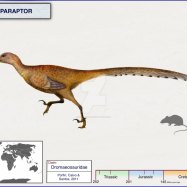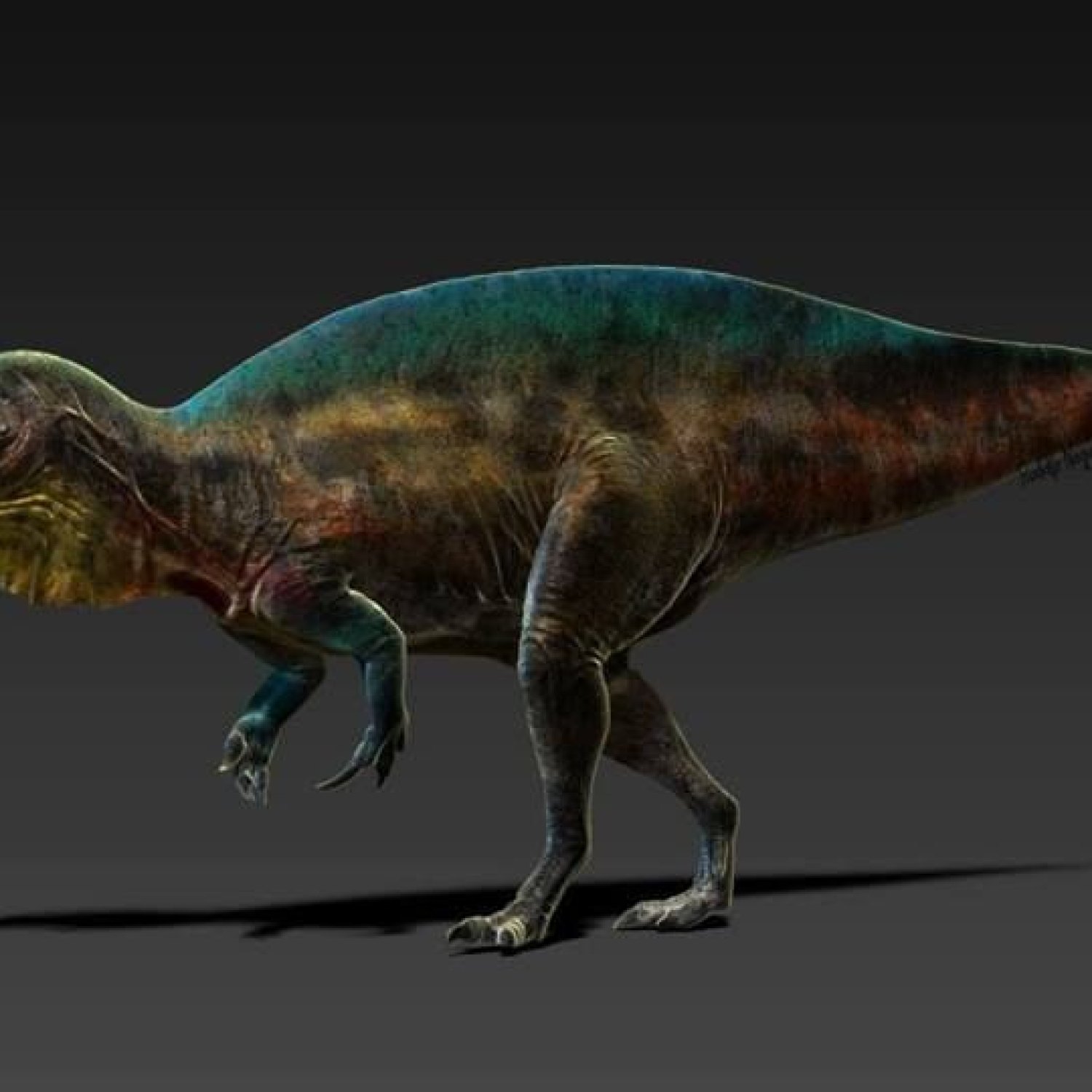
Angaturama
Unknown
Angaturama, a carnivorous dinosaur from Brazil, is named after the Tupi words for narrow mouth. Its skin color remains a mystery, but its impressive speed and sharp teeth make it an apex predator. Discover more about this ancient creature. #Angaturama #dinosaurfacts #Brazilianpredator
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Angaturama
Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
Feeding Behavior: Active predator
The Ferocious Angaturama: A Story of a Predatory Dinosaur
Imagine walking through a dense, coastal mangrove swamp in Brazil, over 65 million years ago. The air is thick with humidity, and the sounds of nature fill your ears. As you look around, you can see trees bending and rustling, but you can't quite pinpoint what's causing it. Suddenly, out of the cover of the trees, a large, ferocious creature emerges Angaturama. It's the Angaturama, a powerful and deadly predatory dinosaur that ruled the late Cretaceous period. In this article, we will explore the intriguing features of the Angaturama and uncover its reign as a top predator in the land of Brazil.First discovered in 1991 by a team of paleontologists in Brazil, the Angaturama has quickly become a well-known and studied dinosaur. Its scientific name, Angaturama, comes from the Tupi Indian language, meaning "giant thunderer." This name is fitting for this massive creature, as it measured between 9-10 meters in length, stood 2-3 meters tall, and weighed in at a whopping 2-3 tons. Its size alone would have made it an intimidating presence in its native habitat.
Like many other carnivorous dinosaurs, the Angaturama had sharp, serrated teeth designed for tearing through flesh. These teeth were part of its formidable feeding behavior. The Angaturama was an active predator, known for hunting in packs Agilisaurus. This predatory behavior gave it an advantage over its prey, allowing it to take down larger animals that it would not have been able to hunt on its own. Its teeth, combined with its hunting strategy, made the Angaturama a formidable predator and a force to be reckoned with.
The Angaturama was native to the coastal mangrove swamps of Brazil, where it thrived in the warm tropical climate. This unique habitat provided various options for food and shelter, making it the ideal location for this carnivorous dinosaur to rule. As top predators, the Angaturama would have roamed these swamps, taking down large prey and establishing itself as the dominant species in the area.
While the Angaturama was primarily found in Brazil during the late Cretaceous period, its geographical distribution may have extended beyond just this South American country. As a tropical species, the Angaturama may have been found in other areas with similar warm climates, possibly even crossing over into other regions. Unfortunately, due to the limited fossil record, the exact extent of the Angaturama's geographic distribution remains unknown.
One of the most equally intriguing and mysterious aspects of the Angaturama is its speed. Unlike other predatory dinosaurs, there is no evidence to suggest that the Angaturama was an exceptionally fast runner. However, some experts believe that its large size and powerful muscles would have given it the ability to run at high speeds for short distances. This would have been an advantage when hunting in packs, as it would have allowed the Angaturama to quickly and efficiently take down its prey.
It's fascinating to imagine what the Angaturama would have looked like in its native habitat, yet we have very little information about its appearance. Unlike some other dinosaurs, scientists have not uncovered any skin or coloration specimens of the Angaturama. This lack of physical evidence leaves much room for speculation about its skin color and texture. Some experts suggest that it may have had smooth, scaly skin, while others believe it may have had feathers like some other Late Cretaceous dinosaurs. As for its skin color, we can only guess, but due to its tropical habitat, it may have had a vibrant and colorful appearance, providing excellent camouflage in the dense vegetation.
The Angaturama may have also had some unique adaptations to its environment that aided in its survival. For example, its nostrils were positioned high up on its snout, allowing it to breathe while its head was underwater. This feature would have been useful in its coastal swamp habitat, where it would have been surrounded by water.
Unfortunately, like many other dinosaurs, the Angaturama went extinct at the end of the Cretaceous period. Scientists believe that a catastrophic event, such as an asteroid impact, likely caused this extinction. While we may never know for sure, what we do know is that the Angaturama left a significant impact on the world during its reign as a top predator.
In conclusion, the Angaturama was a formidable and ferocious predator that ruled the warm, tropical land of Brazil during the late Cretaceous period. Its sharp teeth, hunting strategy, and size made it a top predator in its native habitat, and its unique adaptations likely aided in its survival. While we may never have a complete picture of what the Angaturama looked like, its existence continues to captivate our imaginations and provide insights into the diverse and fascinating world of dinosaurs.

Angaturama
Dinosaur Details Angaturama - Scientific Name: Angaturama
- Category: Dinosaurs A
- Scientific Name: Angaturama
- Common Name: Angaturama
- Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
- Length: 9-10 meters
- Height: 2-3 meters
- Weight: 2-3 tons
- Diet: Carnivorous
- Feeding Behavior: Active predator
- Predatory Behavior: Hunting in packs
- Tooth Structure: Sharp and serrated teeth
- Native Habitat: Coastal mangrove swamps
- Geographical Distribution: Today's Brazil
- Preferred Temperature: Warm tropical climate
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown
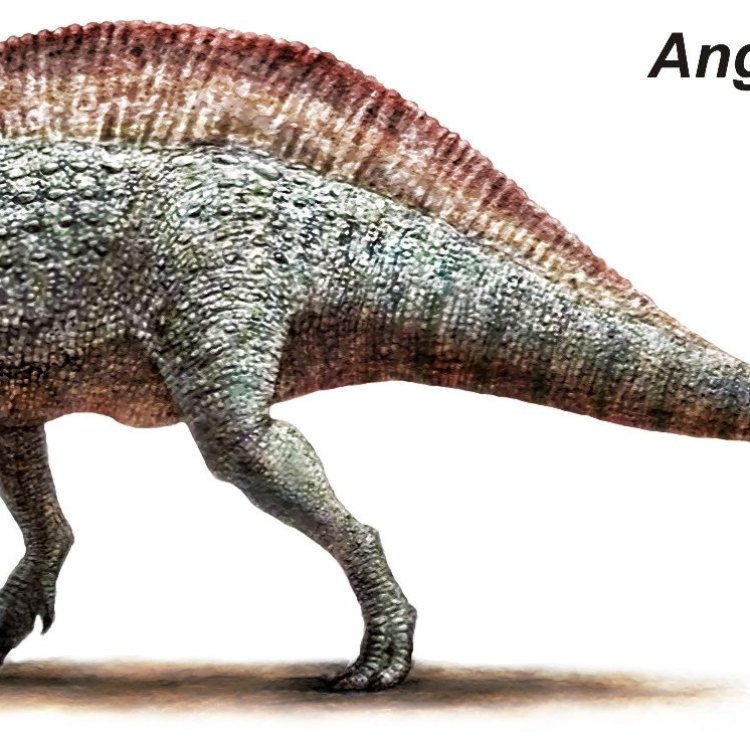
Angaturama
- Bone Structure: Lightweight and hollow bones
- Reproduction Type: Egg laying
- Activity Period: Diurnal
- Distinctive Features: Crest on the top of the head
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Sharp teeth and hunting behavior
- Largest Species: Unknown
- Smallest Species: Unknown
- Fossil Characteristics: Fragmentary remains
- Role in Ecosystem: Top predator
- Unique Facts: Possibly lived in social groups
- Predator Status: Apex predator
- Discovery Location: Brazil
- Discovery Year: 2000
- Discoverer's Name: Alexander Kellner

Angaturama
The Dinosaur with a Crest: Exploring the Unique Features of Angaturama
When we think of dinosaurs, we often imagine giant, fearsome creatures roaming the earth. And while there were certainly plenty of large dinosaur species, there were also smaller, more specialized creatures with their own unique features. One such dinosaur is Angaturama, a species that has intrigued scientists and dinosaur enthusiasts alike since its discovery in 2000.Angaturama, which means "lively beast" in the Tupi language, is a genus of theropod dinosaur that lived during the early Cretaceous period, about 112 million years ago OnTimeAiraz.Com. It is believed to have inhabited what is now modern-day Brazil. While there is still much to learn about this dinosaur, let's explore the known features and characteristics that make Angaturama a truly unique species.
Bone Structure: Lightweight and Hollow Bones
One of the most distinctive features of Angaturama is its bone structure. Unlike many other dinosaurs, its bones are lightweight and hollow. This adaptation is commonly seen in birds, and it is believed that Angaturama's bone structure may have also helped it to fly.
However, it is also possible that these lightweight bones were a result of its habitat. Angaturama is thought to have lived in a wet, swampy environment, and lighter bones would have made it easier for the dinosaur to navigate through the dense vegetation and water.
Reproduction Type: Egg Laying
Angaturama is classified as a member of the Theropoda clade, which includes all types of carnivorous dinosaurs. Like other theropods, Angaturama is believed to have reproduced by laying eggs Arcovenator. Fossil evidence has shown that it may have laid its eggs in nests protected by vegetation, similar to modern birds.
This method of reproduction was likely an evolutionary adaptation that allowed the species to reproduce efficiently and ensure the survival of its offspring.
Activity Period: Diurnal
The activity period of a dinosaur can tell us a lot about its behavior and way of life. While most theropods were thought to be active during both day and night, recent studies have suggested that Angaturama may have been primarily diurnal, meaning it was active during the day.
This is supported by evidence of its lightweight and hollow bones, which would have allowed it to move quickly and efficiently during the daytime. It may have also used its crest as a way to communicate or attract mates during the daytime.
Distinctive Features: Crest on the Top of the Head
Perhaps the most striking feature of Angaturama is the crest that adorns the top of its head. This crest is made up of fused bones and is thought to have been used for display purposes, similar to the crests seen in modern-day birds.
The crest may have also served as a way for Angaturama to communicate with other members of its species, possibly indicating social hierarchy or attracting potential mates. However, the exact function of the crest is still unknown and remains a topic of debate among scientists.
Communication Method: Unknown
While we know that Angaturama had a crest on its head, its communication method is still a mystery. Unlike some other dinosaurs, there is no fossil evidence of any vocalizations or elaborate displays. It is possible that the crest itself was used for communication, or that the species used other methods such as scent or visual cues.
Further research and fossil discoveries are needed to fully understand how Angaturama communicated and interacted with others of its kind.
Survival Adaptation: Sharp Teeth and Hunting Behavior
Like many other theropods, Angaturama was a carnivorous predator. Its sharp, serrated teeth were perfectly suited for tearing through flesh, and its hunting behavior was likely similar to that of modern-day predators.
As an apex predator, Angaturama played an important role in its ecosystem by keeping the population of herbivorous dinosaurs in check. This allowed for a more balanced and stable environment, contributing to the overall diversity of the Cretaceous period.
Largest Species: Unknown
Unfortunately, due to the limited fossil evidence, we do not know the exact size of the largest Angaturama species. However, based on the fragmentary remains that have been discovered, scientists estimate that it was likely around 5 to 6 meters in length.
This would make it a medium-sized theropod, with some larger species such as Tyrannosaurus Rex and some smaller species like Velociraptor.
Smallest Species: Unknown
Similar to the largest species, the size of the smallest Angaturama remains unknown. As with many extinct species, it is possible that there were variations in size within the genus. Further discoveries and research may reveal more about the size range of Angaturama.
Fossil Characteristics: Fragmentary Remains
The fossil remains of Angaturama were initially discovered in 2000 by Alexander Kellner, a prominent Brazilian paleontologist. However, these remains were highly fragmented, making it difficult for scientists to fully understand the anatomy of this dinosaur.
Since then, more fossils have been discovered, including vertebrae, leg bones, and even a nearly complete skull. However, there is still a lot to be discovered about Angaturama, and scientists are actively searching for more fossils to piece together its history and appearance.
Role in Ecosystem: Top Predator
As an apex predator, Angaturama played a crucial role in maintaining the balance of its ecosystem. Its sharp teeth and hunting behavior allowed it to maintain a dominant position in the food chain, ensuring the survival of its species and contributing to the overall health of its environment.
Without the presence of top predators like Angaturama, the delicate balance of the Cretaceous ecosystems may have been disrupted, leading to a decline in biodiversity.
Unique Facts: Possibly Lived in Social Groups
While there is no definitive evidence, some paleontologists have theorized that Angaturama may have lived in social groups. This hypothesis is based on the discovery of multiple individuals in close proximity to each other, as well as a possible nesting site with numerous eggs.
If this is true, it would make Angaturama one of the few known dinosaurs to have lived in groups, similar to modern-day social animals like wolves and lions.
Predator Status: Apex Predator
As mentioned earlier, Angaturama was an apex predator, meaning it was at the top of the food chain in its ecosystem. Its sharp teeth, lightweight bones, and hunting behavior made it a formidable predator that likely played a significant role in shaping its environment.
However, like all apex predators, Angaturama was not invincible and faced threats from other large predators of the time.
Discovery Location: Brazil
All known fossil remains of Angaturama have been discovered in Brazil, specifically in the northeastern part of the country. This area is known for its rich deposits of fossils, including those of other dinosaurs and extinct species.
This location also provides valuable insight into the geographical distribution and diversity of dinosaurs during the early Cretaceous period.
Discovery Year: 2000
The first evidence of Angaturama was discovered in 2000 by Alexander Kellner and colleagues. This discovery was significant as the fragmented remains allowed scientists to identify and name a new genus and species of dinosaur.
Since then, more fossils have been discovered, adding to our knowledge of this fascinating species.
Discoverer's Name: Alexander Kellner
The discoverer of Angaturama, Alexander Kellner, is a well-respected Brazilian paleontologist known for his contributions to the field of paleontology. He has played a major role in the discovery and classification of various new dinosaur species in Brazil.
Thanks to his efforts and those of other scientists, we can continue to learn more about Angaturama and its place in the prehistoric world.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Angaturama is a dinosaur with many unique features and adaptations that make it a fascinating species to study. Its lightweight bones, egg-laying reproduction, diurnal activity, and distinctive crest all contribute to its place in the dinosaur kingdom.
While there is still much to learn about Angaturama, it is clear that this species played a significant role in its ecosystem and adds to the diversity of prehistoric creatures that once roamed the earth. As more fossils are discovered and studied, we may gain a better understanding of this remarkable dinosaur and its place in history.

The Ferocious Angaturama: A Story of a Predatory Dinosaur
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.