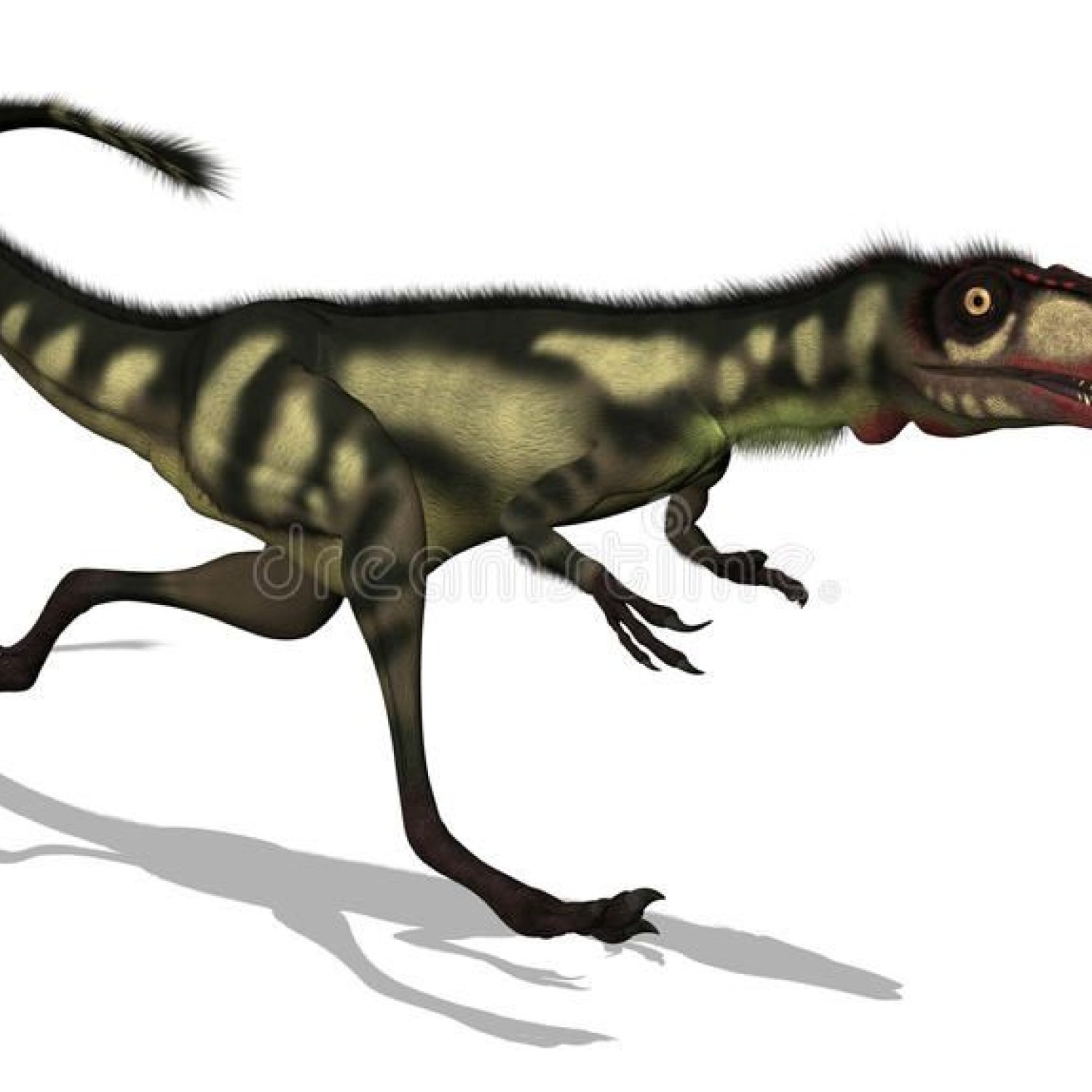
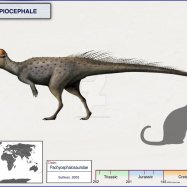
Dilong
Unknown
Dilong is a fascinating dinosaur from China with unknown skin color. Belonging to the carnivorous category, it's maximum speed is still a mystery. Learn more about this ancient beast and its possible capabilities. #Dinosaurs #China #Carnivorous
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Dilong
Geological Era: Early Cretaceous
Feeding Behavior: Active hunter
Dilong: Unveiling the Secrets of China's Early Cretaceous Carnivore
Heading back to the Early Cretaceous period, about 130 million years ago, we encounter a fierce and elusive predator – Dilong. Though not as well known as its close relative, Tyrannosaurus rex, Dilong's discovery has revolutionized our understanding of the evolution and characteristics of theropod dinosaurs.The Discovery of Dilong
The first Dilong fossils were discovered in 2004 in the Yixian Formation in western Liaoning province, China. This location is renowned for its rich deposits of feathered dinosaur fossils, and Dilong's remains were no exception Dilong. The four-foot-long skeleton was nearly complete, with some preserved soft tissue and feathers.Paleontologists have identified two species of Dilong, Dilong paradoxus, and Dilong puellus. Both species belong to the family of feathered dinosaurs known as tyrannosauroids, which includes some of the largest carnivores ever to walk the earth.
Tantalizing Physical Characteristics
Though not a giant among dinosaurs, Dilong was still a formidable predator. It measured approximately 2 meters in length, 0.5 meters in height, and weighed around 10 kilograms. Its elongated skull was adorned with sharp, serrated teeth that were perfectly adapted for hunting and killing prey.One of the most striking features of Dilong was its feathers. It's thought to be one of the earliest definitive examples of a feathered theropod dinosaur, shedding light on the evolution of feathers in dinosaurs Dyslocosaurus. The feathers were long and downy, covering the body and tail, similar to those of modern birds. However, due to the lack of pigmentation in the fossil, the color of its feathers remains a mystery.
Another intriguing feature of Dilong is its long arms with three-fingered hands. Unlike its later relative, Tyrannosaurus rex, which had stubby arms, Dilong's arms were long and well-muscled, capable of grasping and manipulating prey. This goes against the popular notion that all tyrannosaurids had short arms and highlights the diversity within this group of dinosaurs.
Diet and Feeding Behavior
Being a theropod dinosaur, Dilong was a carnivore, which means it primarily fed on meat. Due to its sharp teeth and strong jaw muscles, it's believed that Dilong was an active hunter, actively pursuing its prey. Its feathers may have provided insulation, making it a better predator in colder climates, such as the forested habitat it lived in.Dilong's diet likely consisted of smaller animals, such as small mammals, reptiles, and possibly even other dinosaurs. The sharp and serrated teeth were perfect for slicing through flesh, and its strong jaw muscles allowed for a powerful bite force.
Predatory Behavior and Socialization
As a solitary predator, Dilong likely lived and hunted alone. Its sharp senses, including binocular vision and acute hearing, would have helped it locate prey and avoid larger predators. Its feathered appearance may have also provided camouflage, allowing it to remain hidden and strike at the right moment.Studies of Dilong's brain and inner ear structure have indicated that it had good balance and coordination, traits necessary for an active hunter. Its large olfactory bulbs also suggest a keen sense of smell, which would have been crucial for tracking prey.
Despite being solitary, Dilong likely exhibited some social behavior. Studies of its fossils have revealed that it lived in close proximity to other Dilong individuals, suggesting that they may have formed small packs or had temporary groupings during mating seasons.
Native Habitat and Geographical Distribution
Being native to the Yixian Formation in China, Dilong's natural habitat would have been a forest. At the time, this area was a region of lush vegetation, providing ample cover and food for Dilong and its prey. The forest habitat would have also influenced its physical characteristics, such as its feathered coat.Though most Dilong fossils have been found in this region, some remains have also been discovered in other parts of China, suggesting a wider geographical distribution during its time.
The Climate and Adaptation
During the Early Cretaceous period, the earth's climate was much warmer than it is today. However, the climate in the Yixian Formation was moderate, with temperatures ranging from 10 to 20 degrees Celsius. Dilong's feathers would have provided insulation against the colder weather, making it well adapted to its habitat.It's also believed that Dilong was a fast runner, attaining high speeds of up to 40 kilometers per hour. This agility would have been crucial for hunting prey and escaping from larger predators, making Dilong a formidable opponent.
Unveiling the Secrets of Dilong
The discovery of Dilong has not only provided a fascinating glimpse into the life of one of the earliest feathered dinosaurs, but it has also contributed to our knowledge of theropod dinosaur evolution. It's clear that these creatures were not just large and fierce, but they also exhibited a variety of physical and social behaviors that make them even more fascinating.With the ongoing study of Dilong fossils and advancements in technology, we hope to uncover even more secrets and insights into this intriguing dinosaur. Who knows what other surprises Dilong may have in store for us?
In Conclusion
Though Dilong may not be as famous as other dinosaurs, its discovery has added valuable information to our understanding of the diverse world of theropod dinosaurs. From its physical characteristics and feeding behaviors to its native habitat and adaptation, Dilong has left us in awe and continues to fascinate paleontologists and dinosaur enthusiasts alike.So next time you take a walk in the forest, take a moment to imagine the world of Dilong and how these fearsome predators once roamed the earth.
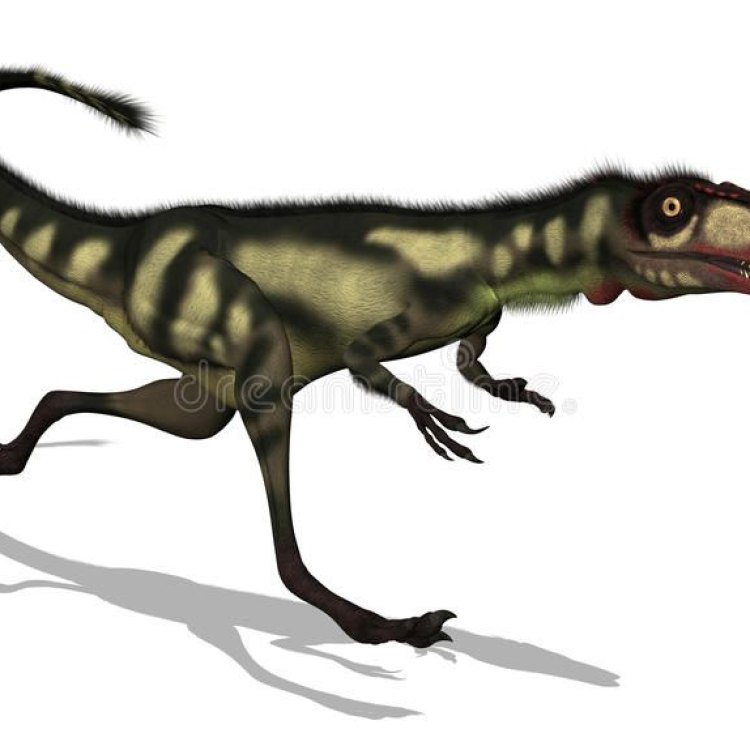

Dilong
Dinosaur Details Dilong - Scientific Name: Dilong
- Category: Dinosaurs D
- Scientific Name: Dilong
- Common Name: Dilong
- Geological Era: Early Cretaceous
- Length: 2 meters
- Height: 0.5 meters
- Weight: 10 kilograms
- Diet: Carnivorous
- Feeding Behavior: Active hunter
- Predatory Behavior: Solitary
- Tooth Structure: Sharp and serrated teeth
- Native Habitat: Forest
- Geographical Distribution: China
- Preferred Temperature: Moderate
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown
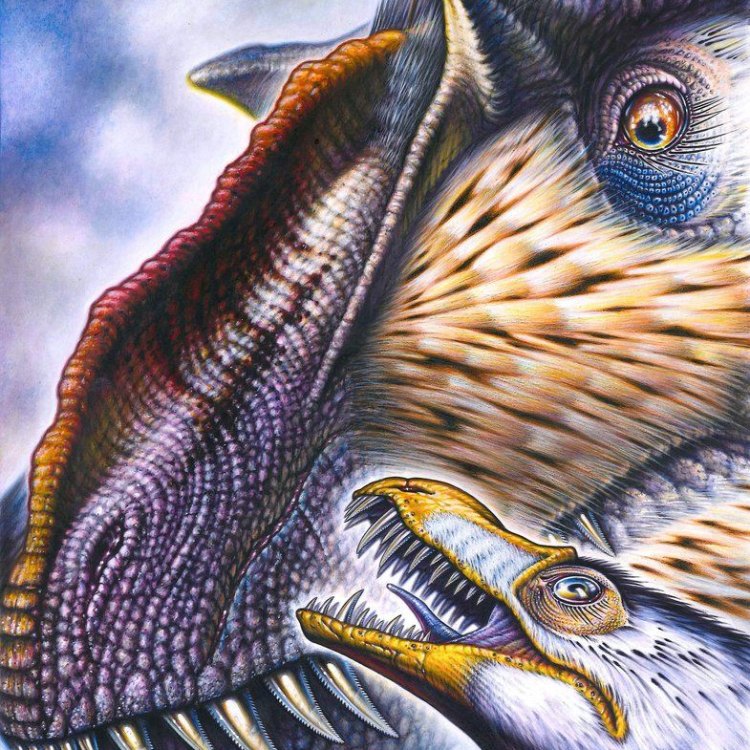

Dilong
- Bone Structure: Lightweight
- Reproduction Type: Egg-laying
- Activity Period: Daytime
- Distinctive Features: Crest on its head
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Unknown
- Largest Species: Dilong paradoxus
- Smallest Species: Dilong yangi
- Fossil Characteristics: Skull and partial skeleton
- Role in Ecosystem: Top predator
- Unique Facts: One of the earliest feathered dinosaurs
- Predator Status: Extinct
- Discovery Location: Liaoning Province, China
- Discovery Year: 2004
- Discoverer's Name: Xu Xing

Dilong
The Dilong: Uncovering the Secrets of the Feathered Dinosaurs
The world of dinosaurs has always been a source of fascination and wonder for scientists and enthusiasts alike. From the towering and ferocious Tyrannosaurus Rex to the herbivorous and peaceful Brachiosaurus, these prehistoric creatures continue to capture our imagination.But amidst the plethora of well-known dinosaurs, there are some that remain mysterious and elusive, hidden in the depths of time. One such creature is the Dilong, a small but significant dinosaur that has recently been discovered and is shrouded in a veil of mystery OnTimeAiraz.Com.
Let's take a journey into the past and uncover the unique features and adaptations of this fascinating creature, the Dilong.
A Unique Bone Structure: The Key to its Lightweight
The Dilong was a relatively small dinosaur, growing up to only 1.5 meters in length. But what makes it stand out from its larger and more well-known counterparts is its remarkably lightweight bone structure.Unlike other dinosaurs, the Dilong had hollow bones that were filled with air pockets, giving it a lighter body weight. This adaptation made it easier for the Dilong to move quickly and swiftly, making it a formidable hunter.
Egg-laying: Its Mode of Reproduction
One of the most common methods of reproduction among dinosaurs is egg-laying. And the Dilong was no exception to this rule. The discovery of fossilized eggs in China provides evidence that the Dilong reproduced by laying eggs, similar to birds today Dubreuillosaurus.Interestingly, this form of reproduction indicates that the Dilong was closely related to birds, a theory that has been further supported by recent findings.
Daytime Warriors: The Dilong's Activity Period
The Dilong was a diurnal creature, meaning it was active during the day. Unlike some dinosaurs that were active at night, the Dilong preferred to hunt and roam during the daytime.This behavior suggests that the Dilong was well adapted to the light and had excellent vision. Its daytime activity also meant that it avoided competition with other nocturnal predators, giving it an advantage in the ecosystem.
A Crest on its Head: A Distinctive Feature
Amidst its lightweight bone structure and daytime activity, the Dilong's most distinctive feature is the crest on its head. This crest was made up of feathers, similar to those found on modern-day birds.The purpose of this crest is still unknown, but scientists speculate that it may have been used for display during courtship or as a form of communication with other Dilongs.
A Silent Communicator: The Dilong's Communication Method
While we can speculate about the purpose of the Dilong's crest, one thing that remains a mystery is its method of communication. As of now, there is no evidence to suggest how the Dilong communicated with others of its kind or with other dinosaurs.But with new discoveries and advancements in technology, scientists are hopeful that this enigma will soon be solved.
An Unknown Adaptation for Survival
The Dilong's lightweight structure, daytime activity and distinctive crest all seem to have been adaptations for survival. But there could be more to this dinosaur that we have yet to discover.Scientists are still searching for answers about other unique adaptations that may have helped the Dilong survive in its ecosystem. Perhaps, with further research, we will uncover the secrets of this elusive creature.
The Largest and Smallest Species of Dilong
The Dilong paradoxus, discovered in Liaoning Province, China in 2004, is the largest species of Dilong ever found. It was estimated to be around 1.5 meters in length and was a fearsome predator in its ecosystem.On the other end of the scale is the Dilong yangi, the smallest species of Dilong discovered so far. It is thought to have been only 60cm in length, making it one of the tiniest dinosaurs to have ever roamed the earth.
Fossils - A Window into the Past
The Dilong's existence was brought to light when a partial skeleton and a skull were discovered in Liaoning Province, China in 2004 by paleontologist Xu Xing.The fossils were remarkably well-preserved, with remarkable details of the Dilong's bone structure and its unique features, such as the crest. These fossils have helped scientists reconstruct the Dilong's appearance and understand its place in the ecosystem.
Role in the Ecosystem: A Top Predator
For a small dinosaur, the Dilong played a crucial role in the ecosystem as a top predator. Its lightweight structure and sharp teeth allowed it to chase and hunt other small creatures, making it an apex predator in its environment.Without the Dilong, the balance of the ecosystem may have been disrupted, and other species may have flourished unchecked.
Unique Facts: One of the Earliest Feathered Dinosaurs
The Dilong is not only unique for its distinctive features, but it also holds a significant place in the history of dinosaurs. It is one of the earliest feathered dinosaurs to have ever existed, making its discovery and study even more crucial.Its feathers were different from those of birds today, and studying these ancient feathers can provide valuable insights into the evolution of birds.
An Extinct Predator: The Dilong's Fate
Unfortunately, like many other dinosaurs, the Dilong met its demise and became extinct millions of years ago. Scientists speculate that the rise of larger and more advanced predators, such as the Tyrannosaurus Rex, may have played a significant role in the Dilong's extinction.But even in its extinction, the Dilong has left an indelible mark in the world of dinosaurs. Its unique features and adaptations continue to fascinate scientists, and further research on this enigmatic creature may lead to even more discoveries about the world of dinosaurs.
In Conclusion...
The Dilong may not be the most well-known or significant dinosaur, but its discovery and study have shed light on the history and evolution of these prehistoric creatures.From its lightweight bone structure to its distinctive features, the Dilong continues to pique the curiosity of scientists and the imagination of enthusiasts. With new discoveries and advancements in technology, who knows what other secrets the Dilong may have in store for us?

Dilong: Unveiling the Secrets of China's Early Cretaceous Carnivore
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.