Evolution
Unknown
Discover the fierce world of North American carnivorous dinosaurs! From the speedy Velociraptor to the mighty T-Rex, learn about their unknown skin colors and how they evolved to reach speeds of up to 20 mph. The perfect read for any dino lover! #dinosaurs #carnivores #NorthAmerica
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Tyrannosaurus rex
Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
Feeding Behavior: Active predator
Tyrannosaurus Rex: The King of the Dinosaurs
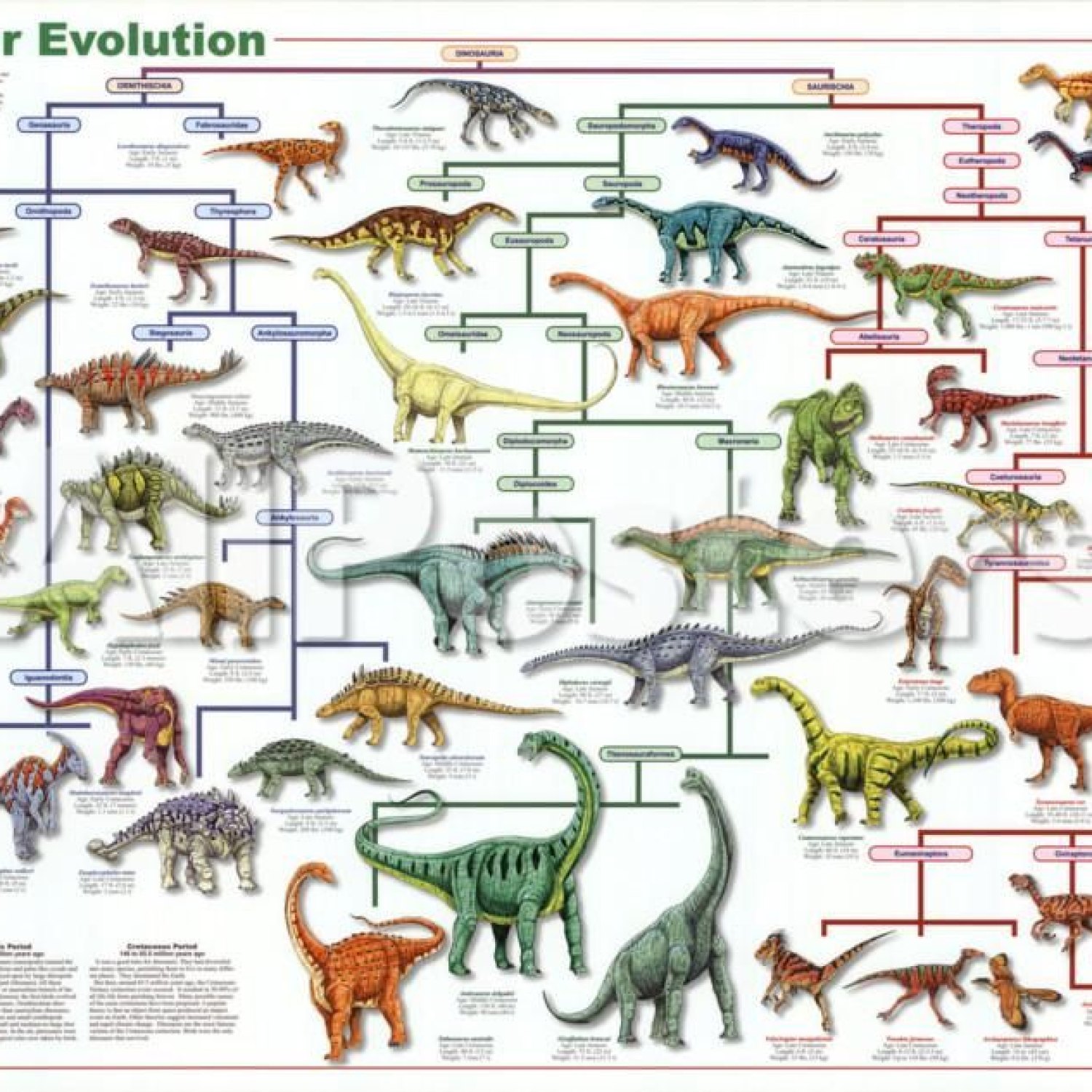
It's hard to discuss dinosaurs without mentioning the most iconic and feared predator of all time - the Tyrannosaurus rex. Known for its massive size, sharp teeth, and formidable presence, this dinosaur has captured the imagination of people for centuries. In this article, we will take a closer look at the evolution, physical characteristics, behavior, and habitat of this ancient creature.Evolution
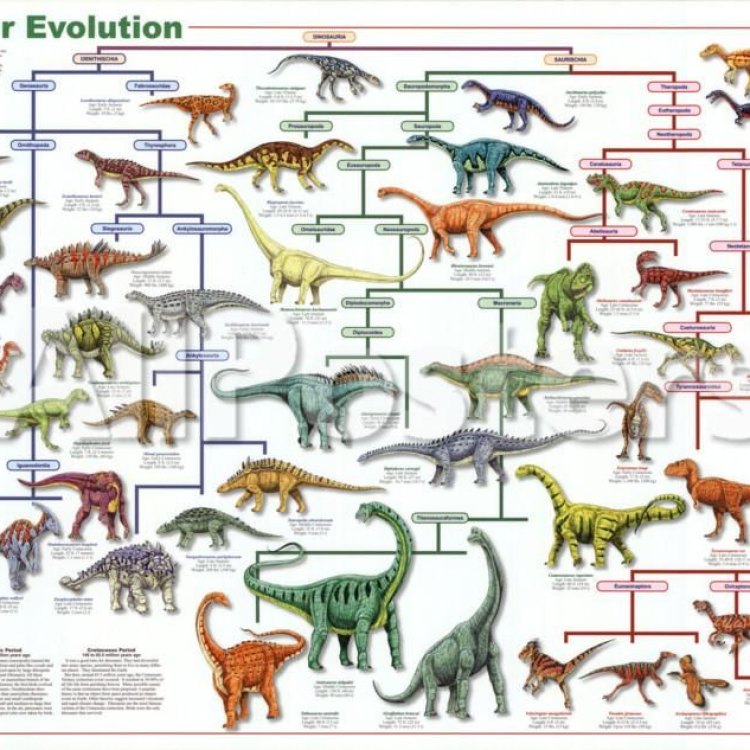
The Tyrannosaurus rex, also known as the "tyrant lizard king," lived approximately 68 to 66 million years ago during the Late Cretaceous period Evolution. Its scientific name is also Tyrannosaurus rex, which comes from the Greek words "tyrannos" meaning tyrant and "sauros" meaning lizard. The name was first given by paleontologist Henry Fairfield Osborn in 1905.The first T. rex fossils were discovered in Montana by legendary paleontologist Barnum Brown in 1902. It wasn't until 1905 that the world got its first glimpse of this giant predator when the American Museum of Natural History unveiled the first mounted skeleton of T. rex.
Over the years, more T. rex fossils have been found in North America, mainly in the western part of the United States. These discoveries have provided scientists with a better understanding of the evolution and biology of this prehistoric creature Epidexipteryx.
Physical Characteristics
T. rex was one of the largest theropod dinosaurs, measuring 12 to 13 meters in length and standing 4 to 6 meters tall at the hips. It weighed anywhere from 5 to 7 tons, making it one of the heaviest land animals to have ever existed. Its powerful legs and muscular tail helped to support its massive frame, allowing it to move and hunt with ease.One of the most distinctive features of T. rex was its head, which could measure up to five feet in length. Its skull was large and had a long, narrow snout with powerful jaws and sharp, serrated teeth. Its teeth were up to six inches long and could exert a force of about 12,000 pounds, making it one of the strongest bites of any animal. This impressive bite force allowed T. rex to quickly tear and crush the bones of its prey.
Despite its size, T. rex had relatively small, two-fingered hands, each with only two claws. The purpose of these small arms is still debated among scientists, with some speculating that they were used to grasp onto struggling prey, while others believe they were too small to be of any use.
Behavior
T. rex was a highly active predator, constantly on the hunt for its next meal. It is estimated that it could cover up to 40 miles per day, making it one of the fastest land predators of its time. Its maximum speed was estimated to be around 20 mph, making it a formidable force to be reckoned with.As an apex predator, T. rex was at the top of the food chain and had no natural predators. Its only competition for food would have been other large carnivorous dinosaurs. Its diet mainly consisted of other dinosaurs, and it's believed that T. rex could consume up to 500 pounds of meat in one bite.
T. rex was an active predator, using its powerful legs to chase down prey and its massive jaws to deliver a deadly bite. Its keen sense of smell and excellent vision allowed it to locate potential targets from a far distance, making it a successful hunter.
Habitat and Distribution
T. rex was primarily found in North America during the Late Cretaceous period, with the majority of fossils discovered in the western part of the continent. It is believed that this dinosaur preferred a warm climate, as fossils have been found in areas with a semi-tropical climate.Due to the fragmented nature of fossils, scientists have had a difficult time determining the exact native habitat and range of T. rex. However, based on the study of its fossils, it's believed that T. rex lived in densely forested areas near rivers and lakes, where it had an abundance of prey.
Conclusion
The Tyrannosaurus rex truly is the king of the dinosaurs. From its sheer size and power to its status as an apex predator, it continues to captivate the imagination of people of all ages. Through the discovery and study of its fossils, we have gained a better understanding of this magnificent creature and its role in the prehistoric world.The T. rex may long be extinct, but its legacy continues to live on through popular culture, scientific research, and our fascination with this ancient giant. As we uncover more about its evolution, behavior, and habitat, we gain a deeper appreciation for this remarkable and fearsome predator.
Evolution
Dinosaur Details Evolution - Scientific Name: Tyrannosaurus rex
- Category: Dinosaurs E
- Scientific Name: Tyrannosaurus rex
- Common Name: Tyrannosaurus rex
- Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
- Length: 12 - 13 meters
- Height: 4 - 6 meters
- Weight: 5 - 7 tons
- Diet: Carnivorous
- Feeding Behavior: Active predator
- Predatory Behavior: Apex predator
- Tooth Structure: Large, sharp, and serrated teeth
- Native Habitat: North America
- Geographical Distribution: North America
- Preferred Temperature: Warm climate
- Maximum Speed: Up to 20 mph
- Skin Color: Unknown
Tyrannosaurus rex
- Bone Structure: Large and strong bones
- Reproduction Type: Egg laying
- Activity Period: Diurnal
- Distinctive Features: Large head, short arms with two fingers
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Excellent sense of smell and vision, strong jaws
- Largest Species: Tyrannosaurus rex
- Smallest Species: Unknown
- Fossil Characteristics: Large, strong teeth and bones
- Role in Ecosystem: Apex predator, regulating the population of herbivorous dinosaurs
- Unique Facts: One of the largest carnivorous dinosaurs
- Predator Status: Apex predator
- Discovery Location: Montana, Wyoming, South Dakota, and Alberta
- Discovery Year: 1902
- Discoverer's Name: Henry Fairfield Osborn

Tyrannosaurus rex
The Fascinating Evolution of the Mighty Tyrannosaurus Rex
The Tyrannosaurus rex, or T. rex for short, is one of the most iconic and well-known dinosaurs in history. Its massive size, powerful jaws, and short, two-fingered arms have captivated the imaginations of people for generations. But beyond its reputation as one of the most fearsome predators to have roamed the earth, the T OnTimeAiraz.Com. rex has a rich evolutionary history that is both fascinating and complex.Throughout this article, we will take a closer look at the evolution of the T. rex, from its bone structure to its unique features and survival adaptations. We will also delve into its role in the ecosystem and its status as an apex predator, as well as the discovery and study of this legendary dinosaur.
The Bones Speak: The Large and Strong Structure of the T. rex
One of the most distinctive features of the T. rex is its large and strong bone structure. This dinosaur was built to be a fierce predator, with its powerful legs and massive frame making it a formidable force in the animal kingdom. The T Erlikosaurus. rex had one of the strongest bite forces of any land animal, with its jaws able to exert a force of 8,000 pounds – enough to crush bone and even metal.This strength was made possible by the T. rex's robust bones, which were thick and sturdy, able to withstand its powerful movements and enormous weight. The bones were also filled with air pockets, making them lighter and allowing the T. rex to move more quickly and efficiently.
But it wasn't just the size and strength of the T. rex's bones that made it such a formidable predator. The structure of its bones also contributed to its agility and speed, giving it the ability to chase down its prey with ease. Its legs were positioned directly underneath its body, providing balance and stability, while its tail acted as a counterbalance, allowing for quick turns and sharp movements.
Egg Laying: The Unique Reproduction Method of the T. rex
Like all dinosaurs, the T. rex was an egg-laying species. This reproductive method is known as oviparity and is still widely used by many animals today. However, unlike modern birds, who lay eggs in nests, the T. rex's eggs were laid in underground nests.The average T. rex egg measured about 43 centimeters long and 14 centimeters wide – roughly the size of a cantaloupe. This may seem large, but considering the size of the T. rex, it was actually quite small. It is believed that the T. rex laid several eggs at a time, similar to modern reptiles, with the nest acting as a temporary nursery for their young.
The Diurnal Lifestyle of the T. rex
The T. rex was a diurnal species, meaning that it was most active during the day and slept at night. This is in contrast to some other dinosaurs who were nocturnal or crepuscular (active at dawn and dusk).Being diurnal allowed the T. rex to take advantage of the full spectrum of light available during the day, giving it better visibility and the ability to hunt and defend its territory more effectively. It also meant that the T. rex had to compete with other diurnal predators, such as other carnivorous dinosaurs, for food and resources.
Distinctive Features: The Large Head and Short Arms of the T. rex
The T. rex had numerous distinctive features that set it apart from other dinosaurs. Its head, for example, was massive, measuring up to five feet long and containing over 50 teeth – the largest of any known carnivorous dinosaur.But perhaps the most iconic feature of the T. rex was its short arms, with only two fingers on each hand. This may seem odd for such a large and powerful predator, but scientists believe that these arms were used for grasping and holding onto prey, rather than for active hunting.
The Mystery of Communication: How Did the T. rex Communicate?
One aspect of the T. rex that remains a mystery to scientists is its method of communication. While we know that many animals, including dinosaurs, use vocalizations, body language, and other methods to communicate with each other, there is no evidence of how the T. rex communicated.Some theories suggest that they may have used low-frequency sounds that humans cannot hear, similar to modern elephants, while others propose that they may have had visual displays or chemical signals. However, until more evidence is found, the communication methods of the T. rex will remain a mystery.
Survival Adaptations: The T. rex's Excellent Sense of Smell and Vision
Despite its already formidable features, the T. rex also had excellent survival adaptations that made it a successful and efficient predator. Its sense of smell, in particular, was highly developed, thanks to its large nasal passage and olfactory bulbs. It is estimated that the T. rex had a sense of smell 13 times more powerful than that of a bloodhound.The T. rex also had excellent vision, with forward-facing eyes that gave it depth perception and the ability to focus on prey from a distance. Its eyes were also adapted to low light conditions, allowing it to see and hunt during the dimmer periods of the day.
Another notable survival adaptation of the T. rex was its strong jaws. In addition to its powerful bite force, the T. rex had teeth that were continuously replaced throughout its lifetime, making it easier for the dinosaur to consume its prey without worrying about losing a tooth.
The Largest Known Carnivorous Dinosaur: Interesting Facts About the T. rex
Standing up to 20 feet tall and weighing over 9 tons, there's no denying that the T. rex was a massive beast. But did you know that it is also known as one of the largest carnivorous dinosaurs ever to exist?The T. rex was not only the largest of the tyrannosaurid dinosaurs, but it was also one of the largest land carnivores to ever roam the earth. Its closest rival in size was the Gigantosaurus, which roamed South America at the same time as the T. rex but was still slightly smaller.
Apex Predator: The T. rex's Role in the Ecosystem
As an apex predator, the T. rex played a crucial role in regulating the population of herbivorous dinosaurs, acting as a top-down control on the food chain. By keeping the numbers of herbivores in check, the T. rex helped to maintain a balance in the ecosystem and prevent overgrazing and habitat destruction.The T. rex also played an important role in nutrient cycling, as their large carcasses provided food for scavengers and helped to fertilize the soil. Without the T. rex, the ecosystem of the Cretaceous period would have looked very different.
Fossil Characteristics: The Clues Left Behind by the T. rex
The T. rex is one of the most well-studied dinosaurs in history, thanks in large part to the numerous fossils that have been discovered. These fossils contain important clues and information that have helped scientists to understand the T. rex's appearance, behavior, and evolution.Most T. rex fossils consist of large, strong teeth and bones, with some also containing remnants of soft tissue. These soft tissues have provided valuable insights into the T. rex's biology and have even allowed scientists to extract and analyze DNA samples, giving us a better understanding of this incredible creature.
The Discovery and Study of the T. rex
The first T. rex fossil was discovered in 1902 by paleontologist Henry Fairfield Osborn in Montana, but it wasn't until the 1960s and 1970s that more complete specimens were found. Since then, countless fossils have been discovered and studied, shedding more light on the T. rex's evolutionary history and behavior.Through careful examination of these fossils, scientists have been able to piece together how the T. rex lived and evolved over millions of years. And while much is still unknown, the study of the T. rex continues to be a fascinating and ongoing subject of research.
The Legacy of the Mighty T. rex
Today, the T. rex continues to capture our imagination and inspire us with its incredible size, strength, and intelligence. Its iconic status in pop culture and its importance in scientific research make it one of the most remarkable and beloved dinosaurs in history.As we continue to unearth more evidence and learn more about this fascinating creature, one thing is for sure – the T. rex will continue to fascinate and captivate us for generations to come.

Tyrannosaurus Rex: The King of the Dinosaurs
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.