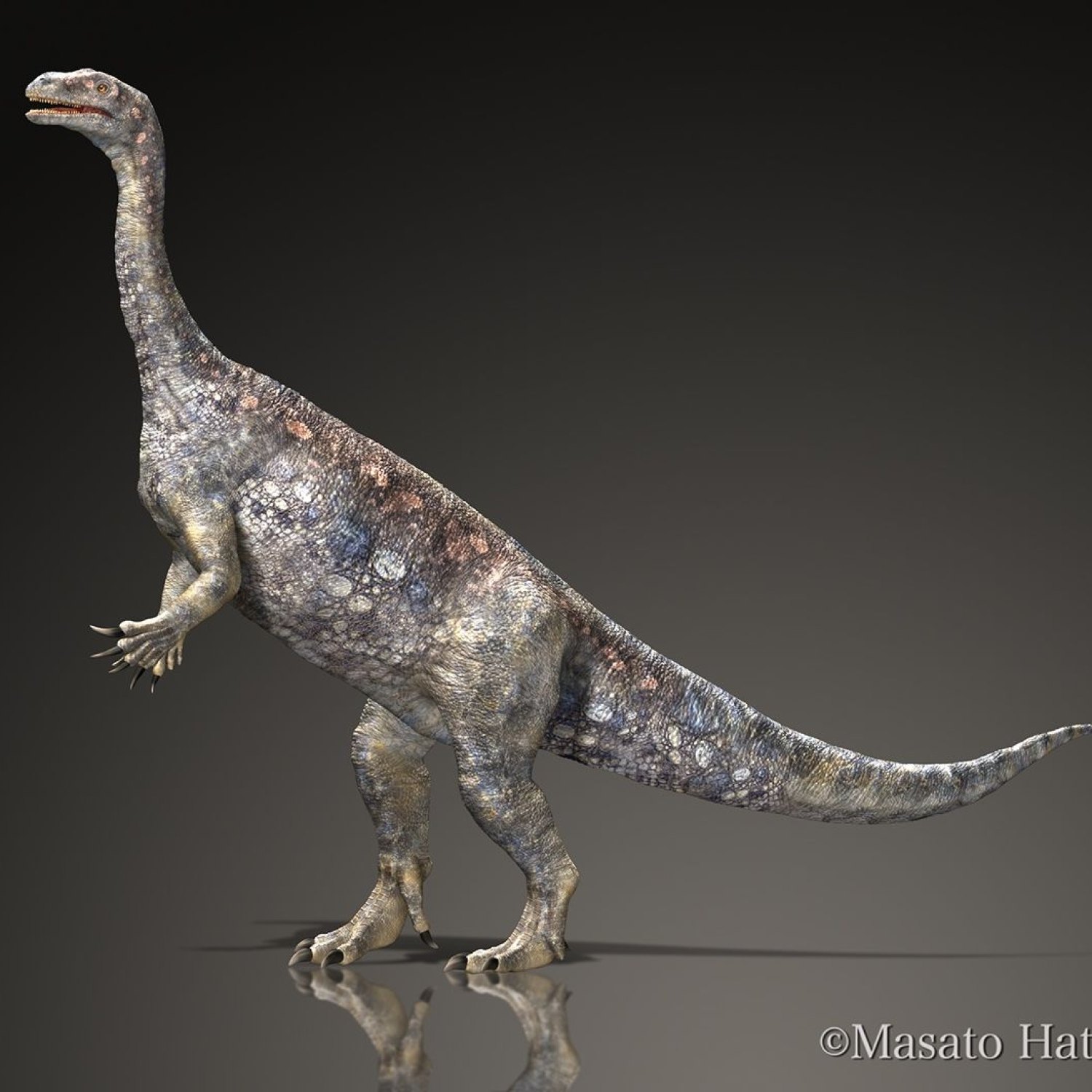
Unaysaurus
Unknown
Unaysaurus, a lesser-known dinosaur from South America, remains a mystery due to its elusive skin color and unknown top speed. This herbivorous creature may not be as famous as T-rex, but its impressive size and diet make it a crucial part of the dinosaur kingdom. #dinosaurs #unaysaurus #southamerica
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Unaysaurus
Geological Era: Middle Triassic
Feeding Behavior: Browsing
Unaysaurus: Discovering the Ancient Herbivore of South America
Imagine walking through the lush forests of South America during the Middle Triassic era, around 240 million years ago. As you wander, you come across a majestic creature, peacefully grazing on leaves and plants with its unique heterodont tooth structure. This was Unaysaurus, a herbivore that roamed the earth long before the dinosaurs even existed.Unaysaurus, whose scientific name means "Unay's lizard," is a fascinating specimen that is relatively unknown to the general public Unaysaurus. However, its discovery has brought us a wealth of information about the ancient history of South America and the diverse species that once inhabited it. In this article, we will dive deep into the world of Unaysaurus, learning about its appearance, behavior, and habitat.
Appearance of Unaysaurus
Unaysaurus was a medium-sized dinosaur, reaching a length of 5 meters and standing at a height of 1.5 meters. It may not sound impressive compared to some of the larger dinosaurs, but for its time, Unaysaurus was a notable creature. It weighed around 500 kg, making it a relatively small herbivore compared to its contemporaries.One of the most interesting features of Unaysaurus was its heterodont tooth structure, which means it had different types of teeth for different purposes. This was a unique trait among herbivores, as most of them have similarly shaped teeth for crushing and grinding plants. Unaysaurus, on the other hand, had teeth that were specialized for specific tasks, such as tearing leaves or cutting plant material Unescoceratops.
Despite its diverse teeth, Unaysaurus had a relatively small head and a slender body, giving it an almost deer-like appearance. Its limbs were also well-muscled, allowing it to move with agility and speed.
Behavior and Diet
As mentioned, Unaysaurus was a herbivore, which means that its diet consisted mainly of plants and vegetation. Its heterodont tooth structure allowed it to efficiently browse on a variety of plant material, from soft leaves to tougher stems. It is believed that Unaysaurus had a flexible neck, enabling it to reach for food in higher branches, giving it an evolutionary advantage over other herbivores.Unaysaurus was also a non-predatory creature, meaning that it did not actively hunt for prey. Instead, it relied on its unique set of teeth and browsing behavior to survive. It was a relatively peaceful creature, and it is unlikely that it engaged in any aggressive behavior towards its own kind or other species.
Habitat and Distribution
Unaysaurus was a terrestrial dinosaur, meaning that it lived on land, not in the water or the air. Its native habitat was South America, specifically in present-day Brazil, during the Middle Triassic era. This was a time when South America was still part of the supercontinent Pangaea, surrounded by vast oceans and primitive landmasses.The geographical distribution of Unaysaurus is limited to South America, with no evidence of its existence in other parts of the world. This is not surprising, as many herbivorous dinosaurs were often confined to a specific region, as they relied on the plants and vegetation in their natural habitat for survival.
Preferred Temperature and Adaptations
As Unaysaurus lived during a time when the Earth was still warming up after the Permian extinction, it is believed that it preferred a warmer climate. This is backed up by the fact that Unaysaurus had a relatively small body size, as larger animals tend to have a harder time regulating their body temperature in warmer climates.Unaysaurus also had some adaptations that helped it survive in its environment. Its long, flexible neck allowed it to reach higher branches for food, and its well-muscled limbs enabled it to move quickly. Additionally, its heterodont tooth structure was a significant adaptation, as it allowed it to efficiently feed on a variety of plants, giving it a competitive edge over other herbivores.
The Discovery of Unaysaurus
Unaysaurus was first discovered in the Dinodontosaurus Assemblage Zone of the Santa Maria Formation in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil, in 1998 by paleontologist Rodrigo Temp Müller. Along with the remains of Unaysaurus, Müller also found the fossils of other dinosaurs, including the famous Staurikosaurus and Herrerasaurus.Staurikosaurus, a carnivorous dinosaur, and Herrerasaurus, a possible omnivore, lived alongside Unaysaurus during the Middle Triassic era. This means that Unaysaurus was part of a diverse ecosystem, sharing the environment with both plant-eating and meat-eating dinosaurs. The discovery of Unaysaurus and other dinosaurs in the same area gives us a glimpse into the paleobiogeography of South America, shedding light on the ancient ecosystems of the region.
Unaysaurus fossils have also been found in other locations in Brazil, including the Rio Grande do Sul and Santa Catarina states. These findings further expand our knowledge of the distribution and habitat of this fascinating herbivore.
The Importance of Unaysaurus in Paleontology
The discovery of Unaysaurus has been crucial in adding to our understanding of the paleobiology of the Middle Triassic era. By studying its fossils, paleontologists have been able to piece together the evolutionary chain of herbivorous dinosaurs, helping us understand the origins of this group of creatures.Additionally, Unaysaurus's unique features, such as its heterodont teeth, provide valuable insight into the evolutionary process of herbivorous dinosaurs. These creatures have evolved to have different teeth shapes and sizes, depending on their diet, and Unaysaurus was one of the first to show this adaptation.
The Legacy of Unaysaurus
Unaysaurus may not be as well-known as some of the other dinosaurs, but its legacy lives on through the valuable information it has provided to paleontologists and researchers. Its fossils have helped us understand the ancient history of South America and the diverse species that once roamed its forests.Furthermore, Unaysaurus serves as a reminder of the vast diversity of life that has existed on our planet and the evolutionary changes that have occurred over millions of years. By studying Unaysaurus and other creatures, we can continue to unravel the mysteries of our past and better understand our present.
As we continue to make new discoveries and learn more about Unaysaurus and other dinosaurs, let us not forget the incredible journey these creatures have taken to become the fossilized remains that we find today. Unaysaurus may have roamed the earth millions of years ago, but it will continue to capture our fascination and curiosity for many years to come.
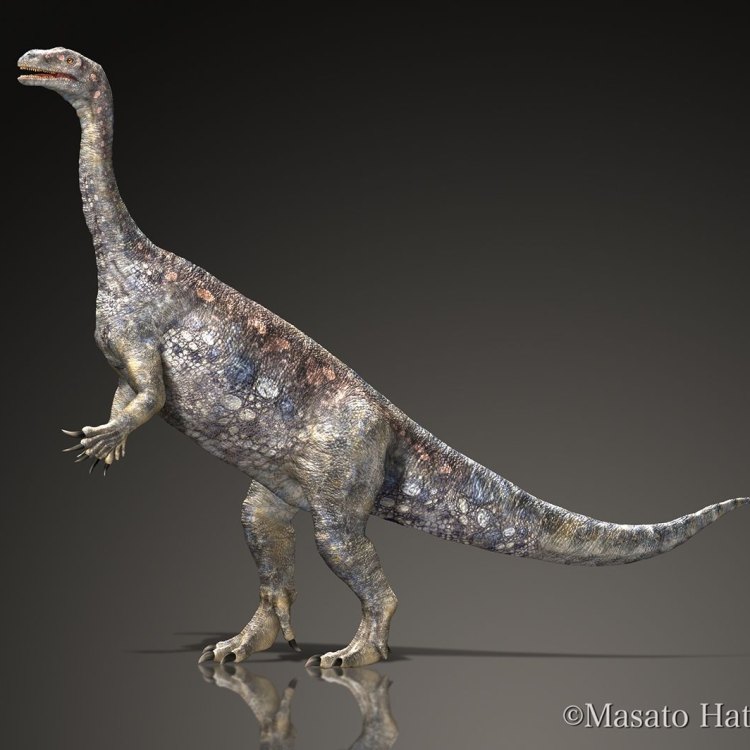

Unaysaurus
Dinosaur Details Unaysaurus - Scientific Name: Unaysaurus
- Category: Dinosaurs U
- Scientific Name: Unaysaurus
- Common Name: Unaysaurus
- Geological Era: Middle Triassic
- Length: 5 meters
- Height: 1.5 meters
- Weight: 500 kg
- Diet: Herbivore
- Feeding Behavior: Browsing
- Predatory Behavior: Non-predatory
- Tooth Structure: Heterodont
- Native Habitat: Terrestrial
- Geographical Distribution: South America
- Preferred Temperature: Warm
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown
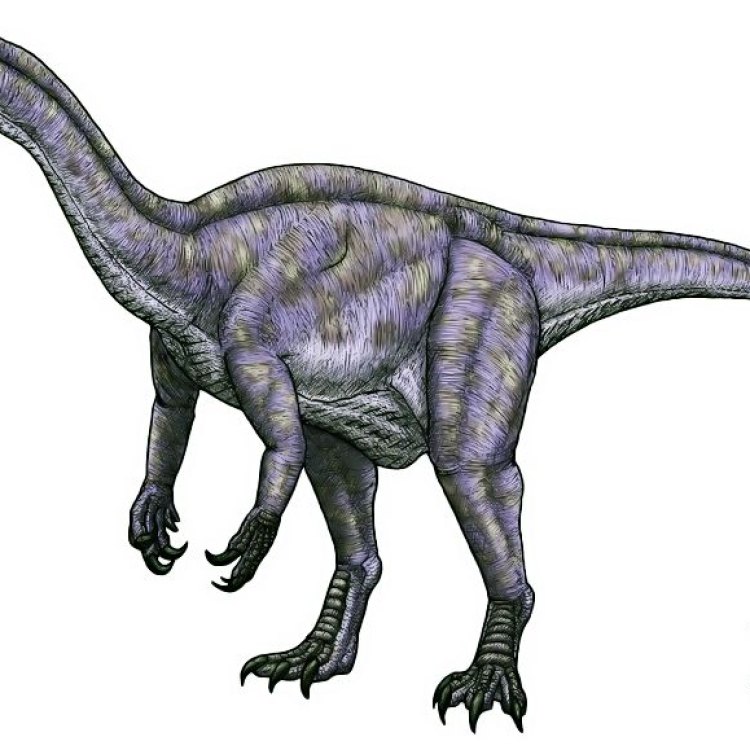
Unaysaurus
- Bone Structure: Largely preserved
- Reproduction Type: Egg-laying
- Activity Period: Diurnal
- Distinctive Features: Large canines, long forelimbs
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Unknown
- Largest Species: Unaysaurus tolentinoi
- Smallest Species: Unaysaurus glaucus
- Fossil Characteristics: Incomplete skeleton
- Role in Ecosystem: Herbivore
- Unique Facts: One of the earliest known dinosaurs from South America
- Predator Status: Non-predatory
- Discovery Location: Brasil
- Discovery Year: 1998
- Discoverer's Name: Rogério N. Soares
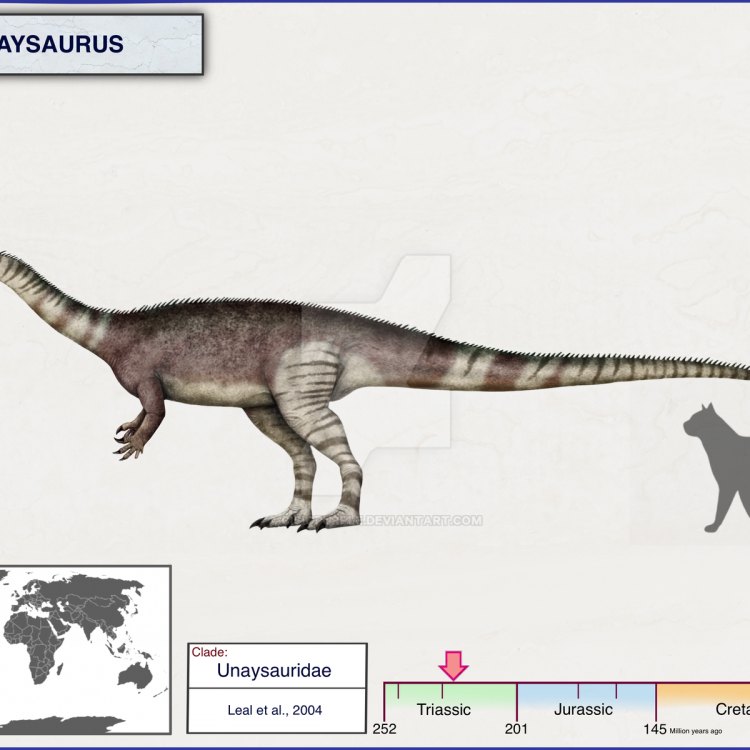
Unaysaurus
The Fascinating Universe of Unaysaurus: Exploring a Prehistoric Dinosaur from South America
The study of dinosaurs and other prehistoric creatures has always been a subject of fascination for scientists and the general public alike. These creatures, who roamed the Earth millions of years ago, have left behind a wealth of information for us to uncover and understand. With new discoveries being made every year, it seems that we are constantly expanding our knowledge about the diverse array of species that existed in the prehistoric world.One such fascinating creature is the Unaysaurus, a unique dinosaur that was discovered in Brazil in 1998 OnTimeAiraz.Com. With its distinctive features and intriguing history, Unaysaurus has captured the attention of paleontologists and dinosaur enthusiasts worldwide. In this article, we will take a deep dive into the world of Unaysaurus, exploring its bone structure, reproduction type, distinctive features, and more.
The Bone Structure and Fossil Characteristics of Unaysaurus
Unaysaurus was a sauropodomorph dinosaur, belonging to the family of primitive herbivorous dinosaurs. Its fossil remains were largely preserved, providing scientists with valuable insights into its physical features and behavior. The largest known species of Unaysaurus, Unaysaurus tolentinoi, is estimated to have reached a length of up to 7 meters (23 feet) and weighed around 300 kilograms (660 pounds). On the other hand, the smallest known species, Unaysaurus glaucus, was significantly smaller in size.
One of the distinct features of Unaysaurus was its long and powerful forelimbs, which were longer than its hind legs. This physical adaptation allowed the dinosaur to use its arms for activities such as foraging and browsing for food, in addition to walking. Unaysaurus also had a long neck, which helped it reach high branches to feed on leaves and foliage Ultrasauros.
The most remarkable aspect of Unaysaurus' bone structure was its large canines. These sharp, pointed teeth were a significant contrast to the flat teeth found in most other sauropodomorph dinosaurs, indicating that Unaysaurus may have had a unique diet. While some experts speculate that Unaysaurus may have been a carnivore, others believe that its canines could have been used for defense or competing with other males during the mating season.
As a herbivorous dinosaur, Unaysaurus would have had a large gut and an incredible digestive system to support its plant-based diet. Its fossil remains also suggest that it could have had a slow metabolism, allowing it to conserve energy and survive in harsh conditions where food was scarce.
However, despite the abundance of Unaysaurus fossils discovered, their skeletons are still incomplete. This means there are still many unanswered questions about the dinosaur's bone structure, behavior, and physical capabilities.
The Reproduction Type, Activity Period, and Communication Methods of Unaysaurus
Unaysaurus was an egg-laying dinosaur, commonly known as an oviparous species. This means that females would have laid eggs and incubated them until they hatched. Its large size may have allowed Unaysaurus to lay a larger number of eggs compared to other smaller dinosaur species.
Based on the bone structure and skeletal remains, Unaysaurus was a diurnal creature, meaning it was active during the day. This is supported by the fact that it had large eyes, suggesting that it relied heavily on its sense of vision to navigate its surroundings and find food.
Unfortunately, due to the incomplete fossils, the communication method of Unaysaurus remains unknown. However, scientists speculate that the large canines and long forelimbs may have been used for display or communication with other members of its species. It is also possible that Unaysaurus had a unique vocalization or body language to communicate with its herd or potential mates.
The Adaptations and Role of Unaysaurus in the Ecosystem
As with any prehistoric creature, survival was a top priority for Unaysaurus. Its large size, long forelimbs, and sharp canines were all adaptations that aided its survival in its habitat. With its long arms, Unaysaurus could reach high branches to feed on plants, while its large canines could have been used for self-defense against predators.
As a herbivore, Unaysaurus played a crucial role in the ecosystem. By consuming plants and vegetation, it helped maintain the balance of the ecosystem and prevent overgrowth. Its large size may have also made it a prime target for larger predators, ensuring that its numbers were kept in check.
The Discovery of Unaysaurus
The first Unaysaurus fossil was discovered in Brasil in 1998 by paleontologist Rogério N. Soares. The name Unaysaurus is derived from the Tupi word "Unui," meaning small, and the Greek word "sauros," meaning lizard. The specific epithet, tolentinoi, is in honor of the geologist Jorge Lacerda de Tolentino, who helped with the excavation of the first fossil.
Since its discovery, several more Unaysaurus fossils have been found in South America, including in Argentina, Uruguay, and Brazil, further adding to our understanding of this unique dinosaur species.
Unique Facts and Legacy of Unaysaurus
Unaysaurus is one of the earliest known dinosaurs from South America, making it a significant find for paleontologists. Its discovery has helped expand our knowledge of the diversity of dinosaurs in South America and their evolution over time.
Unaysaurus is also notable for being one of the few known sauropodomorph dinosaurs with large canines, setting it apart from other herbivorous species. Its unique characteristics have made it a subject of interest for scientists, who are continually studying and trying to unlock the secrets of this prehistoric creature.
The Predator Status of Unaysaurus
While most herbivorous dinosaurs were preyed upon by larger carnivorous species, Unaysaurus is believed to have been a non-predatory dinosaur. Its long forelimbs and sharp canines may have given it a fearsome appearance, but experts believe that it was not actively hunting and feeding on other animals.
Instead, Unaysaurus likely used its sharp canines for defense, either against predators or during rival competitions for a mate. This behavior is not uncommon in the animal world, with many species using elaborate displays and displays of strength when faced with a threat or competing for a partner.
In Conclusion
The discovery of Unaysaurus has added another layer to our understanding of prehistoric creatures and their evolution. Its intriguing bone structure, reproduction type, distinctive features, and other characteristics make it a unique dinosaur worthy of study and fascination. With ongoing research and new discoveries, we can expect to learn even more about this enigmatic species and its role in the South American ecosystem. So, let us continue on the journey of uncovering the mysteries of the fascinating universe of Unaysaurus.

Unaysaurus: Discovering the Ancient Herbivore of South America
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.