Edmontosaurus
Unknown
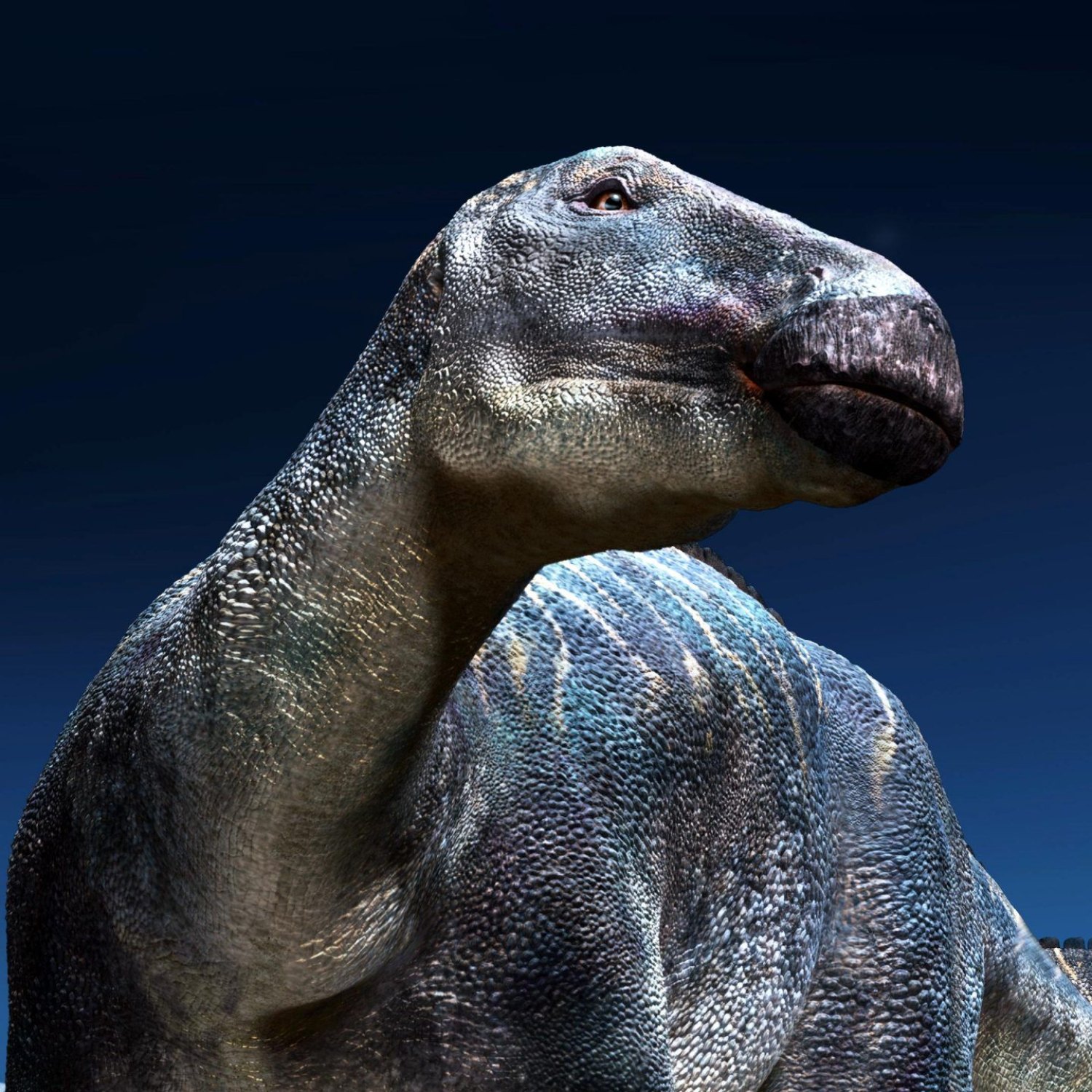
Edmontosaurus was a massive herbivorous dinosaur that roamed the North American continent. Despite its size, its skin color remains a mystery. Scientists are still unsure of its top speed, but with its powerful legs, it could have moved quite swiftly. Discover more about this fascinating dinosaur and its mysterious features. #Edmontosaurus #Dinosaurs #NorthAmerica
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Edmontosaurus
Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
Feeding Behavior: Browsing
Uncovering the Mysteries of Edmontosaurus: A Fascinating Herbivorous Dinosaur
When we think of dinosaurs, we often imagine fierce predators roaming the earth. But not all dinosaurs were hunters - some were gentle giants that fed on plants. One such dinosaur is Edmontosaurus, a fascinating herbivorous creature that lived during the Late Cretaceous period. In this article, we will dive into the world of Edmontosaurus, uncovering its unique features, behavior, and habitat Edmontosaurus.Edmontosaurus, also known as "Edmonton lizard," was a large dinosaur that lived around 73 to 65 million years ago. Its scientific name, Edmontosaurus, comes from the Edmonton Formation in Alberta, Canada, where the first skeleton was discovered in 1910. This massive creature was named after the city of Edmonton, making it the first dinosaur to be named after a Canadian city.
With its long body and a duck-like bill, Edmontosaurus may not look intimidating, but it was an impressive creature. It measured around 10-13 meters in length, stood 3-4 meters tall, and weighed 2-4 tons, making it one of the largest herbivorous dinosaurs of its time. Its large size was a result of living in a favorable environment with an abundance of food.
As a herbivore, Edmontosaurus had a specialized diet of plants and vegetation. Its diet consisted of conifers, leaves, fruits, and seeds, which it fed on by browsing. Browsing is a feeding behavior where herbivorous animals pick and eat fruits and leaves from trees, rather than grazing on plants on the ground Edmarka.
Unlike carnivorous dinosaurs with sharp teeth, Edmontosaurus had a unique tooth structure known as the "battery of teeth in cheeks." It had up to 60 teeth in its mouth, arranged in multiple rows along its cheeks. This tooth structure allowed it to chew and grind tough vegetation more efficiently, making it well-suited for its browsing behavior. The worn-down teeth suggest that Edmontosaurus had a lifespan of around 10-12 years.
While many dinosaurs were known for their predatory behavior, Edmontosaurus was a gentle giant that posed no threat to any creature. Its large size and herbivorous diet meant that it had no reason to hunt and kill other animals. Instead, it lived peacefully, while also remaining vigilant for potential predators.
Edmontosaurus likely lived in herds, as evident from multiple skeletons found together. Living in groups allowed them to protect against predators and find food more efficiently. Their herding behavior is also suggested by the fact that they laid their eggs in large communal nests, which have been found in North America, indicating their preference for living in groups.
The floodplains of North America were the native habitat of Edmontosaurus. They lived in areas near rivers and streams, where there was an ample supply of water and food. During the Late Cretaceous period, this region experienced a warm and temperate climate, making it an ideal environment for these giant herbivores. However, they were not limited to North America, as fossils have also been found in Mexico and Alaska, suggesting a wider geographical distribution.
One of the most intriguing things about Edmontosaurus is its skin color. While there is no evidence of its exact skin color, scientists have been able to determine that it was most likely a mottled pattern of dark and light colors. This patterning would have helped it camouflage and hide from predators. Some researchers also believe that Edmontosaurus may have had a comb-like structure on its head, similar to the ones found on some modern-day duck species.
With its large size and strong built, one may assume that Edmontosaurus was a fast runner. However, its maximum speed remains unknown, with scientists speculating it to be around 25-30 miles per hour. Its speed would have been sufficient to escape predators, but it was not designed for long-distance running.
Scientists have also found evidence of an interesting behavior known as abrupt dives in Edmontosaurus. This behavior suggests that these giant creatures could dive into shallow water bodies, possibly to cool off in hot weather or to escape predators. This behavior has been observed in modern-day animals, including elephants and rhinos, making it a plausible theory for Edmontosaurus.
Despite its massive size, Edmontosaurus had no known predators. Its herding behavior, tough skin, and large size may have protected it from most predators. However, the arrival of Tyrannosaurus Rex, a large and fierce predator, towards the end of the Late Cretaceous period, may have posed a threat to Edmontosaurus.
In conclusion, Edmontosaurus was a fascinating and gentle dinosaur that roamed the earth millions of years ago. Its unique features, behavior, and habitat make it a subject of interest for scientists and dinosaur enthusiasts alike. With further research and discoveries, we may be able to unravel more mysteries surrounding this incredible herbivorous creature.

Edmontosaurus
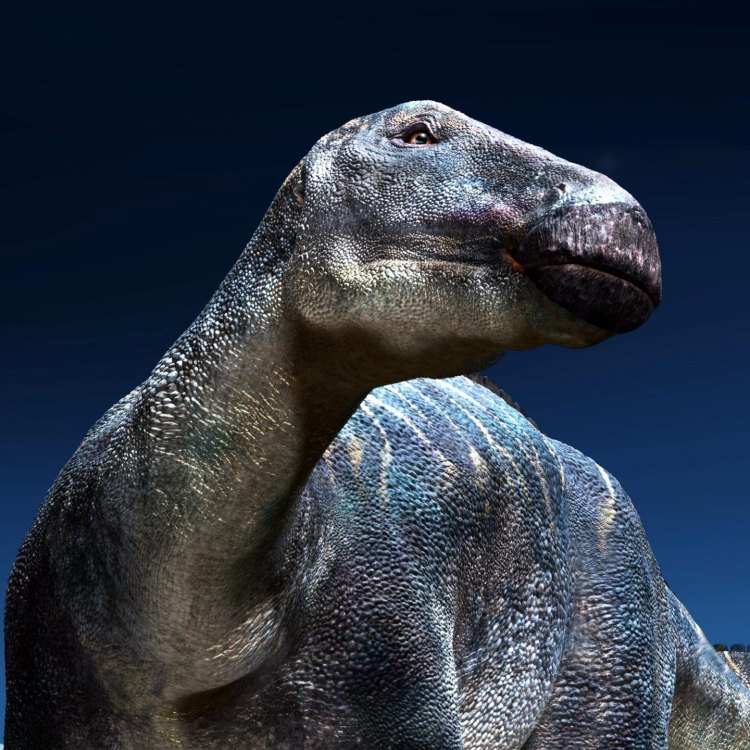
Dinosaur Details Edmontosaurus - Scientific Name: Edmontosaurus
- Category: Dinosaurs E
- Scientific Name: Edmontosaurus
- Common Name: Edmontosaurus
- Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
- Length: 10-13 meters
- Height: 3-4 meters
- Weight: 2-4 tons
- Diet: Herbivorous
- Feeding Behavior: Browsing
- Predatory Behavior: Non-predatory
- Tooth Structure: Battery of teeth in cheeks
- Native Habitat: Floodplains
- Geographical Distribution: North America
- Preferred Temperature: Temperate climate
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown

Edmontosaurus
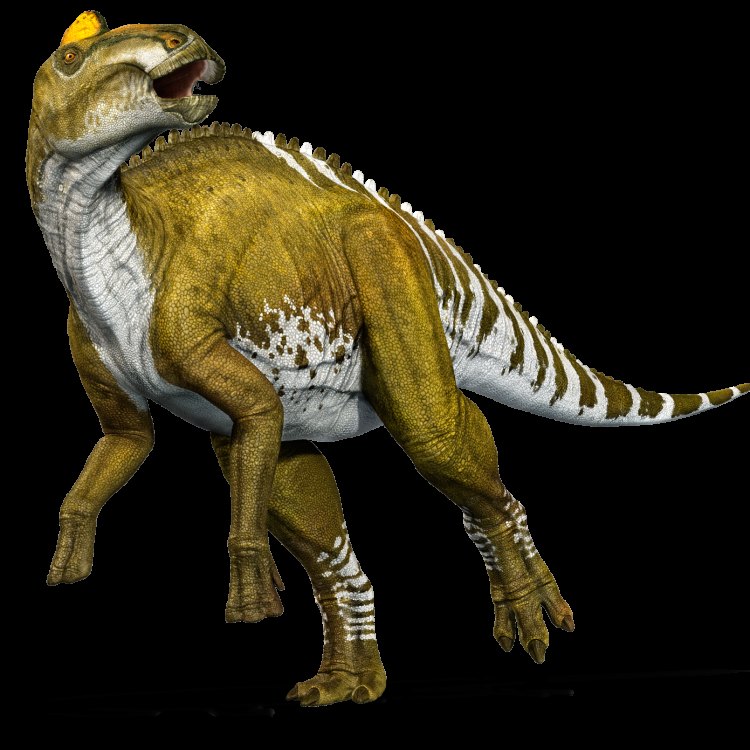
- Bone Structure: Large and sturdy
- Reproduction Type: Egg-laying
- Activity Period: Diurnal
- Distinctive Features: Crest on top of the head
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Unknown
- Largest Species: Edmontosaurus annectens
- Smallest Species: Unknown
- Fossil Characteristics: Abundant fossil remains
- Role in Ecosystem: Herbivore and food source for carnivores
- Unique Facts: Possibly lived in herds
- Predator Status: Prey
- Discovery Location: North America
- Discovery Year: 1917
- Discoverer's Name: Lawrence M. Lambe

Edmontosaurus
The Remarkable Edmontosaurus: A Look at the Majestic Herbivore
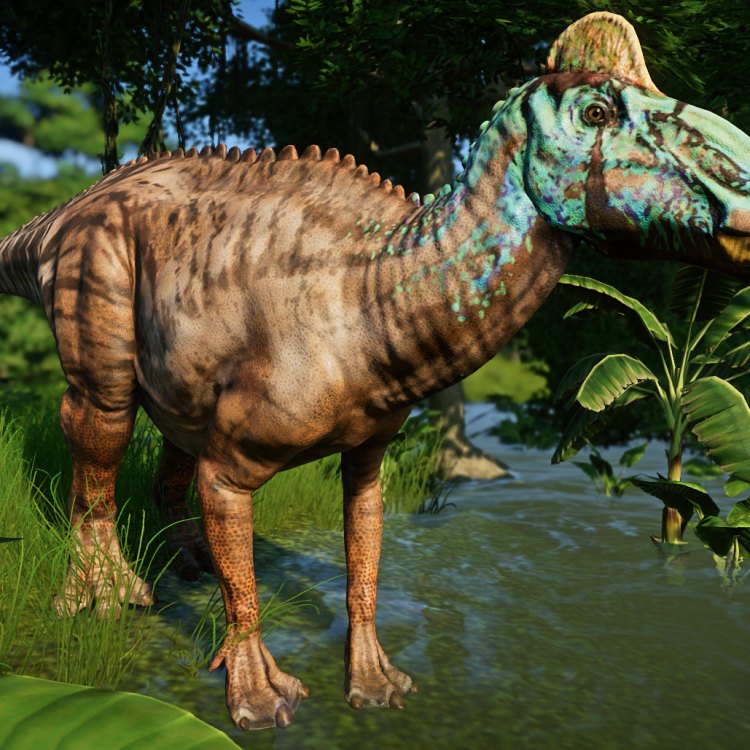
Millions of years ago, during the Cretaceous period, North America was home to some of the most magnificent creatures to ever walk this Earth. One of these creatures was the Edmontosaurus, a large and sturdy herbivorous dinosaur with a distinctive crest on its head. The Edmontosaurus has left an undeniable mark in the world of paleontology, with its abundant fossil remains and interesting characteristics. In this article, we will delve deeper into the world of the Edmontosaurus and explore its bone structure, reproduction type, activity period, unique features, communication method, survival adaptations, largest and smallest species, role in the ecosystem, incredible facts, and its status as a prey animal OnTimeAiraz.Com.Discovery and Naming
The Edmontosaurus was first discovered in 1917 by Lawrence M. Lambe, a Canadian paleontologist, in Dinosaur Provincial Park in Alberta, Canada. It was given its name "Edmontosaurus" in honor of the city of Edmonton, which is near the location where the first fossil was discovered. This dinosaur belongs to the family Hadrosauridae, which includes known species such as Parasaurolophus, Corythosaurus, and Maiasaura.Bone Structure
One of the most striking features of the Edmontosaurus is its large and sturdy bone structure. It had a long and thick tail, which helped with balance while walking and running. Its powerful hind legs were longer than its front legs, allowing it to move at a relatively high speed for a dinosaur of its size. The front legs had five hoofed digits, while the hind legs had only four.Unlike many other dinosaurs, the Edmontosaurus had a flattened and wide chest, which allowed it to process large amounts of plant material for its massive size Eoraptor. It also had a strong and muscular neck that allowed it to reach vegetation up to nine feet off the ground.
The bones of the Edmontosaurus were hollow, similar to modern-day birds, making it a lighter and more efficient animal. Additionally, its teeth were perfectly suited for grinding tough plant material, as they were continually replaced and were tightly packed in its wide jaw.
Reproduction and Activity Period
Just like most dinosaurs, the Edmontosaurus reproduced by laying eggs. They were known for constructing nests in groups, which suggests that they may have lived in herds and had some level of social interaction. Their eggs were also susceptible to predators, making it crucial for them to lay a large number of eggs to ensure the survival of their species.The Edmontosaurus was a diurnal animal, meaning it was active during the day and rested at night. Its large size and herbivorous diet required it to consume vast amounts of food and energy, making daylight hours the most optimal for foraging.
Distinctive Features
One of the most distinguishing features of the Edmontosaurus was the crest on the top of its head. This bony crest was hollow and acted as a resonating chamber, similar to the acoustic structures found in modern-day birds. The exact purpose of this crest is unknown, but scientists believe it may have been used for communication, display, or thermoregulation.Another unique feature of the Edmontosaurus were its cheeks, which were made up of hundreds of small bones that allowed for better chewing and digestion of tough plant material. These cheeks also acted as a storage unit for food, allowing the Edmontosaurus to graze and then retreat to a safe area to slowly digest its food.
Communication and Survival Adaptations
The communication method of the Edmontosaurus is still unknown. However, based on their crest and possible herd behavior, it is believed that they may have used vocalizations to communicate with one another. This may have been especially important during mating and nesting periods.As a large herbivorous dinosaur, the Edmontosaurus faced many predators such as the T-Rex, Albertosaurus, and Troodon. In order to survive, it had to develop some unique adaptations. Its massive size, coupled with its strong and sturdy bone structure, made it difficult for predators to bring down. It could also run at a decent speed, making it an agile target. Its herding behavior may have also helped it survive, as there is safety in numbers, and it could warn others of potential danger.
Largest and Smallest Species
The largest species of Edmontosaurus was the Edmontosaurus annectens, estimated to have reached up to 43 feet in length and weighing up to seven tons. On the other hand, the smallest species of Edmontosaurus is still unknown, as no juvenile fossils have been found to determine the size of a young Edmontosaurus.Fossil Characteristics
The Edmontosaurus is a well-known and well-studied dinosaur due to its abundant fossil remains. These fossils have given scientists a deep understanding of the anatomy, behavior, and evolution of this species. The bones of the Edmontosaurus are often found in large groups, suggesting that they lived and died together, possibly due to environmental factors such as drought or floods.These fossils have also given insight into the diet of the Edmontosaurus. Fossilized stomach contents have shown that they primarily consumed a diet of plants such as leaves, fruits, and seeds. Scientists have also found evidence of gastroliths (stones used for grinding food) in their stomachs, indicating that they had a unique digestive system that required them to consume large amounts of food.
Role in the Ecosystem
As a herbivorous dinosaur, the Edmontosaurus played a crucial role in the ecosystem of the Cretaceous period. They were the primary food source for many carnivorous dinosaurs, and their grazing also helped shape the vegetation and landscape of their environment. Their behavior of nesting in groups also suggests a possible contribution to the soil fertility and nutrient cycling in their ecosystems.Unique Facts
Apart from its distinctive features and adaptations, the Edmontosaurus has several unique and interesting facts that make it stand out among other dinosaurs. As mentioned earlier, they may have lived in herds, making them one of the only known dinosaurs to exhibit this behavior. They also had a high reproductive rate, laying anywhere from 2-20 eggs at a time, increasing their chances of survival.Another remarkable fact is that the Edmontosaurus existed alongside other well-known dinosaurs such as the Triceratops, T-Rex, and the famous duck-billed dinosaur, Parasaurolophus. This just goes to show the incredible diversity and abundance of dinosaur species during the Cretaceous period.
Predator Status
Despite its massive size, the Edmontosaurus was not immune to predators. As mentioned earlier, it faced many threats from ferocious carnivorous dinosaurs. Even its sheer size and strength could not protect it from the forces of nature, as environmental factors such as climate change and food scarcity also played a role in their extinction.Additionally, the Edmontosaurus was also hunted by early humans, known as the Clovis people, who may have contributed to their eventual extinction. The last known fossil record of an Edmontosaurus dates back to about 65 million years ago, which coincides with the end of the Cretaceous period and the famous event that wiped out most dinosaurs - the asteroid impact.
In Conclusion
The Edmontosaurus was a magnificent and incredibly unique dinosaur that has left a lasting impact in the world of paleontology. Its large and sturdy bone structure, distinctive crest, and possible herd behavior make it stand out among other herbivorous dinosaurs. Its role in the ecosystem and its adaptations for survival offer valuable insight into the life and evolution of this fascinating creature. With abundant fossil remains and ongoing research, the Edmontosaurus continues to captivate the minds of scientists and dinosaur enthusiasts worldwide.
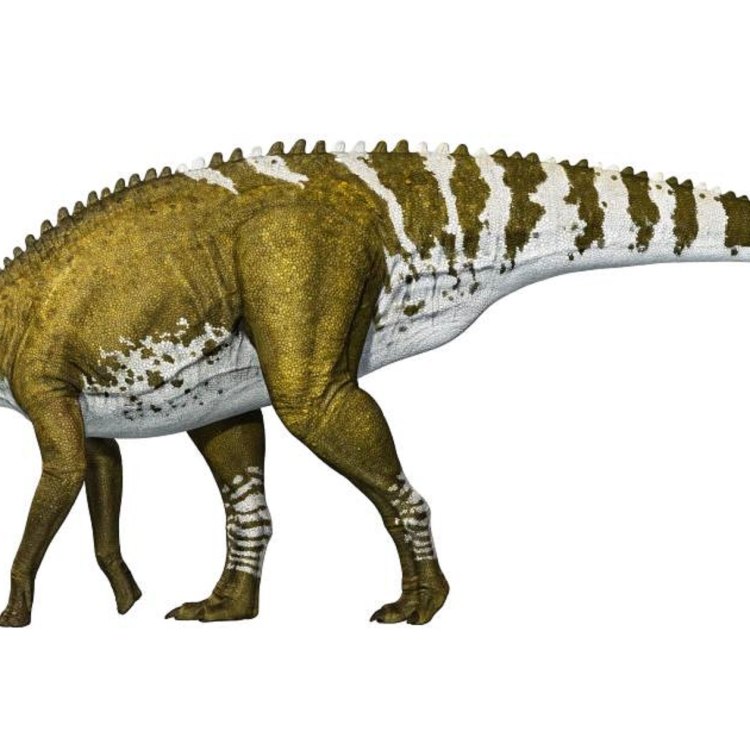
Uncovering the Mysteries of Edmontosaurus: A Fascinating Herbivorous Dinosaur
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.