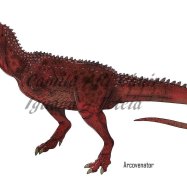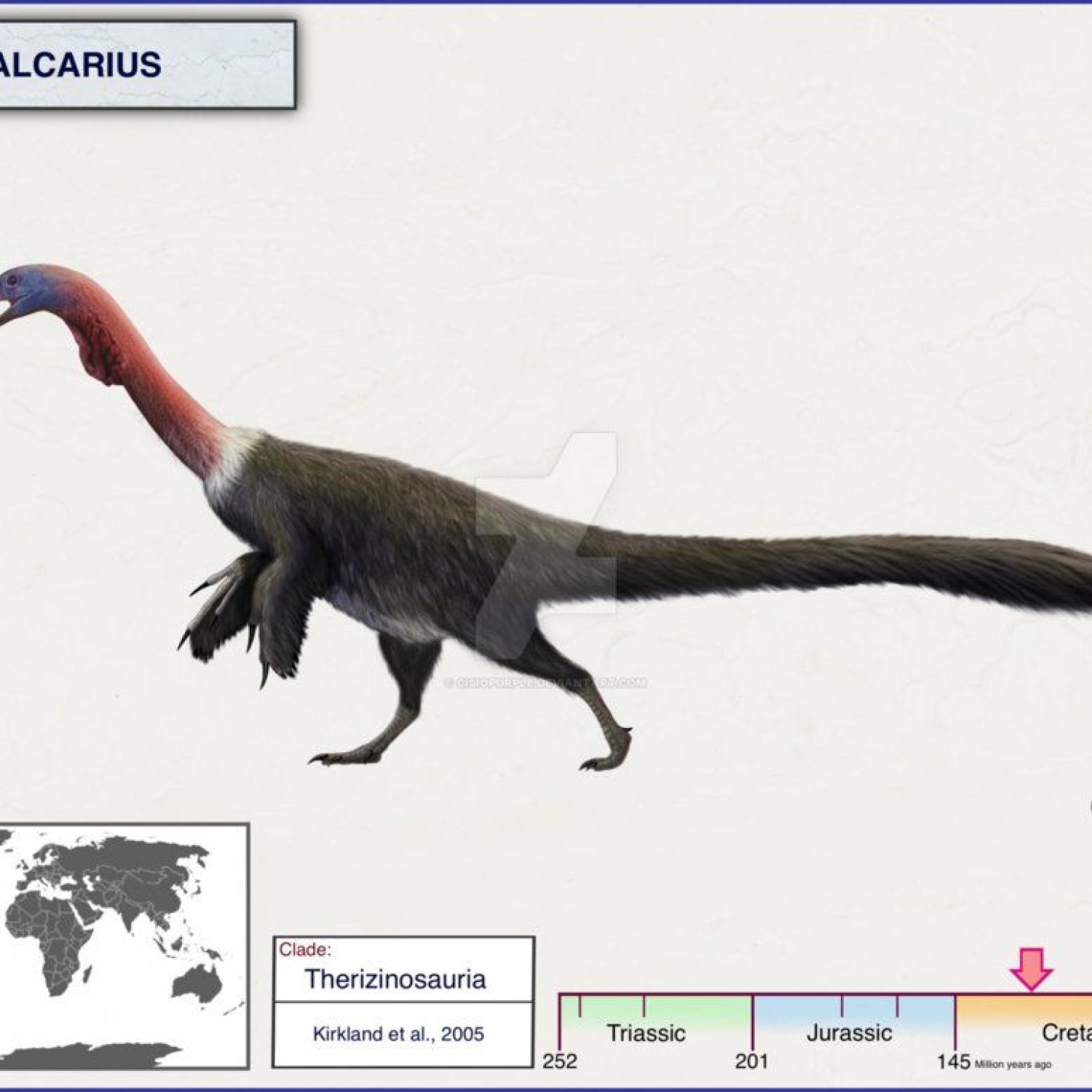
Falcarius
Unknown
Falcarius is a lesser-known dinosaur from North America that roamed the Earth millions of years ago. As an herbivore, it fed on plants and its skin color remains a mystery. While its maximum speed is unknown, this unique dinosaur is believed to have been an important part of the ecosystem in its time. Learn more about Falcarius and other fascinating dinosaurs from North America. #Dinosaurs #NorthAmerica #Falcarius #PrehistoricCreatures
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Falcarius
Geological Era: Early Cretaceous
Feeding Behavior: Browsing
Falcarius: The Mysterious Dinosaur of the Early Cretaceous Era
The world of dinosaurs is full of familiar names like T-Rex, Stegosaurus, and Velociraptor. But there are also lesser-known creatures that played a crucial role in the ecosystem of their time. One such dinosaur is Falcarius, a unique creature that roamed the Earth during the Early Cretaceous period. This captivating and mysterious dinosaur has intrigued scientists and paleontologists for decades, and in this article, we will uncover the secrets of Falcarius Falcarius.Falcarius utahensis, commonly known as Falcarius, is a therizinosaurid dinosaur that lived in present-day North America, about 125 million years ago. Excitingly, this dinosaur was discovered by accident, giving us a small glimpse into the fascinating world of these ancient creatures.
Discovering Falcarius
In 1999, a team of paleontologists was searching for potential fossil sites in eastern Utah when they stumbled upon a skull fragment of a therizinosaurid dinosaur. This discovery puzzled the team as therizinosaurids were rarely found in North America. Further excavations revealed more bones, and after years of study, the findings were finally published in 2005, naming the dinosaur Falcarius utahensis.But why was this discovery so significant? Falcarius provided a missing link in the evolutionary chain of therizinosaurids. This dinosaur had a combination of features that were seen in both their ancestors and descendants, making it a crucial piece of evidence in understanding the evolution of therizinosaurids.
The Physical Description of Falcarius
Falcarius is estimated to have been around 4-5 meters in length, about the size of a modern-day elephant. It stood at 1 Futalognkosaurus.2 meters tall, and its weight ranged between 200-300 kilograms. These statistics make it a relatively small and lightweight dinosaur compared to others of its time.One of the most distinctive features of Falcarius is its long and slender arms with three-fingered hands. This unique feature gave the dinosaur its name, as "falcarius" means sickle in Latin, referring to the sickle-shaped claws on its hands. These claws were used for various purposes, but more on that later.
Its body was covered in feathers, making it one of the earliest feathered dinosaurs ever discovered. However, the color of its skin is still a mystery, as soft tissues like skin and feathers rarely preserve in fossil records.
The Diet and Feeding Behavior of Falcarius
Falcarius was primarily a herbivore, which means it mainly fed on plants and vegetation. Unlike its theropod relatives, Falcarius did not have sharp teeth used for tearing meat. Instead, it had leaf-shaped teeth that were perfect for stripping leaves and twigs off branches.But what's truly fascinating about Falcarius is its unique feeding behavior. Unlike most herbivorous dinosaurs, it was not a grazer. Falcarius had a browsing behavior, which means it would pluck leaves and eat them off branches, similar to a modern-day giraffe.
This browsing behavior, along with its sickle claws and feathered arms, suggests that Falcarius could also climb trees, making it one of the only known dinosaurs to have this ability. This was a groundbreaking discovery, as climbing abilities were previously only seen in smaller dinosaurs like Therizinosaurus.
Not a Predator, but Definitely Not Defenseless
Unlike some of its carnivorous counterparts, Falcarius was not a predator. Its herbivorous diet and lack of sharp claws and teeth suggest that it did not hunt other animals. But that doesn't mean it was defenseless.As mentioned earlier, Falcarius had sickle claws on its hands that were used for various purposes. Its long arms and sickle claws were perfect for reaching and pulling down branches to feed on. But these claws were also used for defense.
Falcarius would often use its sickle claws to fend off predators, and it would not hesitate to use them if provoked. Its tall and slender body, along with its climbing abilities, also allowed it to retreat to the safety of treetops if threatened.
The Native Habitat and Geographical Distribution of Falcarius
Falcarius was a terrestrial dinosaur, meaning it lived on land. Its fossils were found in eastern Utah, indicating that it was native to the North American region. During the Early Cretaceous period, North America had a moderate climate, with temperatures ranging between 59-75 degrees Fahrenheit.This moderate temperature was ideal for Falcarius, as it preferred moderate temperatures in its habitat. However, it is also possible that this dinosaur migrated to other regions during harsh weather conditions, as many modern-day animals do.
The Mysterious Speed and Skin Color of Falcarius
While we know a lot about Falcarius, there are still many mysteries surrounding this dinosaur. One of them is its maximum speed. As of now, there is no concrete evidence to determine how fast Falcarius could run. However, its slender body and long legs suggest that it could move relatively fast when needed.Another mystery is the color of its skin. As mentioned earlier, soft tissues rarely preserve in fossils, making it challenging to determine the color of its skin. However, its feathered arms give us some clues. As per a study published in the journal Evolution, the feathers of therizinosaurids were likely reddish-brown, similar to those of modern-day roadrunners. This could mean that Falcarius had a similar color of feathers, but we can never be sure.
The Legacy of Falcarius
As a relatively new discovery, Falcarius is slowly making its mark in the world of dinosaurs. However, its significance and contribution to our understanding of therizinosaurids are massive. Its unique features, such as its browsing behavior and sickle claws, have given us a new perspective on the evolution and diversity of dinosaurs.Furthermore, Falcarius has become a popular subject for scientific studies and reconstructions, with new discoveries and theories emerging every year. Its mysterious yet captivating nature continues to pique the interest of both scientists and the general public, making it a truly remarkable dinosaur.
The Final Verdict
Falcarius may not be as famous as its larger and more well-known relatives, but it is undoubtedly a unique and intriguing dinosaur that has left an impact on the scientific community. Its slender body, sickle claws, and feathered arms make it stand out among the rest, and its role in the ecosystem of the Early Cretaceous period cannot be underestimated.With more research and discoveries, we can only hope to unravel more mysteries surrounding Falcarius and add to its already impressive legacy. But one thing is for sure, this mysterious dinosaur has captured the hearts and minds of many and continues to fascinate us even millions of years after its extinction.
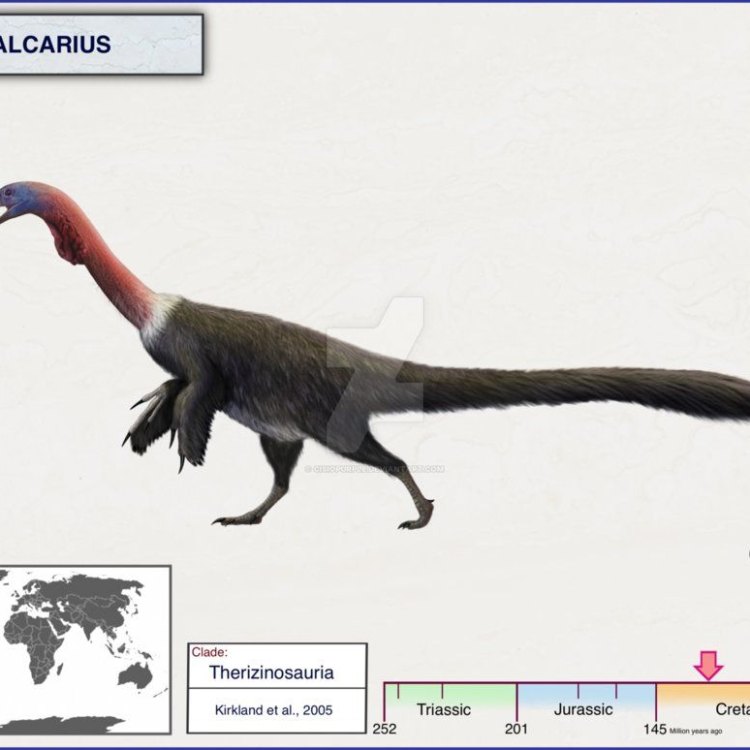
Falcarius
Dinosaur Details Falcarius - Scientific Name: Falcarius utahensis
- Category: Dinosaurs F
- Scientific Name: Falcarius utahensis
- Common Name: Falcarius
- Geological Era: Early Cretaceous
- Length: 4-5 meters
- Height: 1.2 meters
- Weight: 200-300 kilograms
- Diet: Herbivore
- Feeding Behavior: Browsing
- Predatory Behavior: Not predatory
- Tooth Structure: Leaf-shaped teeth
- Native Habitat: Terrestrial
- Geographical Distribution: North America
- Preferred Temperature: Moderate temperatures
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown
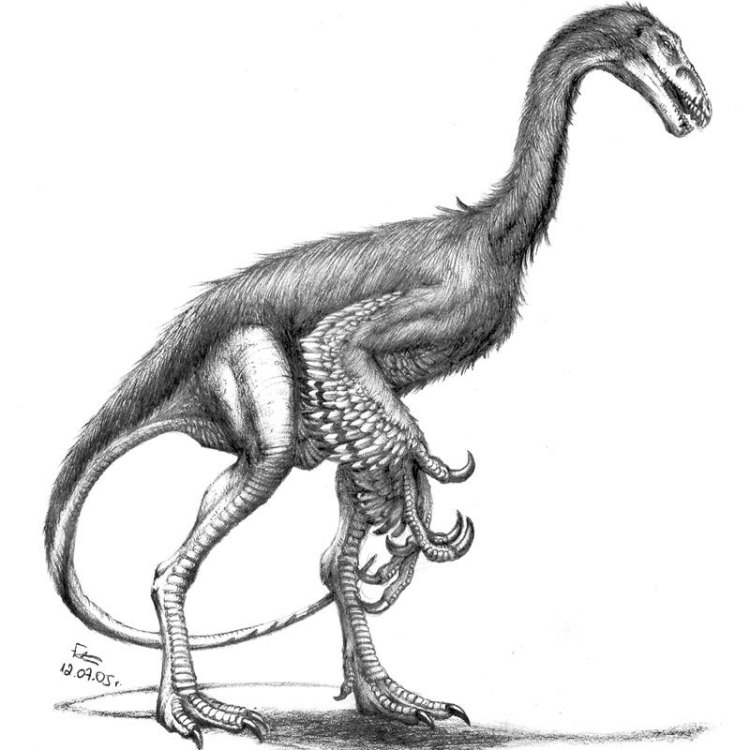
Falcarius
- Bone Structure: Bird-like
- Reproduction Type: Egg-laying
- Activity Period: Unknown
- Distinctive Features: Long arms with sharp, curved claws
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Unknown
- Largest Species: Falcarius utahensis
- Smallest Species: Falcarius utahensis
- Fossil Characteristics: Partial skeletons
- Role in Ecosystem: Herbivorous dinosaur in a Cretaceous ecosystem
- Unique Facts: Possessed a mixture of theropod and herbivorous dinosaur features
- Predator Status: Non-predatory
- Discovery Location: Utah, United States
- Discovery Year: 1999
- Discoverer's Name: James Kirkland
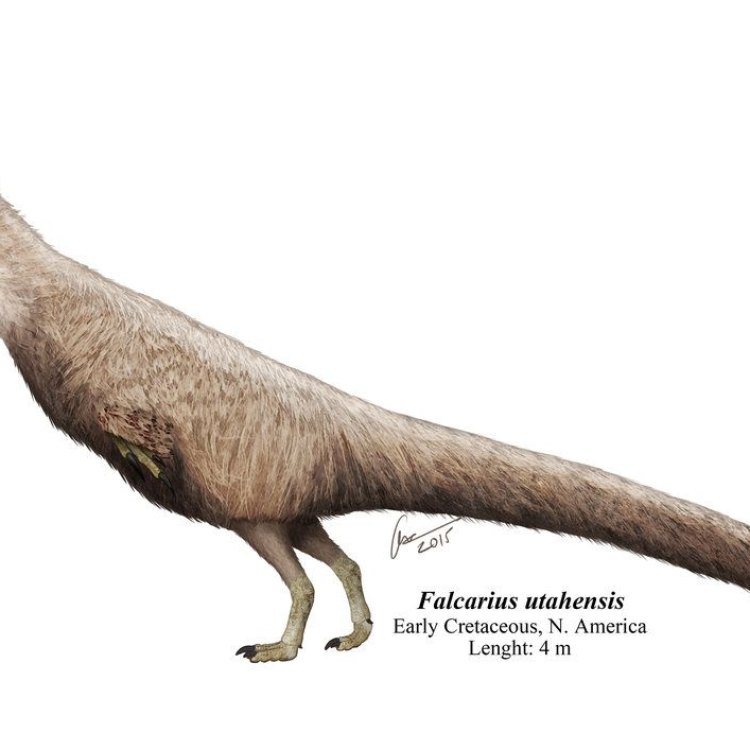
Falcarius utahensis
The Unique Fossil of Falcarius: A Fascinating Hybrid Dinosaur
The world of dinosaurs is full of fascinating creatures, each with their own distinct features and behaviors. One such dinosaur is the Falcarius, a unique species that has captured the attention of researchers and dinosaur enthusiasts since its discovery in 1999 by James Kirkland in Utah, United States.Falcarius belongs to a group of dinosaurs known as therizinosaurs, which are characterized by their bird-like bone structure and egg-laying reproductive method. This herbivorous dinosaur had a long neck and small head, with a mixture of both theropod and herbivorous dinosaur features, making it stand out from any other species OnTimeAiraz.Com.
Let's dive deeper into the details of Falcarius and uncover the mysteries surrounding this intriguing dinosaur.
Bird-like Bone Structure
One of the most distinctive and unusual features of Falcarius is its bird-like bone structure. Unlike other therizinosaurs, which had heavy and bulky bones, Falcarius had hollow, bird-like bones that helped reduce its weight, making it swift and agile.This unique bone structure also enabled Falcarius to move their forelimbs more freely, giving them a wider range of motion. This characteristic is especially evident in their long arms, which were equipped with sharp, curved claws.
Egg-laying Reproduction
Like most dinosaurs, Falcarius reproduced through egg-laying, also known as oviparity. This method of reproduction is more commonly seen in birds and reptiles, making it another interesting feature of this dinosaur.Falcarius eggs were likely laid in nests on the ground or in bushes, and it is believed that the parents did not care for their young after hatching. This is another similarity between Falcarius and modern-day birds, as most bird species do not provide parental care after the eggs hatch Fruitadens.
Unknown Activity Period and Communication Method
As with many extinct species, there is limited information about the activity period and communication methods of Falcarius. Due to their bird-like bone structure, it is assumed that they were diurnal (active during the day) and may have used vocalizations for communication. However, this is just speculation, and further research is needed to confirm these theories.Survival Adaptations
The survival adaptations of Falcarius are still unknown and a subject of ongoing research. However, based on their unique features, we can make some assumptions.Their swift and agile movements, as well as their sharp claws, may have been used for self-defense against predators. Their lightweight bone structure also suggested that they may have been fast runners, helping them escape danger. Additionally, their herbivorous diet may have also played a role in their survival, as they were not competing with other carnivorous dinosaurs for food.
The Largest and Smallest Species of Falcarius
The largest and smallest species of Falcarius is actually the same – Falcarius utahensis. The only fossil specimens that have been found belong to this species, which was estimated to be around 4-5 meters in length and weigh about 500 pounds. Despite being the only known species, Falcarius utahensis has provided a wealth of information about this unique dinosaur.Fossil Characteristics
The fossil remains of Falcarius have been found in Utah, mainly in the Cedar Mountain Formation, which dates back to the early Cretaceous period, around 125 million years ago. Most of the fossil specimens discovered are partial skeletons, containing mostly bones from the arms and upper body.Interestingly, there is also evidence that suggests Falcarius may have lived near a water source, as the fossils were found in clays and mudstones, indicating an aquatic environment. This brings another aspect to the mystery surrounding Falcarius and its role in the ecosystem.
Role in the Ecosystem
As an herbivorous dinosaur, Falcarius played an essential role in the ecosystem during the Cretaceous period. They were essential in maintaining a balance between predators and prey, as well as dispersing seeds through their droppings.Additionally, their unique features and behaviors would have made them stand out from other dinosaurs, adding diversity to the ecosystem. Sadly, with their extinction, a piece of this complex and dynamic ecosystem disappeared forever.
Non-Predatory Status
Another interesting fact about Falcarius is that it was a non-predatory dinosaur. Unlike many of its therizinosaur relatives, which were fierce predators, Falcarius was an herbivore and had no predatory instincts or abilities. This sets it apart from many other therizinosaurs and makes it a unique example within this fascinating group of dinosaurs.The Discovery of Falcarius
Falcarius was first described and named in 2005 by James Kirkland, who discovered the first fossil remains of this species in Utah in 1999. It is believed that these fossils belonged to a herd of Falcarius that perished together in a catastrophic event, possibly a flood.The fact that the only known specimens of Falcarius were found together in one location adds to the mystery surrounding this fascinating dinosaur. Without Kirkland's discovery and subsequent research, we may never have known about the existence of Falcarius.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, Falcarius is a unique and fascinating dinosaur that has captured the attention of researchers and dinosaur enthusiasts for over two decades. Its strange mixture of theropod and herbivorous features, as well as its unknown behaviors and adaptations, make it a captivating subject for study.Through its discovery, we have gained insight into the diverse world of dinosaurs, and Falcarius has become an essential piece of the puzzle to understanding the evolution and diversity of these ancient creatures. As research continues, we may uncover more secrets and information about Falcarius, and shed light on its role in the complex ecosystem of the early Cretaceous period.
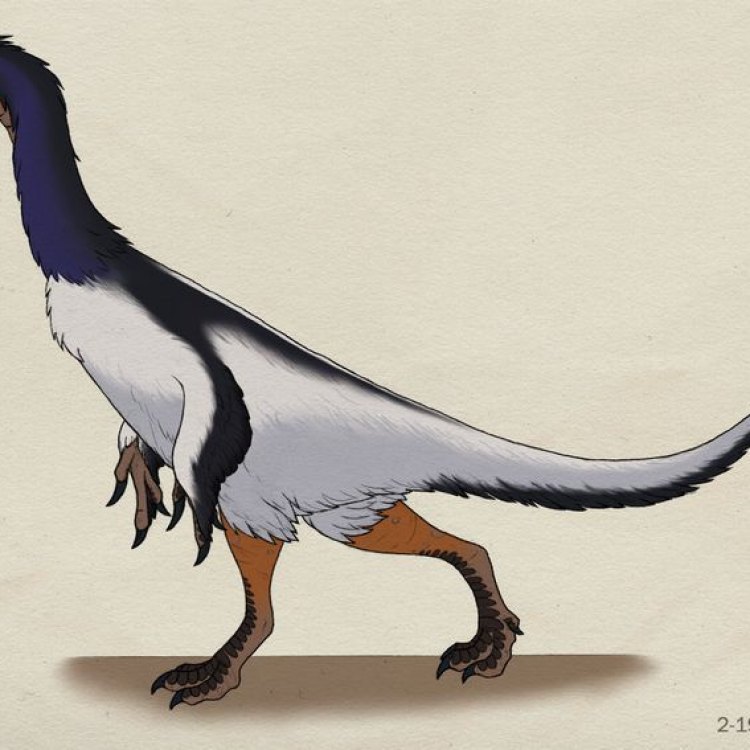

Falcarius: The Mysterious Dinosaur of the Early Cretaceous Era
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.