Kentrosaurus
Unknown
Meet the Kentrosaurus, a lesser-known but fascinating dinosaur from Africa. With its distinctive spiked armor and herbivorous diet, this creature may have roamed the savannas in search of plants. While its top speed is unknown, its unique appearance certainly makes it stand out in the world of dinosaurs. #Kentrosaurus #Dinosaurs #Africa #Herbivore
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Kentrosaurus
Geological Era: Late Jurassic
Feeding Behavior: Browsing
The Fascinating Kentrosaurus: A Jurassic Dinosaur with Unique Features
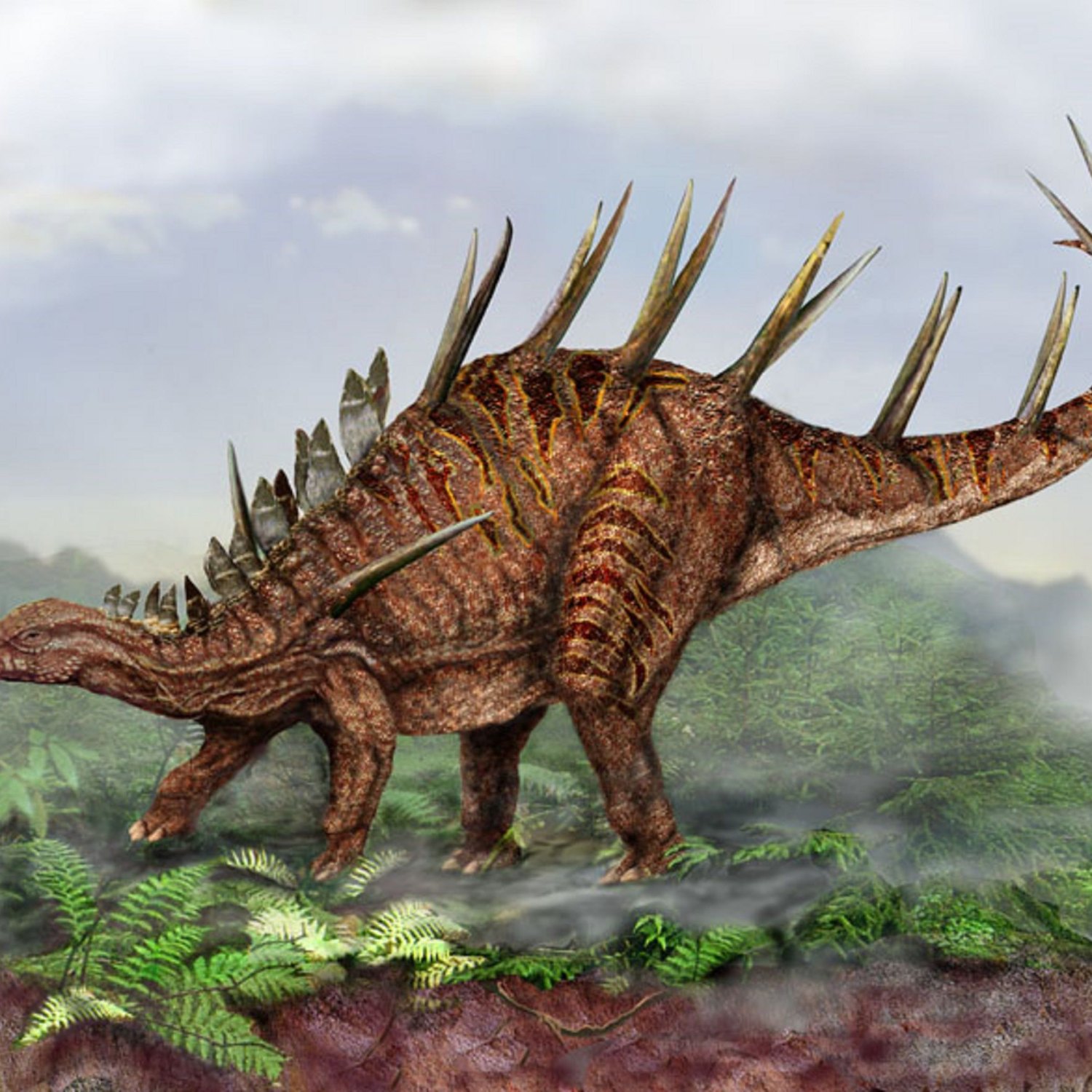
Imagine walking through a dense forest, surrounded by towering trees and lush vegetation. Suddenly, you hear a rustling sound and see a large, fearsome creature emerge from the bushes. But as it comes closer, you realize that it is not as intimidating as you thought. In fact, it is a peaceful herbivorous dinosaur called Kentrosaurus, with its unique features and intriguing behavior Kentrosaurus.Kentrosaurus, an imposing-looking dinosaur, lived during the Late Jurassic period, about 155-150 million years ago. Its scientific name is derived from the Greek words "kentron," meaning sharp-pointed, and "saurus," meaning lizard. It was first discovered in Tanzania, Africa, and is believed to have roamed the woodlands of that region. The name Kentrosaurus was given due to its distinctive feature of sharp spines along its tail.
This ancient creature was about 5-6 meters in length, which is slightly smaller than its close relative, Stegosaurus. It stood at an impressive height of 2.5 meters and weighed around 1.2-2 tons. Its body was supported by four sturdy legs and featured a long neck and small head with a mouth full of leaf-like teeth Kukufeldia. These teeth were uniquely shaped to help in browsing and grinding vegetation.
The Unique Spikes and Plates of Kentrosaurus
The most striking characteristic of Kentrosaurus was its long, sharp spikes and plates that adorned its back and tail. These spikes, known as scutes, were made of keratin, the same material found in our nails and hair. They were about 2 feet long and were arranged in two rows along its back and tail, with some being placed upright and others pointing downward. These spikes acted as a protective armor, providing defense against predators such as Allosaurus and Ceratosaurus, which roamed the same habitat.On the other hand, the plates, also known as osteoderms, were bony protrusions on its back and tail. They provided structural support and helped in regulating the dinosaur's body temperature. Research suggests that these plates might have also played a role in display and communication, as they had blood vessels running through them, giving them a pink or red color when the dinosaur was alive.
Browsing and Nocturnal Behavior
Kentrosaurus was a herbivore, meaning it mainly relied on plant-based food for its survival. Its feeding behavior was that of a browser, which is characterized by eating leaves and young shoots from trees, shrubs, and other low-lying plants. As it was a medium-sized dinosaur, it could reach for plants that were just out of reach for smaller herbivorous dinosaurs. Its leaf-like teeth helped in efficiently tearing through tough plants and grinding them for digestion.Apart from its feeding behavior, Kentrosaurus had a unique predatory behavior that sets it apart from other dinosaurs. It was primarily a nocturnal creature, meaning it was most active during the night. This behavior is thought to have evolved due to competition for resources with other herbivorous dinosaurs during the day. Being active at night gave Kentrosaurus an advantage in finding food and avoiding predators.
The Woodland Dweller from Africa
Kentrosaurus is believed to have inhabited the woodlands of Africa during the Late Jurassic period. Fossil evidence has been found in Tanzania, which suggests a warm and humid climate, with dense forests and rivers. Due to this, it is speculated that Kentrosaurus preferred warm temperatures, as it would have been challenging for such a large animal to regulate its body temperature in colder regions.Due to its preference for woodland habitats, Kentrosaurus most likely shared its home with other herbivorous dinosaurs such as Camarasaurus and Dicraeosaurus. It was also most likely preyed upon by the carnivorous Allosaurus and Ceratosaurus. Apart from sharing its home with other dinosaurs, Kentrosaurus also shared its habitat with other animals like pterosaurs and small mammals.
A Mysterious End
Like most dinosaurs, the exact cause of Kentrosaurus's extinction remains a mystery. With no known predators and its defensive spikes and plates, it is assumed that it was not easily threatened by other creatures. However, factors like disease, natural disasters, and climate change could have played a role in its disappearance. Alternatively, it is believed that the changing environment and competition for resources could have led to the decline of Kentrosaurus's population, ultimately leading to its extinction.Despite its mysterious end, Kentrosaurus remains one of the most fascinating creatures to have walked the Earth. Its unique features, from its sharp spikes and plates to its nocturnal behavior, make it stand out among other dinosaurs. Its small but sturdy frame, combined with its defensive mechanism, proves that these ancient creatures were truly remarkable and well-adapted to their surroundings.
As we continue to uncover more about the fascinating world of dinosaurs, Kentrosaurus will remain a significant and intriguing part of it. Its legacy continues to inspire us and reminds us of the incredible diversity and resilience of life on our planet. So, the next time you walk through a forest, remember that, at one point in time, it was also home to the majestic Kentrosaurus.
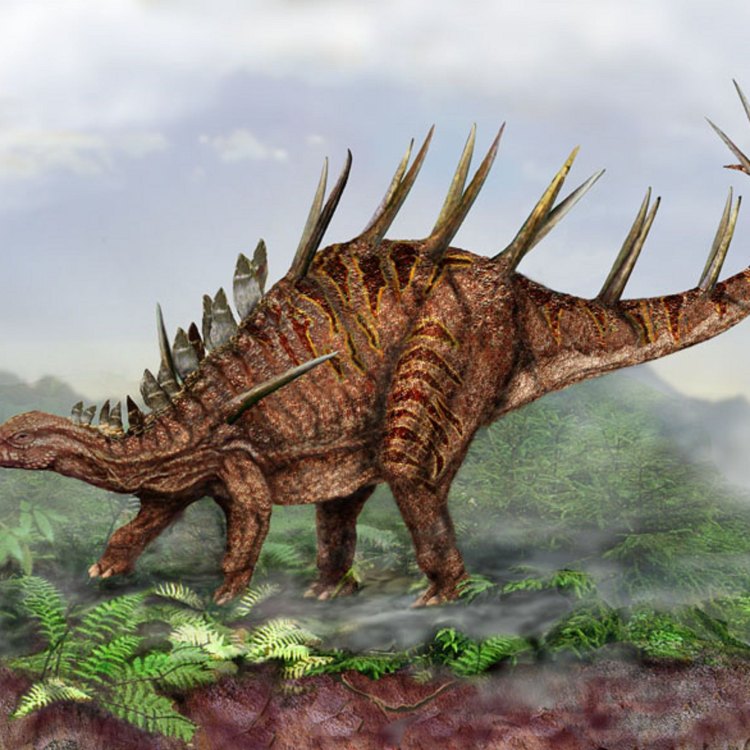

Kentrosaurus
Dinosaur Details Kentrosaurus - Scientific Name: Kentrosaurus
- Category: Dinosaurs K
- Scientific Name: Kentrosaurus
- Common Name: Kentrosaurus
- Geological Era: Late Jurassic
- Length: 5-6 meters
- Height: 2.5 meters
- Weight: 1.2-2 tons
- Diet: Herbivorous
- Feeding Behavior: Browsing
- Predatory Behavior: Nocturnal
- Tooth Structure: Leaf-like
- Native Habitat: Woodland
- Geographical Distribution: Africa
- Preferred Temperature: Warm temperatures
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown
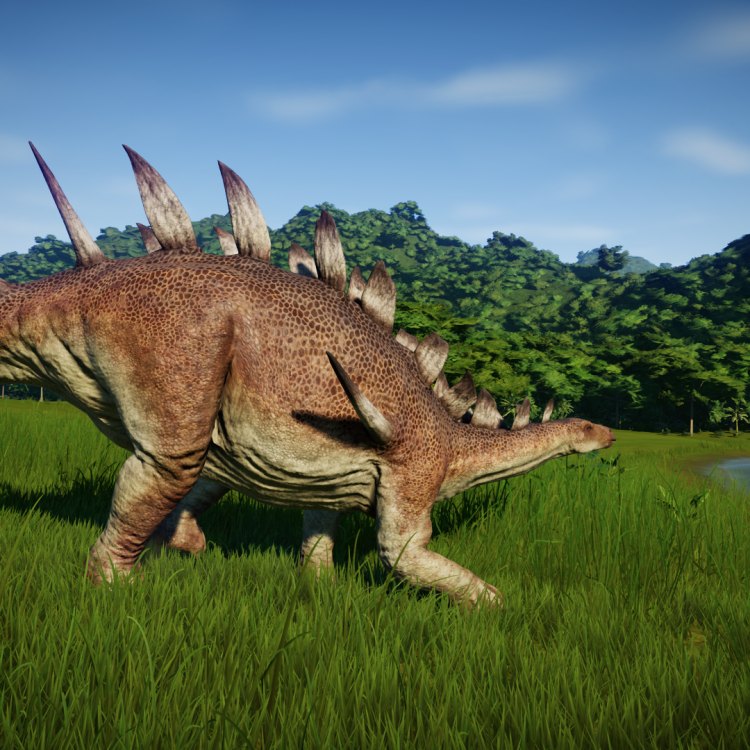

Kentrosaurus
- Bone Structure: Large and sturdy
- Reproduction Type: Egg-laying
- Activity Period: Unknown
- Distinctive Features: Large bony plates along its back
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Protective plates on its body
- Largest Species: Kentrosaurus aethiopicus
- Smallest Species: Unknown
- Fossil Characteristics: Well-preserved skeletal remains
- Role in Ecosystem: Herbivore, possibly served as prey for larger predators
- Unique Facts: One of the best-known stegosaurs
- Predator Status: Prey
- Discovery Location: Tanzania
- Discovery Year: 1909
- Discoverer's Name: Edwin Hennig
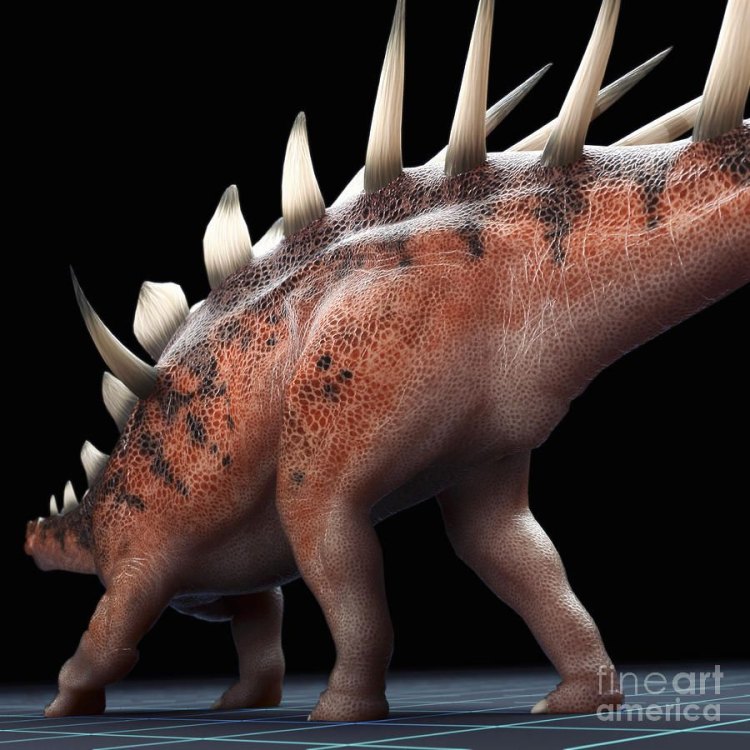

Kentrosaurus
The Sturdy and Unique Kentrosaurus: A Fascinating Dinosaur in the Late Jurassic
Dinosaurs have always been a topic of fascination for people of all ages. These giant creatures roamed the earth millions of years ago, and their mysterious existence continues to intrigue us to this day. One such fascinating dinosaur is the Kentrosaurus, a herbivore from the Late Jurassic period. Kentrosaurus, meaning "spiked lizard," was first discovered in 1909 in Tanzania by a German paleontologist named Edwin Hennig OnTimeAiraz.Com. It is one of the best-known stegosaurs, a group of armored dinosaurs characterized by their large, bony plates along their back.Kentrosaurus is a highly distinctive and intriguing dinosaur, with its large size, sturdy bone structure, and unique survival adaptation. Let's delve into more details about this remarkable creature and uncover its many interesting facts.
The Bone Structure of Kentrosaurus: Strength and Sturdiness
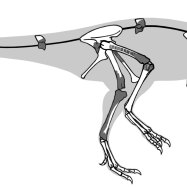
One of the most remarkable features of Kentrosaurus is its bone structure. Its skeletal remains indicate that it had a large and sturdy body, with four thick legs that supported its weight. The front legs were shorter than the back, making its body sloped downward towards its relatively short tail.With an estimated length of 5 meters and a height of 2.5 meters, Kentrosaurus was not the largest dinosaur. However, its strong limbs, large hips, and heavy tail made it a formidable creature in its habitat Khaan. Its skeleton suggests that it was a bipedal dinosaur, meaning it walked on two legs, but it could drop to all fours if needed.
Kentrosaurus had a distinctive bony structure along its spine, which is its most recognizable feature. Instead of having a broad, flat back like other stegosaurs, it had long and narrow plates protruding from its spine. These plates were covered with keratin sheaths, and they served as protection against predators and helped regulate its body temperature.
The Reproduction Type of Kentrosaurus: Egg-laying Dinosaurs
Like most dinosaurs, Kentrosaurus also laid eggs. It was an egg-laying animal, known as an oviparous creature in scientific terms. It is believed that Kentrosaurus laid its eggs in nests or burrows, similar to some modern-day reptiles. However, due to the lack of fossil evidence, their nesting habits remain a mystery.It is estimated that Kentrosaurus eggs were about the size of a grapefruit, which is significantly smaller than other stegosaurs of the same period. This suggests that it may have produced smaller clutches or that its eggs hatched earlier than other stegosaurs.
The reproductive behavior of Kentrosaurus is still unknown, but scientists have speculated that these dinosaurs may have engaged in courtship rituals, similar to modern-day birds. These rituals could have involved using their distinctive plates to attract potential mates.
The Activity Period and Communication Method of Kentrosaurus: Unknown
According to paleontologists, Kentrosaurus lived in the Late Jurassic period, about 155 to 150 million years ago. However, its activity period is still a mystery as there is no fossil evidence to suggest whether it was diurnal (active during the day) or nocturnal (active at night). Some researchers believe that it may have been crepuscular, meaning it was active during dawn and dusk.Another aspect of Kentrosaurus that is yet to be uncovered is its communication method. Unlike some dinosaurs that had distinct vocal organs, there is no evidence to suggest that Kentrosaurus had any vocalization capabilities. They may have used visual communication through their plates, similar to modern-day iguanas.
Survival Adaptation of Kentrosaurus: Protective Plates on its Body
One of the most fascinating features of Kentrosaurus is its survival adaptation. Its most distinctive feature, the large plates along its back, served as a defense mechanism against predators. These bony plates were covered with keratin sheaths, making them hard and sharp. It is believed that they could have been used to fend off predators or even inflict harm to them.In addition to its plates, Kentrosaurus also had long and sharp spikes at the end of its tail, known as a "thagomizer." Scientists speculate that these spikes could have been used as a weapon against predators, as well as for inter-male competition and display.
Kentrosaurus aethiopicus: The Largest and Most Well-known Species
Several species of Kentrosaurus have been discovered, with the largest one being the Kentrosaurus aethiopicus. It was the first species to be described and remains the best-known species of this dinosaur. Its fossils were found in the Tendaguru Formation in Tanzania, making it the first dinosaur to be discovered on African soil.The Kentrosaurus aethiopicus was estimated to be around 5 meters long and weighed around 1 ton. It roamed the earth during the Late Jurassic period, along with other iconic dinosaurs such as Allosaurus and Stegosaurus.
Fossil Characteristics of Kentrosaurus: Well-Preserved Skeletal Remains
The fossils of Kentrosaurus have been found in Tanzania, Germany, and other parts of East Africa. The most well-preserved fossil remains of Kentrosaurus were found in the Tendaguru Formation, where most fossils from this species have been discovered.The fossils of Kentrosaurus have provided valuable information about its bone structure, behavior, and physical characteristics. They have also helped scientists better understand this species and its evolutionary history.
Kentrosaurus in the Ecosystem: A Herbivore and Possible Prey for Larger Predators
Kentrosaurus was a herbivore, meaning it fed on plant matter. Its distinctive plates and thagomizer suggest that it may have been an excellent defense mechanism against predators. However, its relatively small size and slow-moving nature made it a potential target for larger predators such as Allosaurus and Torvosaurus.Its role in the ecosystem was crucial as a herbivorous animal, as it helped to maintain the balance between the plant and animal species. Its remains have also been found alongside those of other herbivorous dinosaurs, suggesting that they may have lived and grazed together in herds.
Unique Facts About Kentrosaurus: A Stegosaur with Exceptional Defense Mechanisms
Kentrosaurus may not be the most popular or iconic dinosaur, but it has its fair share of unique facts that make it a fascinating creature. Its long and narrow plates make it stand out from other stegosaurs, and its well-preserved fossil remains have provided valuable insights into its anatomy and behavior.One of the most interesting facts about Kentrosaurus is that it is closely related to another famous armored dinosaur, Stegosaurus. While Stegosaurus was found in North America and Europe, Kentrosaurus was only discovered in Africa. This has sparked debates among scientists about how and when the two species diverged.
Kentrosaurus: Prey Rather than Predator
With its large bony plates and sharp spikes, one might assume that Kentrosaurus was a formidable predator. However, fossil evidence suggests otherwise. The lack of sharp teeth and any other anatomical features that would suggest hunting abilities indicate that it was a herbivore. Scientists also believe that its small size and slow-moving nature made it an easy target for larger predators.The Discovery of Kentrosaurus: A German Paleontologist Named Edwin Hennig
The first fossils of Kentrosaurus were found in 1909 when a German paleontologist named Edwin Hennig discovered them during an expedition in Tanzania. Hennig named the dinosaur Kentrosaurus because of its distinctive plates, which resembled the spikes on a porcupine's quills.Hennig's discovery of Kentrosaurus and other dinosaurs during the expedition significantly contributed to our understanding of the Late Jurassic period. The fossils he found were among the most well-preserved at the time, providing valuable information about the anatomy and behavior of these ancient creatures.
In Conclusion
Kentrosaurus, with its sturdy bone structure, distinctive plates, and unique defensive adaptations, is a fascinating dinosaur that continues to capture our imagination. From its reproductive behavior and communication methods to its role in the ecosystem, there is still much to learn about this incredible creature. Its popularity may not match that of some other dinosaurs, but its unique features and well-preserved fossils make it a crucial species in our understanding of prehistoric life.
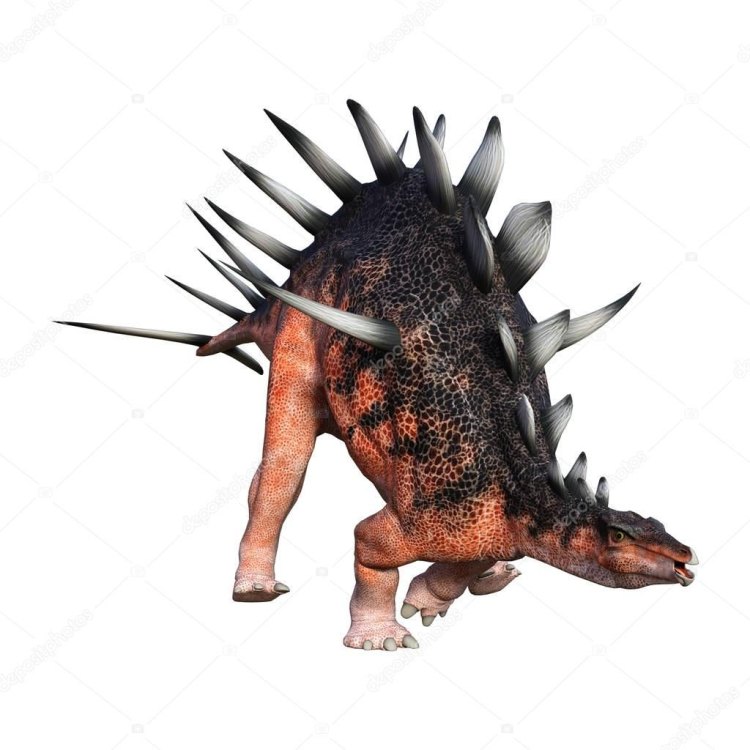

The Fascinating Kentrosaurus: A Jurassic Dinosaur with Unique Features
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.