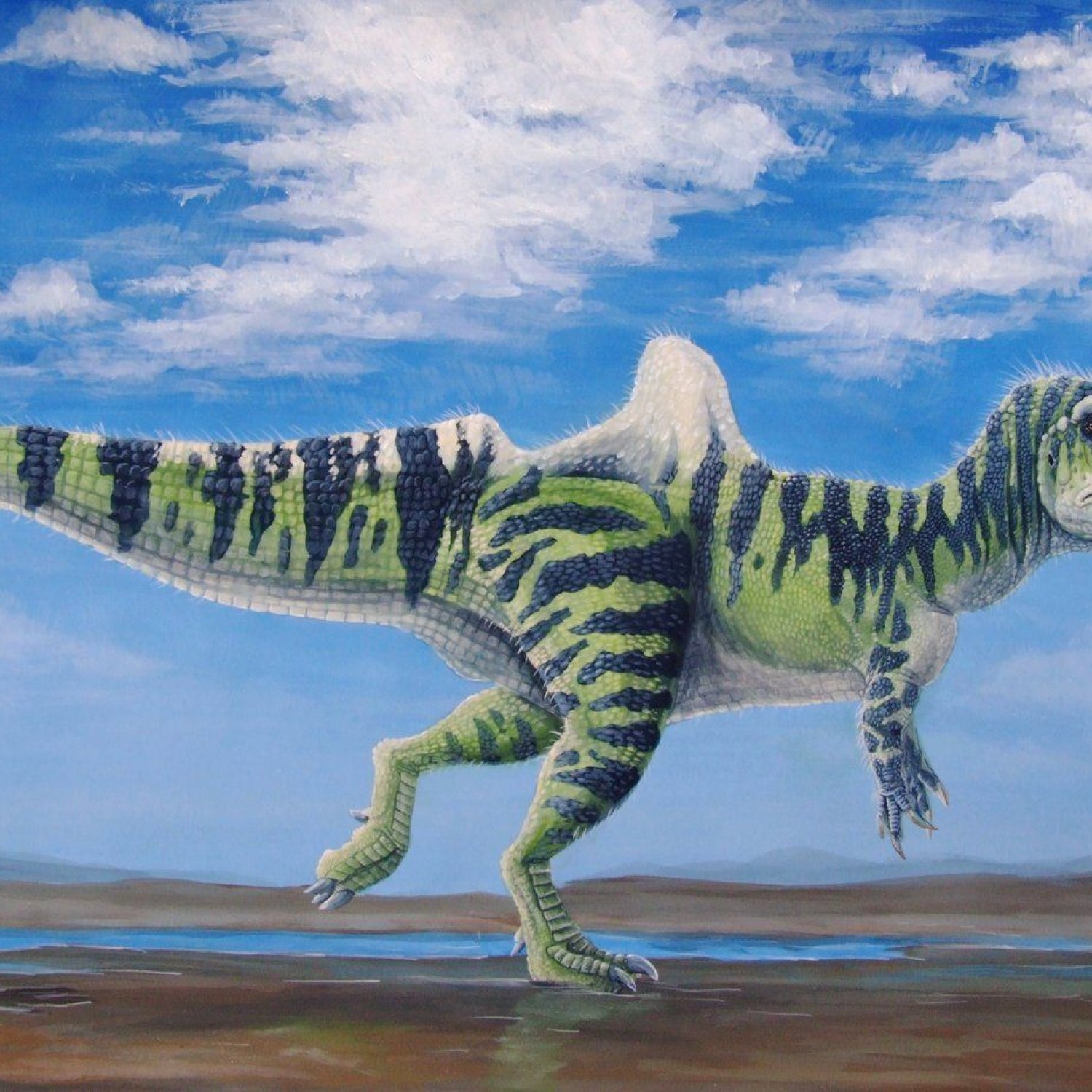
Becklespinax
Unknown
Discover the fierce Becklespinax - a mysterious carnivorous dinosaur from Europe with an unknown skin color and maximum speed. Uncover its secrets and add it to your list of fascinating dinosaurs. #Becklespinax #Dinosaurs #Carnivore #Europe
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Becklespinax
Geological Era: Early Cretaceous
Feeding Behavior: Active predator
The Fascinating Becklespinax: Unearthing Europe's Fierce Carnivore of the Early Cretaceous
The earth's past is filled with awe-inspiring creatures, and one of the most intriguing among them is the Becklespinax. ThisIntroduction to Becklespinax
Becklespinax, also known as "Bexley Spined Lizard," is aPhysical Characteristics of Becklespinax
Based on fossil findings, Becklespinax was estimated to be around 6 to 7 meters in length and stood at a height of about 2 meters. It weighed approximately 1,000 kilograms, making it a medium-sized predator compared to otherOne of the most distinctive features of Becklespinax is its spines, which are believed to have extended from its hip to its tail. The purpose of these spines is still unknown, but scientists speculate that they may have been for display or protection. Its head was small with a narrow snout, and its mouth was filled with sharp, serrated teeth, a common characteristic of theropods.
Diet and Feeding Behavior
Becklespinax was undoubtedly a fierce predator, and its diet mainly consisted of smaller dinosaurs and other animals Bagaraatan. Its sharp, serrated teeth were perfect for tearing through flesh and rending its prey. It was an active predator, meaning it hunted during the day, using its strong hind legs to chase down its prey. Scientists also speculate that Becklespinax may have hunted in packs, a predatory behavior common among theropods.Native Habitat and Geographical Distribution
Becklespinax was a terrestrial dinosaur, which means it lived and hunted on land. Its fossils have been found in various locations in Europe, including England, France, and Germany, indicating a widespread distribution throughout the continent. During the Early Cretaceous period, Europe had a temperate climate, and Becklespinax thrived in this environment.Preferred Temperature and Speed
As mentioned earlier, Europe during the Early Cretaceous had a temperate climate, which was suitable for the survival of Becklespinax. The temperatures were not extreme, making it a comfortable and habitable environment for this fierce predator. As for its speed, there is no concrete evidence to determine its maximum speed. However, based on its body structure, it is believed that Becklespinax was a fast runner and could catch its prey with ease.Unknown Aspects of Becklespinax
Despite numerous fossil findings, there are still many unknown aspects about Becklespinax. Some of these include its skin color and its maximum speed, which we have already discussed. But there are also other mysteries surrounding this creature, such as the purpose of its spines and its behavior in terms of social interaction. These unanswered questions only add to the intrigue and fascination surrounding Becklespinax.Conclusion
Unearthing the world of Becklespinax takes us on a journey to the past, where we can imagine this fierce predator roaming the lands of Europe. With its unique features, hunting behavior, and widespread distribution, Becklespinax is undoubtedly an intriguing and significant dinosaur of the Early Cretaceous period. Although many aspects of this creature are still shrouded in mystery, studying its fossils has provided us with a glimpse into the prehistoric world and reminded us of the rich and diverse creatures that once inhabited our planet. Next time you take a walk in the European countryside, imagine the Becklespinax in its natural habitat, and let the awe and wonder of this remarkable dinosaur fill you.
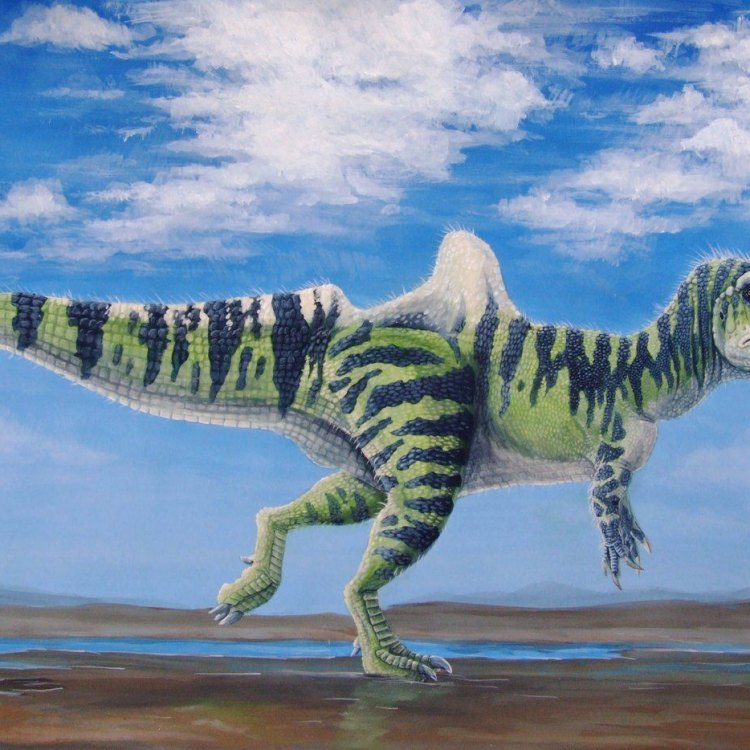

Becklespinax
Dinosaur Details Becklespinax - Scientific Name: Becklespinax
- Category: Dinosaurs B
- Scientific Name: Becklespinax
- Common Name: Becklespinax
- Geological Era: Early Cretaceous
- Length: about 6 to 7 meters
- Height: about 2 meters
- Weight: about 1,000 kilograms
- Diet: Carnivorous
- Feeding Behavior: Active predator
- Predatory Behavior: Hunting in packs
- Tooth Structure: Sharp, serrated teeth
- Native Habitat: Terrestrial
- Geographical Distribution: Europe
- Preferred Temperature: Temperate
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown
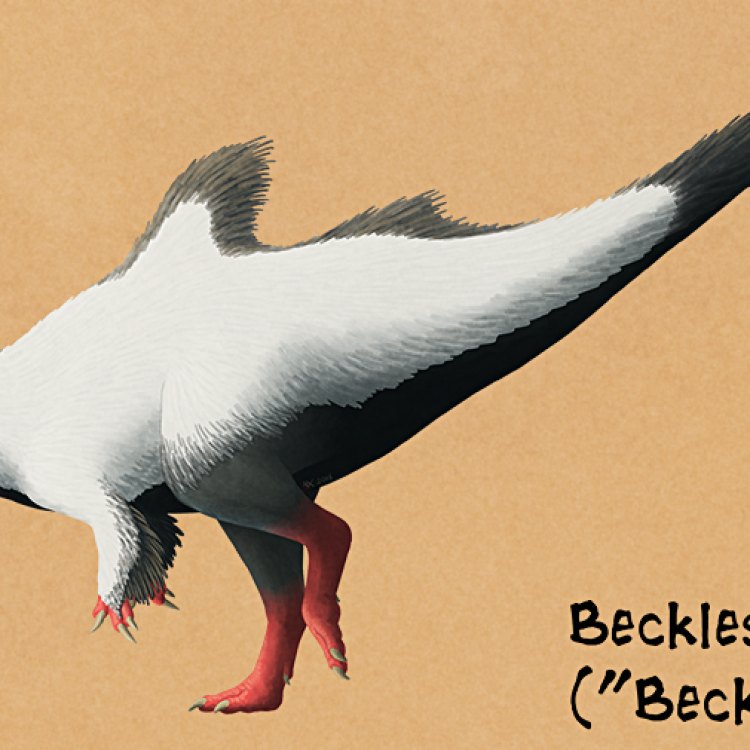

Becklespinax
- Bone Structure: Unknown
- Reproduction Type: Unknown
- Activity Period: Diurnal
- Distinctive Features: Long, slender body with a short tail and large, grasping hands
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Unknown
- Largest Species: Becklespinax altispinax
- Smallest Species: Unknown
- Fossil Characteristics: Fragmentary remains, including vertebrae and limb bones
- Role in Ecosystem: Top predator
- Unique Facts: May have had a sail or hump on its back for display or thermoregulation
- Predator Status: Extinct
- Discovery Location: England
- Discovery Year: 1984
- Discoverer's Name: Richard Owen
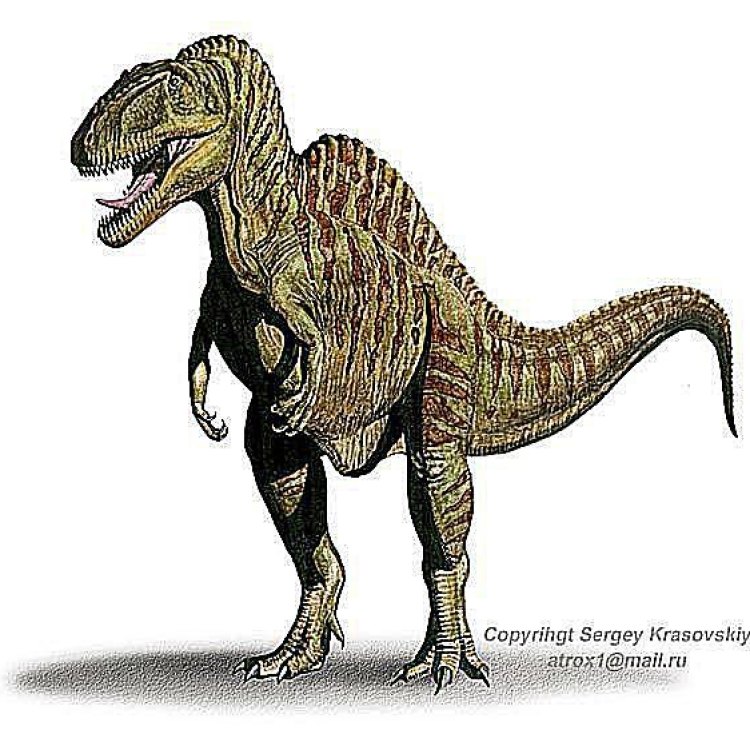
Becklespinax
The Enigmatic Becklespinax: Uncovering the Secrets of a Mysterious Dinosaur
Dinosaurs have always captured the imaginations of people of all ages. From the towering Tyrannosaurus Rex to the horned Triceratops, these prehistoric creatures continue to fascinate us. But among the well-known and popular dinosaurs, there are some that remain shrouded in mystery. One such dinosaur is the enigmatic Becklespinax OnTimeAiraz.Com.Discovered in England in 1984 by Richard Owen, an English biologist and paleontologist, Becklespinax is a dinosaur that has intrigued scientists since its discovery. However, due to limited fossil remains and other factors, there is still much that remains unknown about this ancient giant.
In this article, we will delve into the world of Becklespinax, uncovering the little-known facts about this intriguing dinosaur and trying to piece together the puzzle of its existence.
Bone Structure and Reproduction
One of the most frustrating aspects of studying Becklespinax is the lack of information about its bone structure. While the exact bone structure of this dinosaur remains unknown, scientists have been able to speculate based on its physical features and other related species.
Becklespinax is thought to have had a long, slender body, much like that of its close relative, the carnivorous dinosaur, Allosaurus. It had a short tail and large, grasping hands, indicating it was likely a bipedal predator. Its hind limbs were also long and powerful, suggesting it was a very efficient runner.
The reproductive behavior of Becklespinax is also unknown Batyrosaurus. Scientists have not yet discovered any eggs or nests associated with this dinosaur, making it difficult to determine its reproductive type. However, based on related species, it is believed that Becklespinax was an egg-laying animal.
Diurnal Activity and Communication Method
Becklespinax is speculated to have been diurnal, meaning that it was active during the daytime. This is supported by its large eyes, which would have provided it with excellent vision during daylight hours. This also suggests that Becklespinax may have been a predator that actively hunted its prey.
Another aspect of Becklespinax that remains a mystery is its communication method. Some scientists believe that it may have used visual displays or vocalizations to communicate with other members of its species, while others suggest it may have used a combination of both.
Survival Adaptations and Distinctive Features
Like all dinosaurs, Becklespinax had to adapt to its environment to survive and thrive. However, due to limited fossil remains, it's challenging to determine specific survival adaptations of this dinosaur. Some scientists speculate that it may have had unique characteristics like a sail or hump on its back for display or thermoregulation. However, further research and discoveries are needed to confirm this theory.
One distinctive feature that sets Becklespinax apart from other dinosaurs is its large, grasping hands. This feature suggests that Becklespinax may have been able to manipulate objects and may have been an ambush predator. Its long and slender body may have also given it an advantage in chasing and catching prey.
Largest and Smallest Species
Becklespinax belongs to the family Spinosauroidea, which includes some of the largest known carnivorous dinosaurs. The largest species of Becklespinax is believed to be the Becklespinax altispinax, which reached an estimated 26 feet in length and weighed around 2 tons. This makes it slightly smaller than its cousin, Allosaurus, which could reach up to 40 feet in length.
Unfortunately, due to the limited fossil remains, the smallest species of Becklespinax is still unknown. However, based on related species, it is speculated that it may have been around the same size as the Becklespinax altispinax.
Fossil Characteristics
Becklespinax is known for its fragmentary fossil remains, which make it difficult for scientists to study and understand this dinosaur fully. The fossils discovered consist of vertebrae and limb bones, which have been used to speculate the physical characteristics of Becklespinax.
These fossils were found in the Lower Cretaceous rocks of the Isle of Wight, in southern England. This location is known for its rich fossil deposits, making it an ideal location for paleontologists to discover new and exciting species.
Role in Ecosystem
Despite its limited fossil remains, scientists believe that Becklespinax was a top predator in its ecosystem. Its long limbs, powerful jaws, and sharp teeth would have made it a formidable predator, capable of taking down prey much larger than itself.
As with many top predators, Becklespinax would have played a crucial role in regulating the population of its prey and maintaining the balance of its ecosystem. Its predatory behavior would have also contributed to the shaping of other species' physical and behavioral characteristics through the process of natural selection.
Discovery and Discoverer
Becklespinax was first discovered in 1984 on the Isle of Wight, England, by Richard Owen, an English biologist and paleontologist. The Isle of Wight is a known hotspot for fossil discoveries, and Owen was actively exploring the area for any new dinosaur species.
Owen initially believed that the fossils belonged to a new species of Allosaurus, but further research revealed significant differences between the two, leading to the identification of a new genus, Becklespinax.
Unique Facts
While Becklespinax may not be as well-known as some of its dinosaur cousins, it has many unique attributes that make it a fascinating species to study. One of the most intriguing facts about Becklespinax is the possibility that it may have had a sail or hump on its back.
This speculation is based on the deep, elongated neural spines found in the fossils of this dinosaur. These spines may have supported a ridge of skin, forming a sail or hump that could have had various functions, such as display or thermoregulation.
Predator Status and Extinction
Despite being a top predator in its ecosystem, Becklespinax eventually faced extinction, along with many other dinosaur species. Its remains have been found in the Lower Cretaceous rocks, which date back approximately 130 million years ago.
The extinction of dinosaurs is still a subject of debate among scientists, with theories ranging from volcanic eruptions to asteroid impacts. But one thing is for sure; Becklespinax's reign as a top predator came to an end with the disappearance of dinosaurs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Becklespinax remains a mysterious and enigmatic dinosaur, with much of its story yet to be uncovered. From its unknown bone structure to its unique features and behavior, this dinosaur continues to fascinate and intrigue scientists and dinosaur enthusiasts.
Through the limited fossil remains and continuous research, scientists hope to gain a better understanding of this ancient giant and its significance in the prehistoric ecosystem. But for now, Becklespinax continues to hold onto its secrets and remains an elusive and mysterious creature from a distant past.

The Fascinating Becklespinax: Unearthing Europe's Fierce Carnivore of the Early Cretaceous
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.