top of the food chain in its ecosystem OnTimeAiraz.Com.
But what makes Linheraptor truly unique and intriguing? From its distinctive features to its role in the ecosystem, let's take a closer look at this fascinating creature and discover its secrets.
The Mysterious Bone Structure of Linheraptor
When it comes to the bone structure of Linheraptor, there is still a lot of mystery surrounding this ancient predator. As of now, there is not enough evidence to determine the exact structure and anatomy of Linheraptor. However, based on the specimens that have been discovered, scientists believe that it was a lithe and agile creature, weighing around 50kg. Its body was likely covered in feathers, giving it a more bird-like appearance.One of the most distinctive features of Linheraptor is its large, curved claws on its hands and feet. These sharp and powerful claws were long and slender, curved inwards and were likely used for catching and holding onto its prey. It is believed that these claws were instrumental in making Linheraptor a successful hunter. Its beak-like snout also suggests that it was a predator that relied heavily on its sharp claws to catch and eat its prey Lusotitan.
The Mystery of Linheraptor's Reproduction and Activity Period
One of the biggest mysteries surrounding Linheraptor is how it reproduced and what its activity period was. Because of insufficient evidence, scientists are still unable to determine whether Linheraptor was a solitary creature or if it lived in groups. It is also unknown whether it laid eggs or gave birth to live young.Similarly, the exact activity period of Linheraptor is still a mystery. Some scientists believe that it was an active and agile hunter, while others suggest that it was more of a scavenger. The lack of evidence and its extinct status makes it difficult to determine its behavior and activity period.
Fierce and Unstoppable: Linheraptor's Unique Survival Adaptations
Despite the lack of information about its reproduction and activity period, one thing is clear – Linheraptor was a fierce and powerful predator that had unique survival adaptations. Its large, curved claws were not only used for catching prey, but also as tools for survival. These claws were also helpful in climbing and digging, making Linheraptor a versatile creature. Its agile body and sharp senses also helped it to evade predators and hunt efficiently.Furthermore, Linheraptor's feathers were not only used for warmth, but also for camouflaging and attracting mates. These adaptations helped Linheraptor to survive in its harsh and competitive ecosystem, making it a dominant and successful predator.
The Discovery of Linheraptor: A Breakthrough in Palaeontology
It was in 2008, that the world was introduced to the fierce Linheraptor when a team of Chinese scientists, led by renowned palaeontologist Xu Xing, discovered the first fossil of this creature in Inner Mongolia, China.The discovery of Linheraptor was a breakthrough in the world of palaeontology as it provided valuable insight into the evolution of theropod dinosaurs. The almost-complete skeleton of this ancient predator helped scientists understand the anatomy and behavior of Linheraptor, which was previously unknown.
Since then, more fossils of Linheraptor have been discovered in the same region, providing more evidence and information about this ancient creature.
The Role of Linheraptor in its Ecosystem
As an apex predator, Linheraptor played a crucial role in its ecosystem. It was at the top of the food chain and helped maintain the balance of its ecosystem by controlling the population of other species. Its powerful claws and sharp senses made it a formidable hunter, making it an essential part of the food web.Linheraptor's extinction had a profound impact on its ecosystem, as it left a void in the top predator category. However, the legacy of this creature lives on through its fossils, providing valuable information and insights into our planet's ancient past.
The Legacy of Linheraptor: Unique Facts and Extinction
Aside from its distinctive features and adaptations, there are a few more unique facts about Linheraptor that make it an intriguing creature. Its large clawed hands and feet were likely used for display purposes as well, to attract potential mates or ward off rivals.However, despite its dominance and power as an apex predator, the Linheraptor, like many other creatures, could not stand the test of time and became extinct. The exact reason for its extinction is still unknown, but it is believed that it may have succumbed to climate change or competition from other predators.
Conclusion
Linheraptor may have roamed the plains of Inner Mongolia millions of years ago, but its legacy still lingers on. Its large, curved claws, agile body, and unique adaptations have captivated the minds of many and provided valuable insights into its ancient ecosystem.The remains and discoveries of Linheraptor have also helped scientists understand the evolution and behavior of theropod dinosaurs, making it an essential part of the study of palaeontology.
Although many mysteries still surround this fierce creature, it continues to fascinate and captivate us with its undeniable power and unique characteristics. The Linheraptor will always be remembered as the apex predator of Inner Mongolia, a testament to the wonders and mysteries of our planet's past.
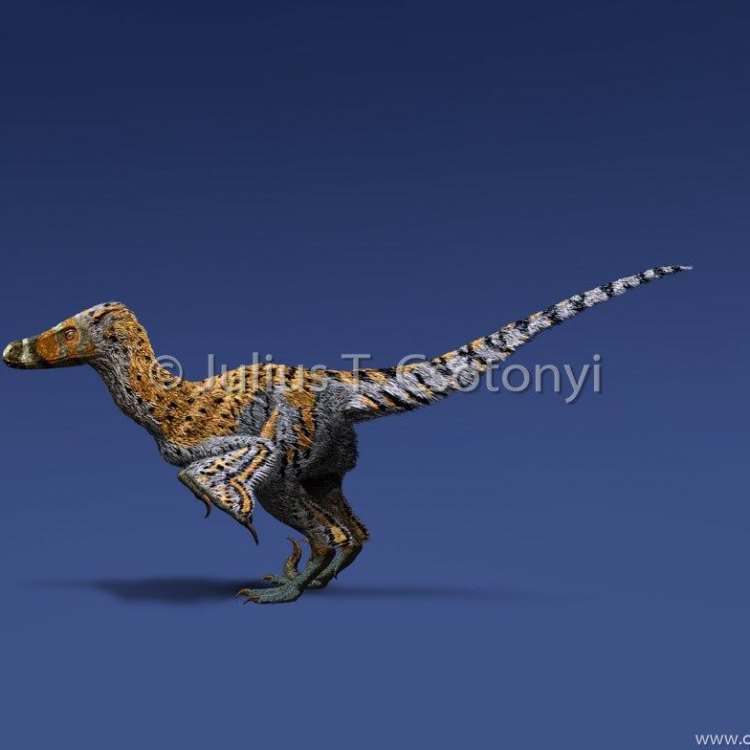

The Fierce Hunter of the Late Cretaceous: Linheraptor
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.