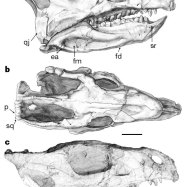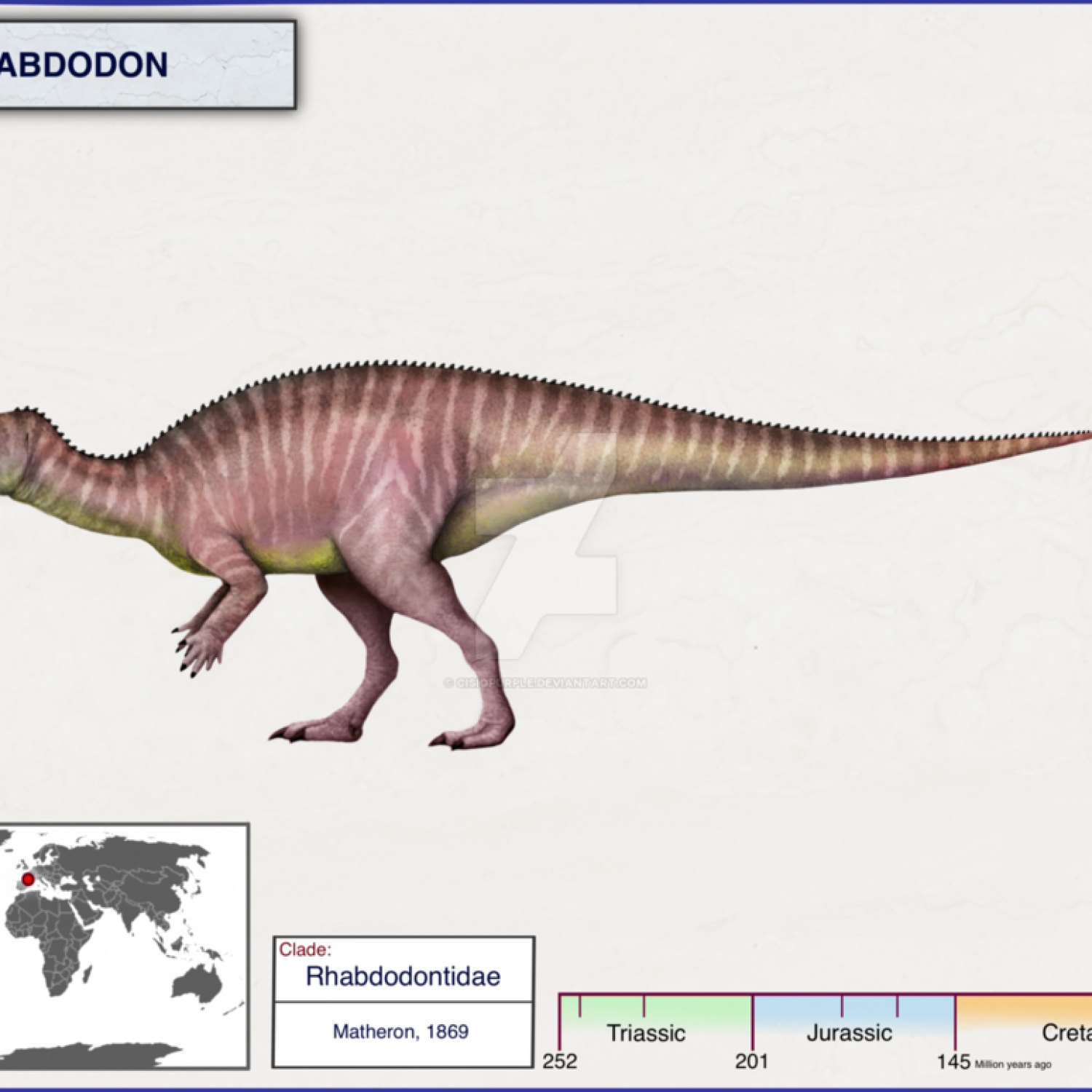
Rhabdodon
Unknown
Rhabdodon, a herbivorous dinosaur from Europe, is a lesser-known species with unknown skin color and speed. Its name means rod-toothed and it is believed to have roamed the Earth during the Cretaceous period. Despite its mysterious features, researchers continue to learn more about this fascinating creature. #Rhabdodon #dinosaurs #Europe #Cretaceous
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Rhabdodon
Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
Feeding Behavior: Browsing
The Fascinating World of Rhabdodon: A Herbivorous Giant from the Late Cretaceous Period
Welcome to the fascinating world of Rhabdodon – a name that may be unfamiliar to many, but is undoubtedly one of the most interesting and unique dinosaurs to have ever roamed the earth. With its distinctive features and intriguing behaviors, Rhabdodon is a dinosaur that deserves to be in the spotlight. In this article, we will take a deep dive into the world of Rhabdodon, exploring its scientific name, physical description, feeding and predatory behaviors, and its geographical distribution. So, buckle up and get ready to be amazed by the incredible Rhabdodon!A Prehistoric Mystery: Unveiling the Scientific Name of Rhabdodon
When it comes to scientific names, Rhabdodon may seem quite simple and straightforward Rhabdodon. But in reality, this name holds a fascinating history. It was first described in 1878 by Austrian paleontologist Ferdinand Broili, who named the dinosaur "Rhabdodon priscus." The word "Rhabdodon" is derived from the Greek words “rhabdos” which means “rod” or “staff”, and “odon” which means “tooth”. This is a reference to its unique leaf-shaped teeth, which we will discuss in detail later. The species name "priscus" comes from the Latin word for “ancient”, indicating its place in prehistory. Over the years, there have been various species of Rhabdodon discovered, but currently, only one species is officially recognized – Rhabdodon priscus.Discovering the Physical Features of Rhabdodon
Rhabdodon was a medium-sized dinosaur, measuring around 5-6 meters in length and 2 meters in height. It weighed between 1 to 2 tons, making it a relatively lightweight dinosaur compared to other herbivorous dinosaurs of its time. But don't let its size fool you – Rhabdodon was still a powerful and impressive creature Ratchasimasaurus.One of the standout physical features of Rhabdodon was its tooth structure. As mentioned earlier, Rhabdodon's name is derived from its unique leaf-shaped teeth, which were ideal for browsing on vegetation. These teeth were arranged in a precise manner, allowing it to efficiently strip leaves from branches and twigs. This indicates that Rhabdodon was a highly specialized herbivore, with a diet primarily consisting of plants.
A Peek into the Feeding and Predatory Behaviors of Rhabdodon
Rhabdodon was a browsing herbivore, which means it fed on low-lying vegetation, primarily leaves, and shoots. This is evident from its leaf-shaped teeth, which were ideal for stripping leaves and chewing plants. Its feeding behavior was also well adapted to its environment. Rhabdodon lived in a temperate climate, with a preferred temperature range of 10-15 degrees Celsius. This was the perfect temperature for plants to thrive, indicating an abundance of food for Rhabdodon to browse on.Despite its size, Rhabdodon was not a predatory dinosaur. As a herbivore, it did not possess any aggressive or predatory behaviors. Instead, it was a peaceful and docile creature, living alongside other dinosaurs and in close proximity to larger predators. This highlights that the ecosystem in which Rhabdodon lived was complex and balanced, with different species coexisting harmoniously.
Uncovering the Geographical Distribution of Rhabdodon
Rhabdodon inhabited the ancient landmass of Europe during the Late Cretaceous Period, over 65 million years ago. Its remains have been found in various countries such as France, Spain, and Romania, indicating a widespread distribution. This highlights that Rhabdodon was a successful and adaptable dinosaur, able to thrive in different environments and compete with other species for resources.The Mysteries of Rhabdodon: Unanswered Questions
Despite its well-documented physical features and behaviors, there are still some mysteries surrounding Rhabdodon. One of the biggest mysteries is its maximum speed. Unfortunately, due to a lack of evidence, we cannot accurately determine how fast Rhabdodon could move. However, we do know that it had strong and powerful hind legs, indicating that it could have been a relatively fast runner for its size.Another mystery surrounding Rhabdodon is its skin color. Unfortunately, no skin impressions have been found, making it impossible to determine its skin color. But based on its geographical distribution and preferred temperature, it is believed that Rhabdodon may have had dark or mottled skin to absorb heat and regulate its body temperature. This is a common adaptation seen in many dinosaurs that lived in temperate climates.
The Legacy of Rhabdodon: Why It Was a Standout Dinosaur
Rhabdodon may not be as well-known as some of its more famous counterparts such as the Tyrannosaurus Rex or the Triceratops, but it is undoubtedly a standout dinosaur. Its unique physical features, peaceful behavior, and broad geographical distribution have made it a crucial part of the scientific understanding of the Late Cretaceous Period. Not only that, its leaf-shaped teeth have also provided valuable information on the evolution of herbivorous dinosaurs and their feeding habits.Rhabdodon has also captured the imagination and interest of paleontologists, who continue to uncover more information about this enigmatic dinosaur. Its discovery has opened up a world of possibilities and sparked further research into the prehistoric world of dinosaurs.
In Conclusion
Rhabdodon is a dinosaur that may not have the same level of popularity as some of its more famous counterparts, but it is undoubtedly a fascinating and unique creature. From its leaf-shaped teeth and peaceful behavior to its widespread distribution and unanswered questions, Rhabdodon continues to intrigue and baffle scientists and enthusiasts alike. Its legacy lives on, and it will forever remain a standout dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Period.
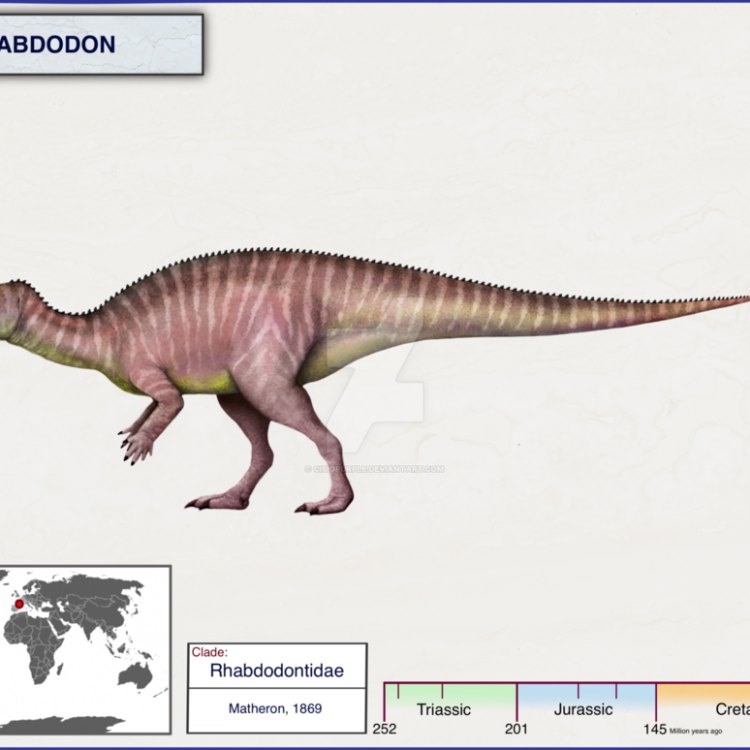
Rhabdodon
Dinosaur Details Rhabdodon - Scientific Name: Rhabdodon
- Category: Dinosaurs R
- Scientific Name: Rhabdodon
- Common Name: Rhabdodon
- Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
- Length: 5-6 meters
- Height: 2 meters
- Weight: 1-2 tons
- Diet: Herbivore
- Feeding Behavior: Browsing
- Predatory Behavior: Non-predatory
- Tooth Structure: Leaf-shaped teeth
- Native Habitat: Terrestrial
- Geographical Distribution: Europe
- Preferred Temperature: Temperate
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown
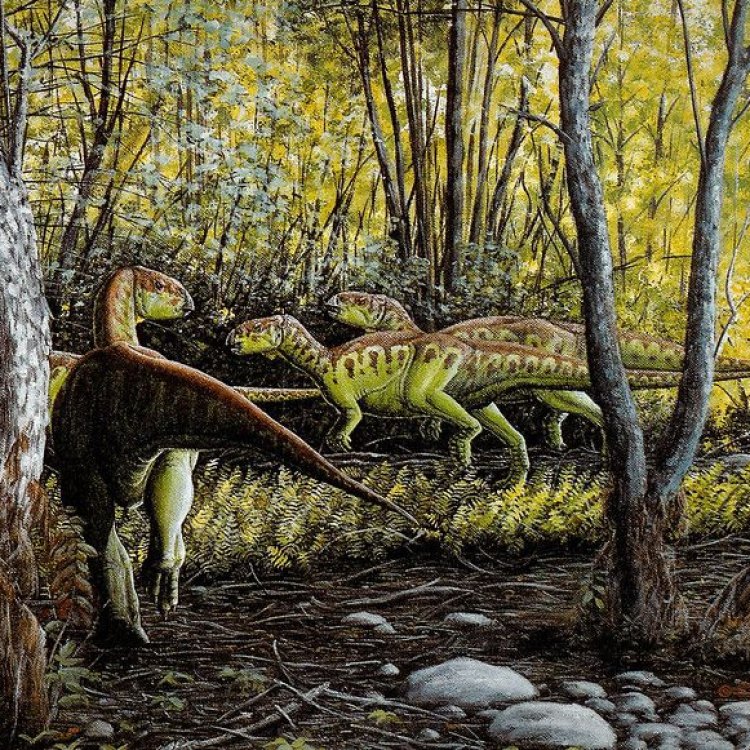

Rhabdodon
- Bone Structure: Lightweight bones
- Reproduction Type: Egg-laying
- Activity Period: Diurnal
- Distinctive Features: Large thumb claws
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Unknown
- Largest Species: Unknown
- Smallest Species: Unknown
- Fossil Characteristics: Partial skeletons and isolated bones
- Role in Ecosystem: Plant seed dispersal
- Unique Facts: Possessed a large claw on each hand
- Predator Status: Non-predator
- Discovery Location: Europe
- Discovery Year: 1879
- Discoverer's Name: Emmanuel Bunzel
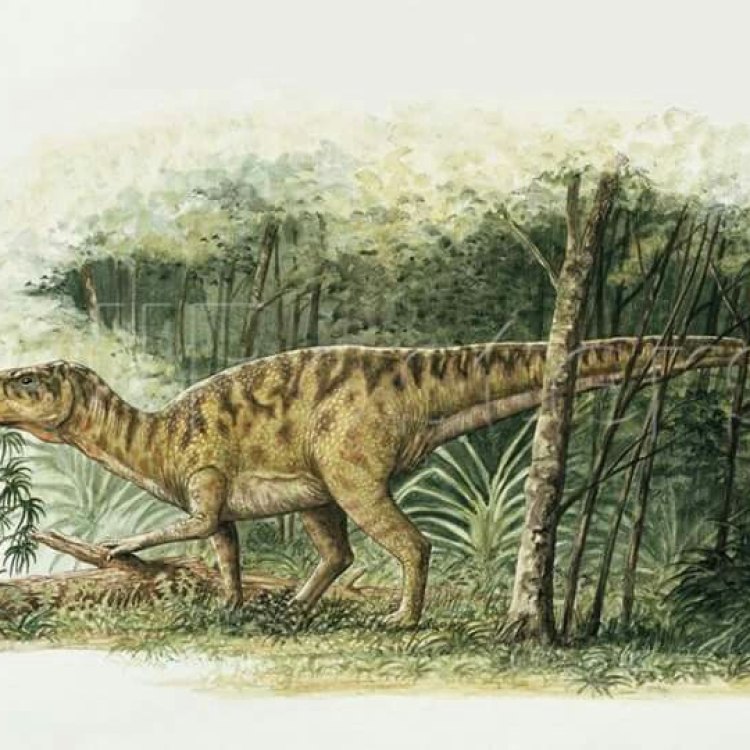

Rhabdodon
The Surprising and Unique Features of Rhabdodon: The Egg-Laying Dinosaur with Large Thumb Claws
When we think of dinosaurs, we often envision fearsome creatures with sharp teeth and large, powerful bodies. But not all dinosaurs fit into this stereotype. Meet Rhabdodon, a lesser-known dinosaur with some truly surprising and unique features.Discovered in 1879 by paleontologist Emmanuel Bunzel, Rhabdodon is a genus of herbivorous dinosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous period, approximately 75 million years ago OnTimeAiraz.Com. It belongs to a group of dinosaurs known as iguanodonts, which were characterized by their beaked mouths and hoofed feet. However, what sets Rhabdodon apart from other iguanodonts are its distinctive features and adaptations, which still leave scientists puzzled today.
In this article, we will delve into the world of Rhabdodon and uncover its fascinating bone structure, reproduction method, activity period, communication methods, and more. From its lightweight bones to its large thumb claws, Rhabdodon proves to be a truly unique and intriguing dinosaur species.
Bone Structure: Lightweight and Strangely Shaped Bones
One of the most distinctive features of Rhabdodon is its lightweight bone structure. Unlike other dinosaurs, which had thick and heavy bones, Rhabdodon's bones were light and hollow, resembling the structure of modern birds.This bone structure was advantageous for Rhabdodon in several ways. First, being lightweight meant the dinosaur could move around more quickly and efficiently, making it easier to escape predators. Second, it allowed Rhabdodon to have a larger lung capacity, enabling it to take in more oxygen and have more stamina Rinconsaurus. Finally, the lightweight bones also made Rhabdodon a less desirable prey for predators, as its flesh would not provide as much sustenance as larger and heavier dinosaurs.
But perhaps the most intriguing aspect of Rhabdodon's bone structure is its unusual shape. Unlike other herbivorous dinosaurs, Rhabdodon had a narrow pelvis and long hind legs, making it more similar to bipedal predators like Velociraptors. This unique shape suggests that Rhabdodon may have been a fast runner, using its long legs to outrun potential threats.
Reproduction Type: Egg-Laying and Life Cycle
Another unique aspect of Rhabdodon is its reproductive methods. Like most dinosaurs, Rhabdodon was an egg-laying species. It is believed that the female dinosaur would lay her eggs in a nest, most likely in a soft area on the ground, and then protect and incubate them until they hatched. This behavior is similar to modern-day birds, which also lay their eggs in nests.However, what makes Rhabdodon's reproductive cycle even more fascinating is the discovery of a potential life cycle. In 2014, a study by researchers from the Autonomous University of Barcelona analyzed the growth lines in Rhabdodon's bones and found evidence of a prolonged growth period. This suggests that Rhabdodon may have had a slow growth rate, which is often seen in long-lived animals.
This finding leads to the theory that Rhabdodon may have had a complex and unique life cycle, much like modern-day reptiles. The young Rhabdodon may have had different dietary needs and behaviors than the adults, and it is possible that they even had different physical appearances. This discovery highlights the complexity and diversity of dinosaurs and their life cycles, challenging the commonly held notion that they were all the same.
Activity Period: Diurnal and Social Species
While some dinosaurs were nocturnal, Rhabdodon is believed to have been a diurnal species, meaning it was active during the day. This is supported by its large eye sockets, which indicate that it had well-developed vision and relied on daylight to navigate and forage for food.In addition to being diurnal, Rhabdodon is also thought to have been a social species. This is based on the discovery of multiple Rhabdodon skeletons in the same location, suggesting that they may have lived and traveled in herds. This social behavior is rarely seen in herbivorous dinosaurs, making Rhabdodon stand out even more.
Distinctive Features: Large Thumb Claws and Mysterious Communication
One of the most distinguishing features of Rhabdodon is its large thumb claws. These claws were much larger than those of other dinosaurs and were similar in size to the claws of the meat-eating Velociraptor. This has led to the theory that Rhabdodon may have used its large claws for defense against predators or for fighting with other members of its species.Another intriguing aspect of Rhabdodon is its unknown communication methods. While some dinosaurs are believed to have made vocalizations, such as roars or honks, it is still unclear how Rhabdodon communicated. It is possible that it used visual signals, such as body postures or displays, to communicate with other members of its species. However, more research is needed to fully understand how Rhabdodon communicated with its fellow dinosaurs.
Survival Adaptation: A Mystery Yet to Be Solved
While we know some of the unique features and behaviors of Rhabdodon, there is still much to uncover about this mysterious dinosaur. One of the biggest questions that remain is what survival adaptations did Rhabdodon possess? As a non-predator, Rhabdodon did not have any obvious defense mechanisms, such as sharp teeth or strong jaws.One theory suggests that Rhabdodon may have used its long legs and large claws to escape and defend itself against predators. However, this does not fully explain how Rhabdodon survived in a world filled with monstrous predators. So, the mystery of Rhabdodon's survival adaptations remains unsolved, leaving room for future research and discoveries.
Largest and Smallest Species: An Unknown Statistic
One significant challenge when studying Rhabdodon is the fact that there is still so much we do not know about this dinosaur. In fact, its largest and smallest species are still unknown. While there have been several discoveries of Rhabdodon fossils, most of them are incomplete, making it challenging to accurately estimate the size of this dinosaur.One of the most complete Rhabdodon skeletons found to date was discovered in Spain in 1995 by the Museu de la Conca Dellà de Isona. This skeleton, named "MiquelCrusafontia," revealed that Rhabdodon may have reached up to 4.5 meters in length, making it a medium-sized dinosaur. However, this is only an estimation, and it is possible that larger or smaller species of Rhabdodon have yet to be discovered.
Fossil Characteristics: Partial Skeletons and Isolated Bones
Rhabdodon fossils have been found in various locations across Europe, including France, Belgium, Spain, and Romania. Most of these fossils consist of partial skeletons or isolated bones, making it challenging to piece together the complete picture of this dinosaur. However, even with these incomplete fossils, scientists have been able to learn a great deal about Rhabdodon and its unique features.Some of the most common fossils found include teeth, limb bones, and vertebrae. These findings, along with the analysis of fossils from similar dinosaurs, have revealed that Rhabdodon had a beak-like mouth, hoofed feet, and a long tail. However, some of the most intriguing fossils found are the large thumb claws, which have baffled scientists and sparked many questions about the behavior and abilities of Rhabdodon.
Role in Ecosystem: Plant Seed Dispersal
Despite its small size and lack of defense mechanisms, Rhabdodon played a significant role in its ecosystem. As a herbivorous species, it primarily fed on plants, which makes it a vital link in the food chain. But it is not just this role as a plant-eater that makes Rhabdodon important; it is also its role in plant seed dispersal.Rhabdodon's diet consisted of various plants, including cycads, conifers, and ferns. When the dinosaur ate these plants, it also ingested their seeds. As it moved around and eventually fertilized, the seeds would be deposited in different locations, helping to disperse the plants and promote growth and diversity in the ecosystem.
Unique Facts: Large Claws and Name Meaning
Lastly, let's explore some unique and fun facts about Rhabdodon. We have already discussed its impressive large claws, but did you know that Rhabdodon is the only dinosaur to possess a large claw on each hand? This makes it stand out even among its dinosaur counterparts, with many researchers still baffled by the purpose of these large claws.Another interesting fact is the meaning behind Rhabdodon's name. The word "Rhabdodon" comes from the Greek words "rhabd" (rod) and "odon" (tooth), referring to the rod-like shape of its teeth. This name was given by Louis Dollo, a Belgian paleontologist who studied the dinosaur in the early 1900s.
In Conclusion
In conclusion, Rhabdodon is a lesser-known yet fascinating dinosaur species with many unique features and behaviors that still puzzle scientists today. From its lightweight bone structure and large thumb claws to its diurnal activity and social behaviors, Rhabdodon proves to be a truly
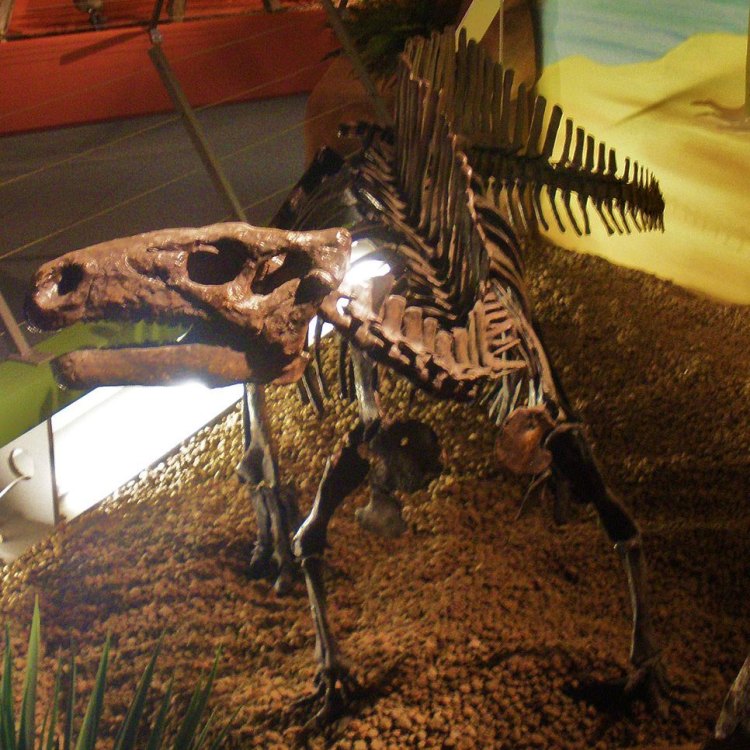

The Fascinating World of Rhabdodon: A Herbivorous Giant from the Late Cretaceous Period
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.