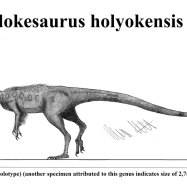
Bistahieversor
Unknown
Discover the fierce and fast Bistahieversor, a meat-eating dinosaur that roamed the lands of North America millions of years ago. Its skin color may remain a mystery, but its hunting skills and maximum speed surely made it a formidable predator. Learn more about these fascinating creatures of the past.
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Bistahieversor
Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
Feeding Behavior: Carnivorous
Bistahieversor – The Active Predator of Late Cretaceous North America
The late Cretaceous period was a time of great diversity and competition among dinosaurs. Among the many fearsome creatures that roamed the earth, one stands out as a particularly skilled hunter – Bistahieversor. This article will explore the features of this active predator, from its scientific name to its preferred habitat, and uncover why it was such a formidable presence in its native North America.The Scientific Name
Bistahieversor is a mouthful of a name, but it holds important clues to the origins and characteristics of this dinosaur Bistahieversor. The name comes from the language of the Navajo people, indigenous to the area where the first fossils of Bistahieversor were found – New Mexico, USA. "Bistahi" means "ruin" and "eversor" translates to "destroyer," a fitting name for a fierce carnivorous dinosaur.The Geological Era and Habitat of Bistahieversor
Bistahieversor lived during the late Cretaceous period, approximately 74-70 million years ago. This was a time when North America was split into two landmasses by a large inland sea, with parts of modern-day New Mexico and surrounding states being in the western landmass. The climate was warm and dry, creating a perfect habitat for this dinosaur.As a terrestrial species, Bistahieversor roamed the plains and forests of North America, likely in search of its next meal. The abundance of prey in its habitat, as well as the warm climate, allowed Bistahieversor to thrive and become an apex predator.
The Size and Physical Features of Bistahieversor
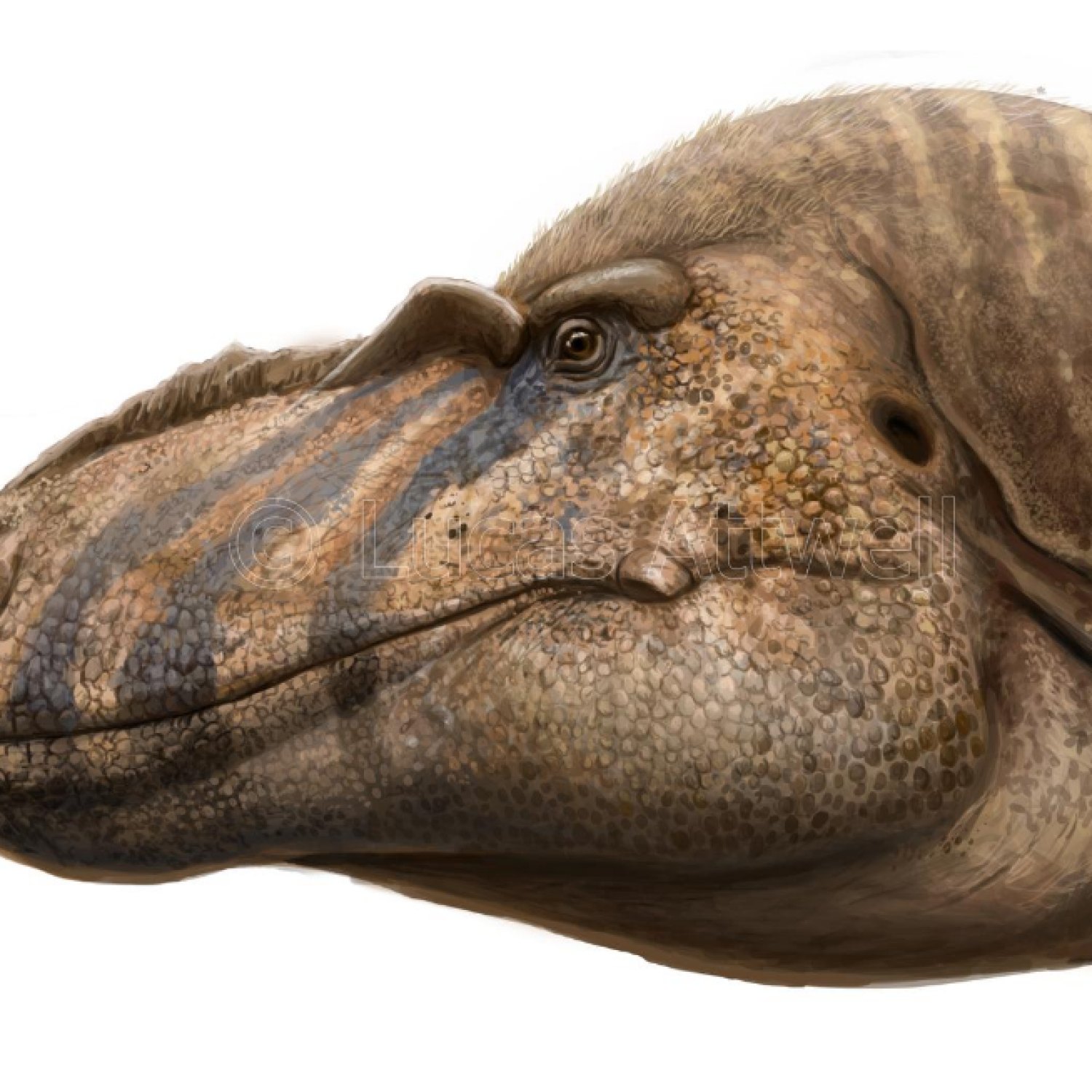
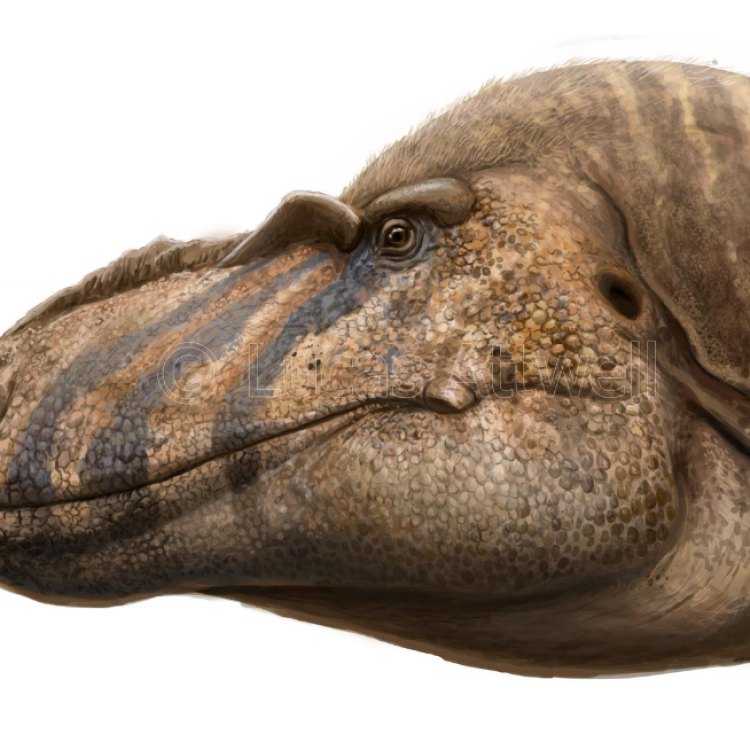
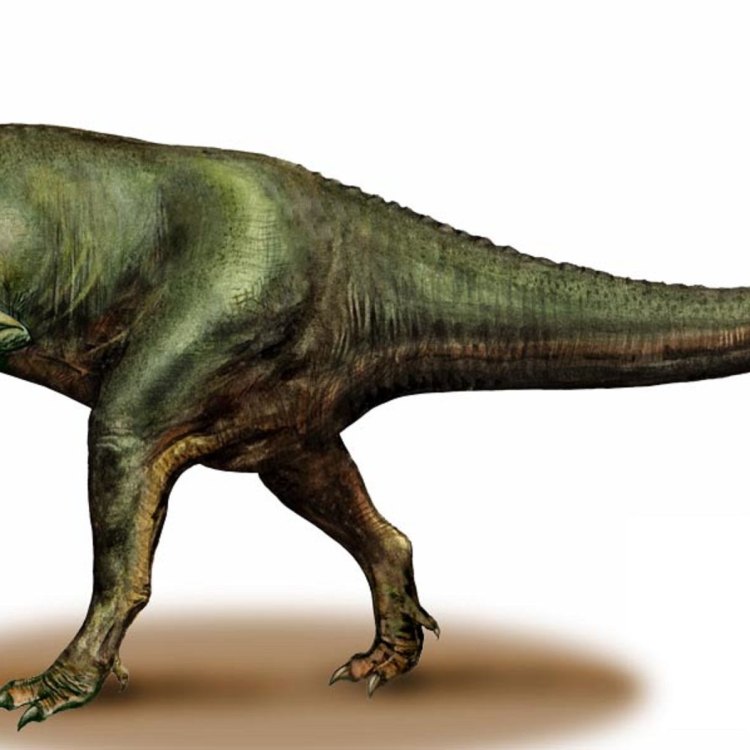
Bistahieversor was a formidable creature, measuring about 9 meters in length and standing at a height of 3 meters. It weighed an estimated 2 tons, making it similar in size to the well-known Tyrannosaurus Rex Brachylophosaurus. However, Bistahieversor was uniquely adapted to its environment and had some distinct physical features that set it apart from its more famous cousin.Firstly, Bistahieversor had sharp and serrated teeth, ideal for tearing through flesh and bone. Its teeth were also shaped differently than other theropod dinosaurs, with small serrations on the front edges and larger ones on the back edges. This helped it to grip and hold onto prey more effectively.
Another notable feature was its long and slender legs, giving Bistahieversor a streamlined and agile appearance. This suggests that it was a swift runner, well-suited for chasing down fast-moving prey.
The Feeding and Predatory Behavior of Bistahieversor
As a carnivorous dinosaur, Bistahieversor had a diet consisting of mostly meat. Its sharp and serrated teeth, along with its powerful bite force, indicate that it was a skilled and proficient hunter. As an active predator, Bistahieversor likely used its speed and agility to outrun and catch its prey, overpowering them with its strong jaws and teeth.Bistahieversor's preferred prey likely included other dinosaurs, as well as smaller animals such as mammals and reptiles. Its size and strength gave it an advantage over smaller predators, allowing it to dominate its food chain and maintain a top position in its ecosystem.
The Geographical Distribution of Bistahieversor
Bistahieversor was primarily found in North America, with its fossils being discovered in the western parts of the continent. It shared its habitat with other well-known dinosaurs such as Triceratops, Ankylosaurus, and Oviraptor. The abundance of food and resources in this region likely contributed to the success and widespread distribution of Bistahieversor.The Mystery of Bistahieversor's Preferred Temperature and Maximum Speed
Despite the extensive research and findings on Bistahieversor, there are still some unknowns about this dinosaur. Its preferred temperature and maximum speed have yet to be determined, leaving room for speculation and further exploration.However, based on its warm and dry habitat, it is likely that Bistahieversor preferred a climate similar to its native environment. As for its maximum speed, it is difficult to estimate without fossilized footprints or trackways. But its long legs and slender build suggest that it was a fast and agile runner, able to reach high speeds in pursuit of prey.
The Skin Color of Bistahieversor: A Matter of Debate
Another mystery surrounding Bistahieversor is the color of its skin. As with many other dinosaur species, the color of Bistahieversor's skin can only be speculated and is open to interpretation. Some researchers believe that it had darker-colored skin, similar to its environment, allowing it to blend in and remain camouflaged. Others speculate that it may have had brightly colored feathers, similar to modern-day birds, possibly used for display or communication.Bistahieversor's Legacy: A Fierce and Dynamic Predator
Bistahieversor may not be the most well-known or popular dinosaur, but its unique features and status as an apex predator make it a fascinating species. As we continue to uncover and learn more about the late Cretaceous period and the creatures that roamed during that time, Bistahieversor remains a standout species.From its scientific name to its preferred habitat, Bistahieversor is a dinosaur that captures our imagination and challenges our understanding of the ancient world. It serves as a reminder of the dynamic and diverse nature of the prehistoric era and the incredible adaptability of these ancient creatures.
In conclusion, Bistahieversor was an active predator of late Cretaceous North America, with a unique set of features that helped it thrive and dominate its ecosystem. Its legacy continues to fascinate and inspire researchers and enthusiasts, giving us a glimpse into the complex and fascinating world of dinosaurs.

Bistahieversor
Dinosaur Details Bistahieversor - Scientific Name: Bistahieversor
- Category: Dinosaurs B
- Scientific Name: Bistahieversor
- Common Name: Bistahieversor
- Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
- Length: 9 meters
- Height: 3 meters
- Weight: 2 tons
- Diet: Meat
- Feeding Behavior: Carnivorous
- Predatory Behavior: Active predator
- Tooth Structure: Sharp and serrated teeth
- Native Habitat: Terrestrial
- Geographical Distribution: North America
- Preferred Temperature: Warm
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown

Bistahieversor
- Bone Structure: Large and robust bones
- Reproduction Type: Egg-laying
- Activity Period: Diurnal
- Distinctive Features: Large head with forward-facing eyes
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Strong limbs and sharp claws
- Largest Species: Bistahieversor sealeyi
- Smallest Species: Unknown
- Fossil Characteristics: Partial skull and skeleton
- Role in Ecosystem: Top predator
- Unique Facts: Named after the Bisti/De-Na-Zin Wilderness where it was discovered
- Predator Status: Extinct
- Discovery Location: New Mexico, United States
- Discovery Year: 1990
- Discoverer's Name: Thomas R. Holtz Jr.
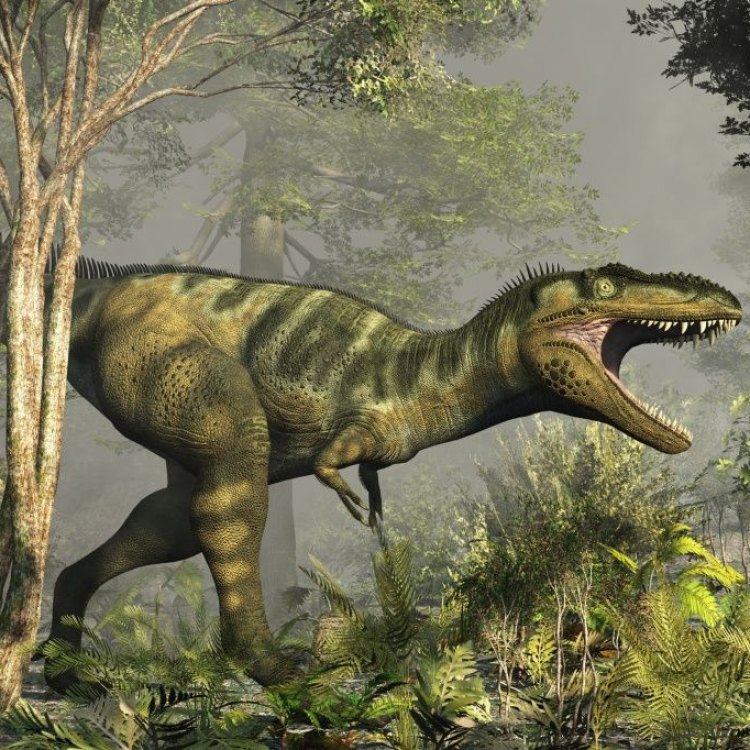

Bistahieversor
Uncovering the Mighty Bistahieversor: The Fierce Predator of the Bisti Badlands
In the rugged and isolated landscape of the Bisti Badlands in New Mexico, United States, lies a fascinating and powerful creature that once roamed the earth. The Bistahieversor, pronounced “Bis-ta-ha-ee-ver-sor,” was a large and dominant predator that lived during the late Cretaceous period, approximately 70 million years ago. This extraordinary creature has captured the attention of paleontologists and dinosaur enthusiasts alike, due to its unique characteristics and mysterious existence. In this article, we will dive deep into the world of the Bistahieversor and learn about its bone structure, reproductive habits, communication methods, and its role in the ecosystem OnTimeAiraz.Com.Named after the Bisti/De-Na-Zin Wilderness where it was first discovered in 1990 by renowned paleontologist Thomas R. Holtz Jr., the Bistahieversor has a fascinating history. Holtz, while conducting research in the Bisti Badlands, unearthed a rare partial skull and skeleton of this fierce predator. After careful examination, he determined that it belonged to a previously unknown species, and thus, the Bistahieversor sealeyi was officially named.
One of the most distinctive features of the Bistahieversor is its large and robust bones. These bones were a vital attribute to its massive size and strength, making it one of the largest members of the Tyrannosaur family. The Bistahieversor was estimated to be around 30 feet long and weigh over 3 tons, making it slightly bigger than its cousin, the famous Tyrannosaurus Rex. In addition to its size, the Bistahieversor had strong limbs and sharp claws, which were essential to its survival Balaur.
Another unique characteristic of the Bistahieversor was its large head with forward-facing eyes. Unlike other theropod dinosaurs, the Bistahieversor had its eyes positioned towards the front of its skull, rather than on the sides. This adaptation gave the Bistahieversor excellent depth perception, allowing it to accurately judge distance and hunt its prey with precision. Its large head, combined with a powerful jaw and sharp serrated teeth, made the Bistahieversor an apex predator in its ecosystem.
Speaking of its ecosystem, the Bistahieversor played a significant role as a top predator. During the late Cretaceous period, the Bisti Badlands were a vast and diverse landscape, rich in vegetation and home to a variety of creatures, including dinosaurs. The Bistahieversor was at the top of the food chain, preying on other dinosaurs, such as the duck-billed hadrosaurs, horned ceratopsians, and armored ankylosaurs. Its powerful bite and hunting skills made it a dominant force in its environment.
Despite its dominant status in the ecosystem, there is still much we do not know about the Bistahieversor. One of the biggest mysteries surrounding this fierce predator is its communication method. Since there is no solid evidence of vocal cords or structures in its skull that would indicate sound production, it is unknown how the Bistahieversor communicated with others of its kind. However, some theories suggest that, like other theropods, it may have used visual cues and physical displays to communicate.
Another enigma about the Bistahieversor is its reproduction type. While most theropod dinosaurs are known to be egg-layers, it is unclear whether the Bistahieversor followed the same pattern. Despite the lack of evidence, some researchers speculate that the Bistahieversor could have been a live bearer, meaning it gave birth to live young, like modern-day mammals. This theory is based on the discovery of a related species, the Troodon, which was also thought to be an egg-laying dinosaur, but recent research has revealed that it may have been a live bearer instead.
Although we may never have all the answers about the Bistahieversor, its presence in the Bisti Badlands has left a lasting impression. It is a testament to the diversity and unique adaptations of the dinosaurs that once roamed the earth. Sadly, the Bistahieversor, along with all other non-avian dinosaurs, went extinct approximately 65 million years ago, marking the end of the Cretaceous period. The reasons for their extinction are still debated, but many scientists believe it was a mass extinction event caused by an asteroid impact.
Today, the Bistahieversor lives on through its fossils, providing vital clues and information about its existence. Its discovery in the Bisti Badlands has shed light on the diversity of the region and has solidified its reputation as a significant paleontological site. The Bisti Badlands are known for their vast and surreal landscapes, making it a popular destination for hikers, fossil hunters, and nature enthusiasts. And now, with the addition of the mighty Bistahieversor, it has become an even more remarkable location.
In conclusion, the Bistahieversor is a remarkable and awe-inspiring creature that once ruled the Bisti Badlands. With its large and robust bones, forward-facing eyes, and powerful limbs, it was a force to be reckoned with in its ecosystem. Despite its fierce nature, there is still much to learn about the Bistahieversor, including its communication methods, reproductive habits, and even its size and appearance in its juvenile stages. As more research and discoveries are made, we can continue to uncover the mysteries and secrets of this incredible dinosaur, preserving its legacy for generations to come.
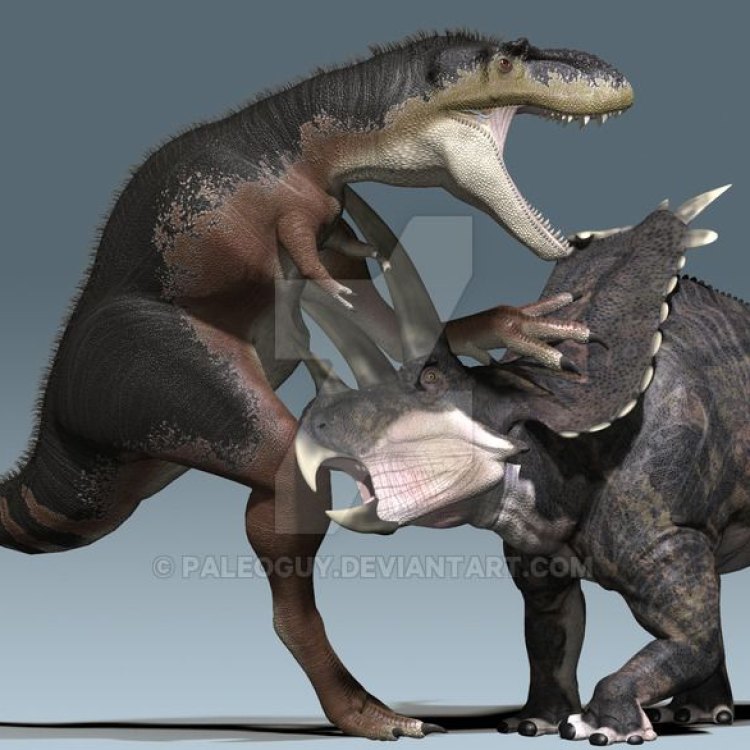

Bistahieversor – The Active Predator of Late Cretaceous North America
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.