Liaoceratops
Unknown
Discover the Liaoceratops, a lesser-known dinosaur from China. Its unique features, such as skin color and diet, make it a fascinating herbivore. Despite not knowing its maximum speed, it's still worthy of being added to your dinosaur knowledge. #dinosaurfacts #Chinadinosaur #Liaoceratops
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Liaoceratops
Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
Feeding Behavior: Grazing
Liaoceratops: Uncovering the Secrets of a Little-known Dinosaur
In the world of dinosaurs, there are big names that capture our imagination – Tyrannosaurus Rex, Stegosaurus, and Triceratops, to name a few. But there are also lesser-known species that are equally fascinating and significant in understanding the evolution of these ancient creatures. One such dinosaur is Liaoceratops, a small herbivore from the Late Cretaceous period that roamed the woodlands of China. Despite its size and relatively unknown status, Liaoceratops has a unique story to tell, and researchers are eager to uncover its secrets and piece together the puzzle of its existence Liaoceratops.The Discovery of Liaoceratops
Liaoceratops was first discovered in the Liaoning Province of China in 2007, by a team of Chinese and Japanese paleontologists. The team was excavating a quarry known for its rich fossil bed, when they stumbled upon a small, nearly complete skeleton of a previously unknown dinosaur species. It was unlike any other dinosaur they had seen before, and they knew it was something special. The discovery was initially kept under wraps to prevent poaching and damage to the site, but as further research was conducted, the world soon became aware of this unique dinosaur – Liaoceratops.Physical Characteristics
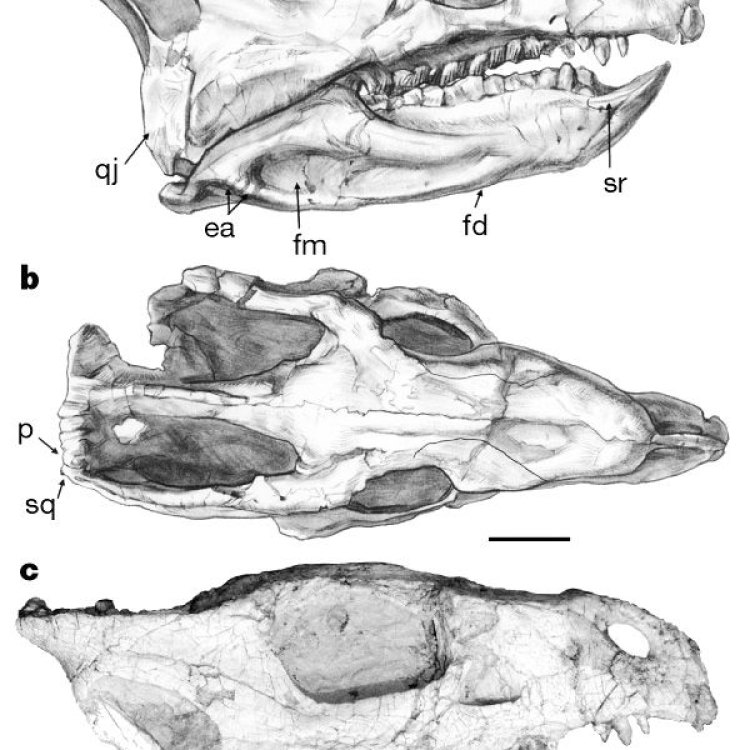
Liaoceratops was a small dinosaur, with a length of around 2.5 meters, a height of 1 meter, and a weight of 100 kilograms. Its body was compact and low to the ground, making it resemble a mini version of its more famous relative, Triceratops. However, unlike Triceratops, Liaoceratops had three horns on its face, with the two horns above its eyes being significantly smaller than the one on its snout. These horns, along with its parrot-like beak, gave Liaoceratops a distinctive appearance Lagosuchus. It also had a bony frill on the back of its head, which was believed to have been used for display purposes or protection.One of the most striking features of Liaoceratops was its tooth structure. Unlike other dinosaurs that had a variety of tooth shapes and sizes, Liaoceratops had uniform, leaf-shaped teeth. This indicates that it was adapted for a specific diet – grazing on vegetation. This discovery was crucial in understanding the feeding behavior of this dinosaur.
Feeding and Predatory Behavior
As mentioned earlier, Liaoceratops was a herbivore and primarily fed on plants. It had a beak and leaf-shaped teeth, which would have been ideal for chewing and breaking down tough vegetation. Its small size and light weight further suggest that it probably had a limited diet and needed to graze constantly to sustain itself.However, what makes Liaoceratops stand out from other dinosaurs is its non-predatory behavior. Most small dinosaurs were either preyed upon by larger carnivorous dinosaurs or took on a predatory role themselves. But Liaoceratops seemed to have adapted to a more peaceful coexistence with other dinosaurs. Coming from a time when the ecosystem was dominated by fearsome predators, this non-predatory nature of Liaoceratops raises many questions about its behavior and survival tactics.
Habitat and Distribution
Liaoceratops was a native of the woodlands of China, specifically the Liaoning Province in northeastern China. During the Late Cretaceous period, this area was covered in lush green forests, providing a perfect habitat for herbivorous dinosaurs like Liaoceratops. The discovery of Liaoceratops adds to the growing list of dinosaur species found in the Liaoning Province, which is known for its high concentration of dinosaur fossils.The geographical distribution of Liaoceratops was limited to this region, and it is not yet known if it existed in other parts of the world. However, given that its fossils were found in a quarry that is still being excavated, there is a possibility of finding more specimens, which could shed light on its distribution and migration patterns.
Climate and Adaptations
During the Late Cretaceous period, the Earth had a warmer climate than it has today. However, the Liaoning Province of China experienced moderate temperatures, which would have been favorable for the survival of Liaoceratops.Being a herbivore, Liaoceratops would have needed to consume a large amount of vegetation to sustain itself. The areas it inhabited were known for their diverse plant life, including ferns, cycads, and conifers, which would have provided a variety of food options for this dinosaur. Its compact size and lightweight body also suggest that it was well adapted to move around in its habitat, making the most of the resources available.
The Importance of Liaoceratops
While Liaoceratops may not be as well-known as its larger, more famous relatives, it still holds immense significance in the world of paleontology. Its unique adaptations and behaviors provide valuable insights into the diversity of dinosaurs and the complex ecosystem they inhabited. It also adds to our understanding of the evolutionary process and the role herbivorous dinosaurs played in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem.Moreover, the discovery of Liaoceratops serves as a reminder that there is still much to uncover about the fascinating world of dinosaurs. As technology and techniques in paleontology continue to advance, we can expect to unearth more secrets and fill in the gaps in our understanding of these ancient creatures.
The Future of Liaoceratops
Currently, there is only one known specimen of Liaoceratops, which is housed at the Jinzhou Paleontological Museum in China. However, with ongoing excavations in the Liaoning Province, there is a possibility of finding more specimens in the future. These future discoveries could provide a better understanding of the physical characteristics, behavior, and habitat of this little-known dinosaur.In addition to further research on the existing specimen, scientists are also using advanced imaging techniques such as CT scanning to study the internal structure of Liaoceratops. This could reveal more about its biology, such as its growth and reproductive patterns, and potentially answer some of the questions surrounding its non-predatory behavior.
In Conclusion
Liaoceratops may be a lesser-known species in the world of dinosaurs, but its discovery has made a significant impact in our understanding of these ancient creatures. Its unique features and behaviors have raised intriguing questions and provided valuable insights into the diversity and evolution of dinosaurs. As research on this fascinating little dinosaur continues, we can expect to uncover even more secrets and further expand our knowledge of the prehistoric world.
Liaoceratops
Dinosaur Details Liaoceratops - Scientific Name: Liaoceratops
- Category: Dinosaurs L
- Scientific Name: Liaoceratops
- Common Name: Liaoceratops
- Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
- Length: 2.5 meters
- Height: 1 meter
- Weight: 100 kilograms
- Diet: Herbivore
- Feeding Behavior: Grazing
- Predatory Behavior: Non-predatory
- Tooth Structure: Leaf-shaped
- Native Habitat: Woodlands
- Geographical Distribution: China
- Preferred Temperature: Moderate
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown

Liaoceratops
- Bone Structure: Unknown
- Reproduction Type: Unknown
- Activity Period: Unknown
- Distinctive Features: Small size and horned frill on the skull
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Unknown
- Largest Species: Liaoceratops yanzigouensis
- Smallest Species: Unknown
- Fossil Characteristics: Partial skull and postcranial remains
- Role in Ecosystem: Unknown
- Unique Facts: One of the earliest known ceratopsians
- Predator Status: Non-predatory
- Discovery Location: Yangmingzi Formation
- Discovery Year: 2007
- Discoverer's Name: Xu Xing

Liaoceratops
The Enigmatic Liaoceratops: Unraveling the Mysteries of a Prehistoric Ceratopsian
It was 2007 when paleontologist Xu Xing made a groundbreaking discovery in the Chinese province of Liaoning. In the Yangmingzi Formation, among the layers of fossilized bones, he unearthed the remains of a strange creature. This creature, with its small size and strange horned frill on its skull, was unlike any other known species. Named after its discovery location, it was called Liaoceratops OnTimeAiraz.Com.Since then, Liaoceratops has remained a mystery, with many aspects of its biology and behavior still being unknown. However, this enigmatic ceratopsian has also provided valuable insights into the early evolution of one of the most famous dinosaur groups – the horned dinosaurs or ceratopsians. In this article, we will delve into the unique features of Liaoceratops and explore its role in the prehistoric ecosystem.
Unknown Bone Structure and Reproduction
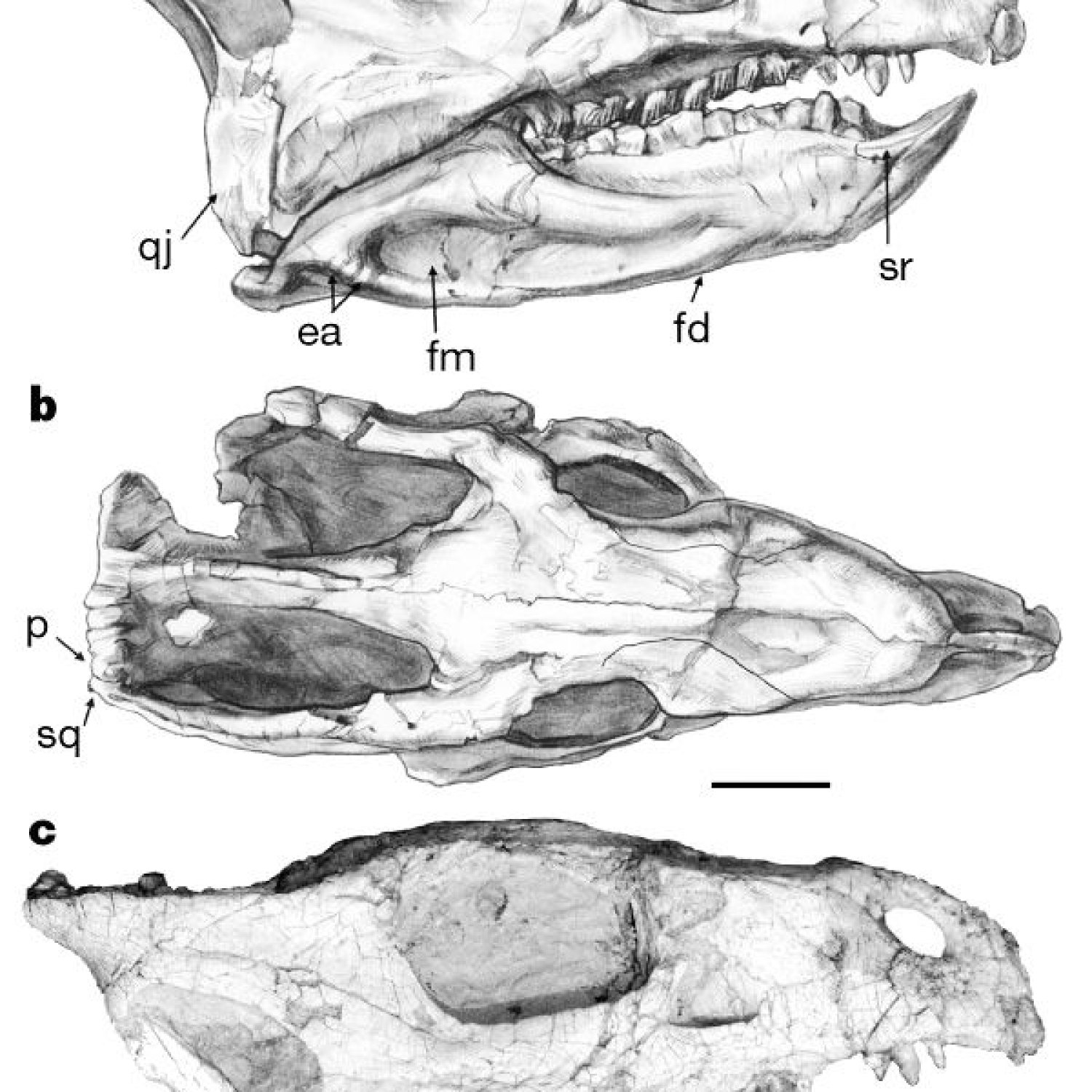
The first notable aspect of Liaoceratops is the lack of information about its bone structure and reproduction. Unlike many other dinosaur species, where extensive fossil evidence has provided insights into their anatomy and reproductive behaviors, this is not the case for Liaoceratops. The only known remains of Liaoceratops are a partial skull and some postcranial bones, which do not provide enough information to determine these aspects of its biology.
Experts believe that this lack of fossil evidence could be due to the fragility of the Liaoning sediments, which may have led to the poor preservation of bones. Therefore, without further fossil discoveries, we may never know the full extent of Liaoceratops’s bone structure and reproductive methods.
Activity Period and Communication Method: Still a Mystery
Another essential aspect that remains a mystery about Liaoceratops is its activity period and communication method Lambeosaurus. As with many other dinosaur species, most information about their behavior and habits comes from studying their fossilized remains. However, due to the limited number of Liaoceratops fossils, little is known about its daily activities or how it communicated with other members of its species.
However, based on its small size and physical features, experts speculate that Liaoceratops was most likely an active diurnal (daytime) creature. Its small size may have allowed it to move quickly, making it an adept runner and forager. As for its communication, it is believed that it may have used visual displays, such as the horned frill on its skull, to communicate with other members of its species.
Distinctive Features: Small Size and Horned Frill
One of the most distinctive features of Liaoceratops is its small size. With a length of only 1.1 meters (3.6 feet) and a weight of about 20 kg (44 lbs), it is one of the smallest known ceratopsians. This tiny size sets it apart from its larger and more well-known relatives, such as Triceratops and Styracosaurus, which could reach lengths of up to 9 meters (30 feet).
Another distinctive feature of Liaoceratops is the unique horned frill on its skull. While other ceratopsians also have horned frills, Liaoceratops’s frill is smaller and more curved than those of its relatives. This feature has prompted experts to speculate that it may have served a different purpose, such as display or defense, compared to other ceratopsians with larger and more triangular frills.
Survival Adaptation: Unknown but Successful
Without much information about its behavior, it is challenging to determine what survival adaptations Liaoceratops may have had. However, its small and agile body size may have allowed it to evade predators and find food efficiently. It may have also had sharp teeth and a beaked jaw, similar to other herbivorous dinosaurs, which would have helped it eat tough vegetation.
Additionally, experts suggest that Liaoceratops may have lived in herds, a common survival adaptation for many herbivorous dinosaurs. Being part of a group would have provided protection from predators and ensured a steady food supply. However, without further fossil evidence, we can only speculate about the particular survival adaptations of Liaoceratops.
Liaoceratops yanzigouensis: The Largest Known Species
While we do not know much about the various species of Liaoceratops, we do know that the largest known species is Liaoceratops yanzigouensis. Discovered in the same formation as Liaoceratops in 2007, this species had a larger skull, measuring about 18 cm (7 inches) in length, and was believed to have been around 1.5 meters (5 feet) in length.
However, as mentioned earlier, the limited number of fossilized remains of Liaoceratops makes it difficult to determine the exact size and characteristics of other species. Therefore, it is possible that there may have been other larger species of Liaoceratops that have yet to be discovered.
Partial Skull and Postcranial Remains: Unique Fossil Characteristics
The fossilized remains of Liaoceratops that were uncovered in 2007 were just a partial skull and some postcranial bones. This limited fossil evidence has made it challenging for experts to fully understand the biology and behavior of Liaoceratops.
However, the partial skull and postcranial bones are still considered a unique fossil characteristic of Liaoceratops. The bones are rich in detail, and the skull fragments provide a glimpse into the skull’s shape and unique features, such as the curved horned frill. Without these fossils, our understanding of this enigmatic ceratopsian would be even more limited.
One of the Earliest Known Ceratopsians
One of the most significant contributions of Liaoceratops to the scientific community was its role in helping us better understand the early evolution of ceratopsians. It is believed to have lived during the late Jurassic period, approximately 161–145 million years ago. This makes it one of the earliest known ceratopsians, with its discovery providing valuable insights into the emergence and diversification of this diverse group of dinosaurs.
Non-Predatory Status: A Friendly Herbivore
Based on its small size, physical features, and lack of sharp claws or teeth, it is believed that Liaoceratops was a non-predatory herbivore. Instead of hunting or scavenging for food, it would have spent its days foraging for plants and avoiding larger predators. Its unique horned frill may have also served as a defensive mechanism, some scientists speculate.
Discovery Location and Year: The Beginning of a New Era
The discovery of Liaoceratops in 2007 marked the beginning of a new era in paleontology. The Liaoning Province in China has become famous for its fossil-rich formations, with discoveries of numerous new species, including the famous feathered dinosaurs. In the past two decades, over 30 new feathered dinosaur species have been unearthed in the province, along with many other significant discoveries.
Discoverer’s Name: Xu Xing – A Legendary Paleontologist
Renowned paleontologist Xu Xing is credited with the 2007 discovery of Liaoceratops. Based at the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology in China, Xu Xing is one of the most influential and prolific paleontologists in the world. He has discovered dozens of feathered dinosaur species, including the feathered tyrannosaur Yutyrannus and the bird-like Anchiornis. Xu Xing’s discoveries have transformed our understanding of the early evolution of birds and dinosaurs.
Conclusion
The Liaoceratops remains an enigmatic and fascinating dinosaur, with many aspects of its biology and behavior still being unknown. However, this small ceratopsian has also provided valuable insights into the early evolution of horned dinosaurs and has played a significant role in the scientific community. With the ongoing research and discoveries in Liaoning Province, there is no doubt that Liaoceratops will continue to reveal its secrets and add to our understanding of the prehistoric world.

Liaoceratops: Uncovering the Secrets of a Little-known Dinosaur
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.