Anatosaurus
Unknown
Meet the Anatosaurus, a giant plant-eating dinosaur that roamed the western United States millions of years ago. Despite its unknown skin color and speed, its massive size and diet make it a fascinating creature to learn about. Discover more about this dinosaur and its habitat in this article!
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Anatosaurus
Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
Feeding Behavior: Grass and leaf eater
The Enigmatic Anatosaurus: Uncovering the Mysteries of This Giant Dinosaur
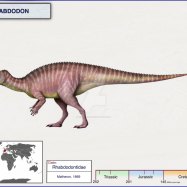
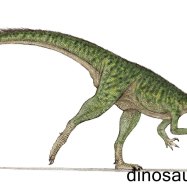
The world of dinosaurs is filled with a wide array of intriguing and sometimes terrifying creatures. From the mighty T-Rex to the gentle giants like Diplodocus, each one has its unique story and significance in the history of the Earth. One such dinosaur that has fascinated scientists and enthusiasts alike is the Anatosaurus.The Anatosaurus, also known as Anatosaurus, was a herbivore that lived during the Late Cretaceous period, approximately 66 million years ago Anatosaurus. Its name translates to "duck lizard," owing to its peculiar flat snout that resembles that of a duck. Its scientific name, Anatosaurus, means "duck dinosaur." Let's take a closer look at this prehistoric giant and uncover some of its mysteries.
Origin and Discovery
The first specimens of Anatosaurus were discovered in 1882 by Professor E. D. Cope in the Hell Creek Formation in Montana, USA. However, he initially believed it to be a species of Trachodon, another duck-billed dinosaur. Later, in 1892, the renowned paleontologist Othniel C. Marsh identified it as a separate genus and named it Anatosaurus Alamosaurus. Since then, several other discoveries have been made, and today, Anatosaurus is classified as a distinct genus within the Hadrosauridae family.Physical Characteristics
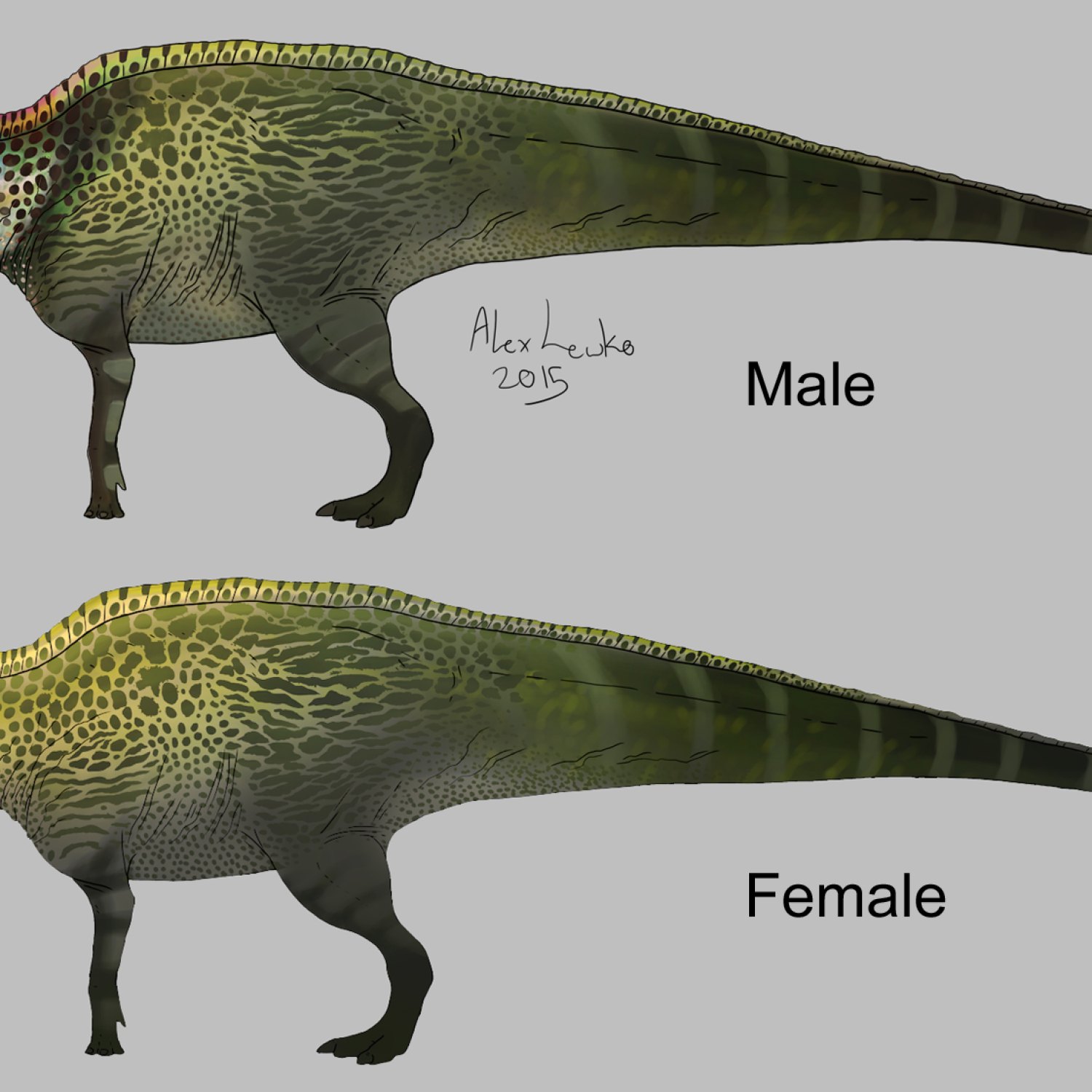
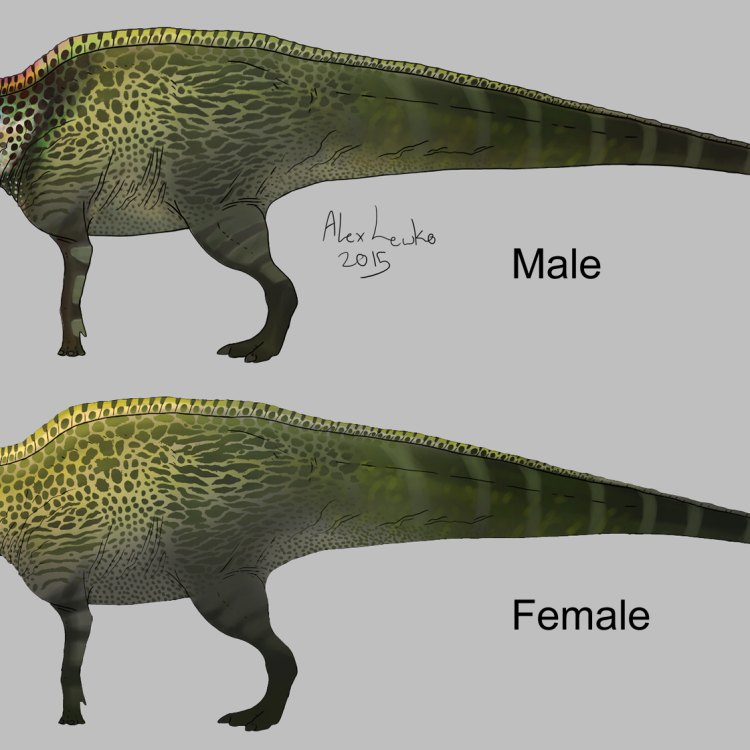
Anatosaurus was a massive dinosaur, measuring around 10-12 meters in length and 3 meters in height. It weighed between 4-6 tons, making it one of the largest duck-billed dinosaurs. Like other hadrosaurids, it had a characteristic long tail, robust hind legs, and smaller front limbs. Its flat, duck-like snout was lined with small teeth, perfect for grinding plant material. It also had a prominent, bony crest on its head, which may have been used for communication and display.Diet and Feeding Behavior
Anatosaurus was a herbivore, which means it only fed on plant material. Its diet primarily consisted of grasses and leaves, and it was well-adapted for this purpose. It had dental batteries, which were rows of tightly packed teeth that allowed it to grind tough plant material efficiently. Unlike other herbivores, Anatosaurus did not have to rely on gastroliths (stones in the stomach) to aid in the digestion of food, thanks to its sophisticated dental structure.Habitat and Distribution
Anatosaurus was native to North America and was widespread in the Western United States. Its fossilized remains have been found in states like Montana, South Dakota, and Wyoming. These areas were once part of the Western Interior Seaway, a large inland sea that existed during the Late Cretaceous period.Predatory Behavior
The Anatosaurus was a non-predatory dinosaur, without any natural defenses like sharp teeth or claws. It was most likely a herd animal, relying on its large size and strength in numbers to ward off predators. However, it is possible that juvenile Anatosaurus may have been targeted by predators like T-Rex or Albertosaurus. Scientists have also found evidence of bite marks on Anatosaurus fossils, indicating that it may have been preyed upon by these predators.Preferred Habitat and Climate
Anatosaurus lived during the Late Cretaceous period when the Earth's climate was significantly warmer than it is today. However, scientists are still unsure about the climate and temperature preferences of this dinosaur. Its fossils have been found in different environments, suggesting that it may have been adaptable and could thrive in various habitats.Speed and Locomotion
With its large body and robust hind limbs, Anatosaurus was not built for speed. Scientists estimate that it could have walked at a leisurely pace of about 5-7 miles per hour. However, it could have moved faster in short bursts if it felt threatened.Mysteries and Controversies Surrounding Anatosaurus
As with many other dinosaurs, Anatosaurus also has its share of mysteries and controversies that have puzzled scientists for years. The most significant debate revolves around its crest, which was initially thought to be hollow and filled with air, similar to that of a bird. But recent studies have revealed that it was solid, filled with keratin, the same material found in human nails and hair.Another hotly debated topic is whether Anatosaurus and Edmontosaurus, another duck-billed dinosaur, are the same species. Some paleontologists believe that they are, while others argue that there are enough differences to separate them into two distinct species.
Uncovering the Mysteries Through Technology
Thanks to advancements in technology, scientists are now able to uncover more secrets about Anatosaurus and other dinosaurs that have long been extinct. High-resolution imaging techniques have allowed them to take detailed CT scans of fossilized bones and reconstruct the internal structures with precision. Three-dimensional computer modeling has also enabled scientists to study the movement, biomechanics, and biology of these ancient creatures digitally.We have even been able to get a glimpse into their skin color and texture, thanks to fossilized skin impressions found in different species of dinosaurs. However, unfortunately, no skin impressions of Anatosaurus have been found, leaving its skin color and texture a mystery.
The Legacy of Anatosaurus
Over the years, Anatosaurus has captured the imagination of people worldwide, thanks to its unique appearance and prominent role in popular culture. It has been featured in numerous movies, TV shows, and books, fueling the curiosity of children and adults alike.But more importantly, Anatosaurus has helped paleontologists broaden their understanding of dinosaur behavior, anatomy, and evolution. Every new discovery and study of this magnificent dinosaur brings us closer to unlocking the secrets of our planet's past.
Conclusion
The Anatosaurus is undoubtedly one of the most distinctive and fascinating dinosaurs to have walked the Earth. Even though it has been over 66 million years since this giant roamed the western United States, its legacy lives on. With new discoveries and advancements in technology, we continue to delve deeper into the mysteries of Anatosaurus, uncovering more about this enigmatic creature with every step. Who knows what other secrets it holds, waiting to be revealed in the years to come.
Anatosaurus
Dinosaur Details Anatosaurus - Scientific Name: Anatosaurus
- Category: Dinosaurs A
- Scientific Name: Anatosaurus
- Common Name: Anatosaurus
- Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
- Length: 10-12 meters
- Height: 3 meters
- Weight: 4-6 tons
- Diet: Herbivore
- Feeding Behavior: Grass and leaf eater
- Predatory Behavior: Non-predatory
- Tooth Structure: Dental batteries for grinding plant material
- Native Habitat: North America
- Geographical Distribution: Western United States
- Preferred Temperature: Unknown
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown
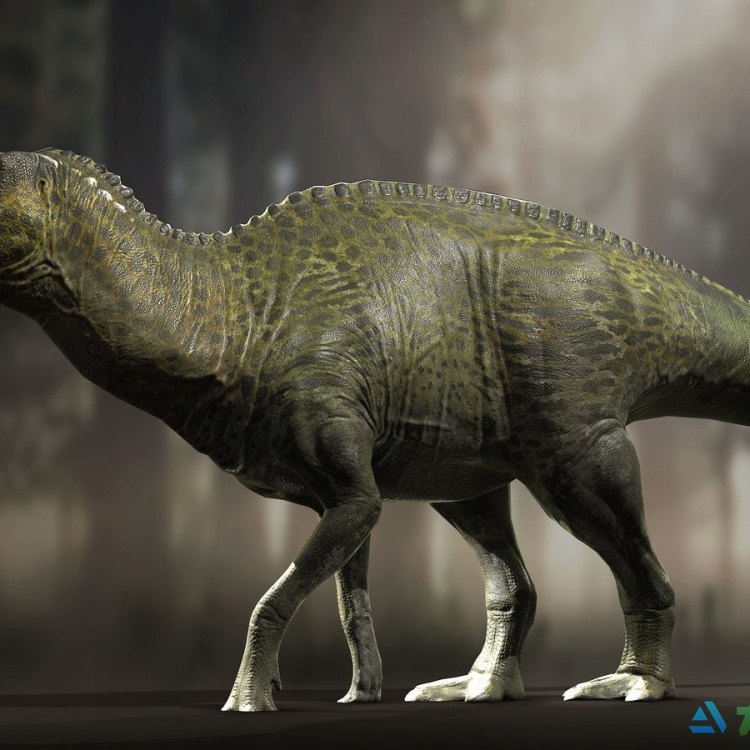

Anatosaurus
- Bone Structure: Large and robust
- Reproduction Type: Egg-laying
- Activity Period: Diurnal
- Distinctive Features: Large size and long, flat snout
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Unknown
- Largest Species: Anatosaurus copei
- Smallest Species: Anatosaurus annectens
- Fossil Characteristics: Fragmented skeletal remains
- Role in Ecosystem: Large herbivore
- Unique Facts: Anatosaurus is closely related to the dinosaur Anatotitan
- Predator Status: Non-predatory
- Discovery Location: United States
- Discovery Year: 1905
- Discoverer's Name: Barnum Brown
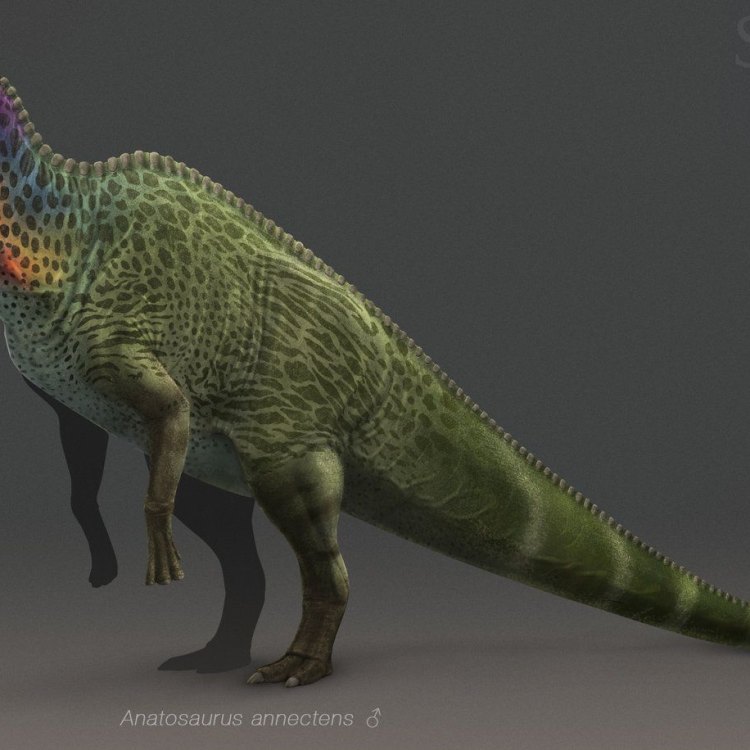

Anatosaurus
Anatosaurus: The Mighty Herbivore of the United States
In the world of prehistoric creatures, the Anatosaurus stands out as one of the largest and most distinctive herbivores. This majestic dinosaur roamed the lands of what is now the United States during the late Cretaceous period, about 65 to 66 million years ago. Its name, which means “duck lizard,” is derived from its long, flat snout that resembles that of a duck’s bill. Let's take a closer look at this fascinating creature and uncover some of its most unique features OnTimeAiraz.Com.Bone Structure and Reproduction
The Anatosaurus was a member of the Hadrosauridae family, commonly known as “duck-billed” dinosaurs. This family includes many notable species, such as the Parasaurolophus and Edmontosaurus. However, the Anatosaurus is often considered the largest of them all, measuring up to 39 feet long and weighing anywhere from 3 to 4.3 tons.The Anatosaurus’ bone structure is a clear indication of its grand size and strength. Its robust limbs and stout body were designed for supporting its massive weight. The dinosaur’s hind legs were longer and stronger than its front legs, allowing it to move with great speed and agility. This was a crucial survival adaptation, as the Anatosaurus was a large target for predators.
In terms of reproduction, the Anatosaurus was an egg-laying species, much like its counterparts Altirhinus. Unlike modern-day reptiles, however, it is believed that this dinosaur species may have cared for its young until they were able to fend for themselves. This suggests that the Anatosaurus had a level of intelligence and social behavior, making it an even more intriguing and complex creature.
Activity and Communication
The Anatosaurus was a diurnal animal, meaning it was active during the day and rested at night. This behavior is often seen amongst modern-day herbivores, as they require sunlight to digest their plant-based diet. The Anatosaurus was a large herbivore, and its diet likely consisted of a variety of vegetation, such as shrubs, leaves, and fruits.Another fascinating aspect of this dinosaur is its long, flat snout. This feature has puzzled scientists for a long time, as its purpose and function are still unknown. It is speculated that the Anatosaurus may have used its snout for digging in the ground for food or for communication purposes. However, until more evidence is uncovered, the exact communication method of this dinosaur remains a mystery.
Fossil Characteristics and Unique Facts
The Anatosaurus is well known for its fragmented skeletal remains, making it challenging for paleontologists to piece together the complete picture of this creature. Its bones were hollow, similar to modern-day birds, making them more susceptible to erosion and destruction over time. Therefore, reconstruction of the Anatosaurus relies heavily on finding enough fossil evidence to complete its skeletal structure accurately.Interestingly, the Anatosaurus and the Anatotitan are closely related species, sharing many physical characteristics. The only significant difference between the two is their size, with the Anatosaurus being the largest. This suggests that the Anatosaurus may have evolved from the Anatotitan, making it a crucial link in the evolutionary chain of the Hadrosauridae family.
Role in Ecosystem and Predator Status
The Anatosaurus played a vital role in the ecosystem of the late Cretaceous period. As a large herbivore, it had a significant impact on the vegetation of its surroundings. It is believed that the Anatosaurus may have traveled in herds, grazing on large areas of land and shaping the vegetation in the process.Despite its size, the Anatosaurus was a non-predatory species, feeding solely on plants. Its main predators were the fierce T. rex and the carnivorous Albertosaurus, both of which were known to hunt and feed on large dinosaurs like the Anatosaurus. The Anatosaurus’ main defense mechanism was its speed and agility, as well as the ability to travel in groups, making it a less appealing target for predators.
Discovery and Discoverer
The Anatosaurus was first discovered in 1905 by Barnum Brown, a renowned American paleontologist. The remains were found in the Hell Creek Formation in the state of Montana, in the United States. It was Brown’s first significant discovery as a young paleontologist, gaining him recognition and acclaim in the field.Since then, multiple specimens of the Anatosaurus have been found in various locations in the United States, including Wyoming and South Dakota. These discoveries have helped scientists gain a better understanding of the species and its impact on the ecosystem during the Cretaceous period.
The Legacy of the Anatosaurus
The Anatosaurus may have roamed the earth millions of years ago, but its legacy continue to fascinate and captivate people of all ages. Its robust bone structure, distinctive snout, and intriguing behavior make it a unique and important species in the world of paleontology.Through ongoing research and discoveries, we continue to learn more about this mighty herbivore and its role in shaping the prehistoric world. The Anatosaurus serves as a reminder of the diversity and complexity of our planet's history, and how every species, no matter how large or small, plays a crucial part in the ecosystem.
So the next time you visit a museum and see the skeletal structure of an Anatosaurus, take a moment to imagine this majestic creature roaming the lands of the United States, and appreciate its unique features that make it truly one of a kind.

The Enigmatic Anatosaurus: Uncovering the Mysteries of This Giant Dinosaur
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.