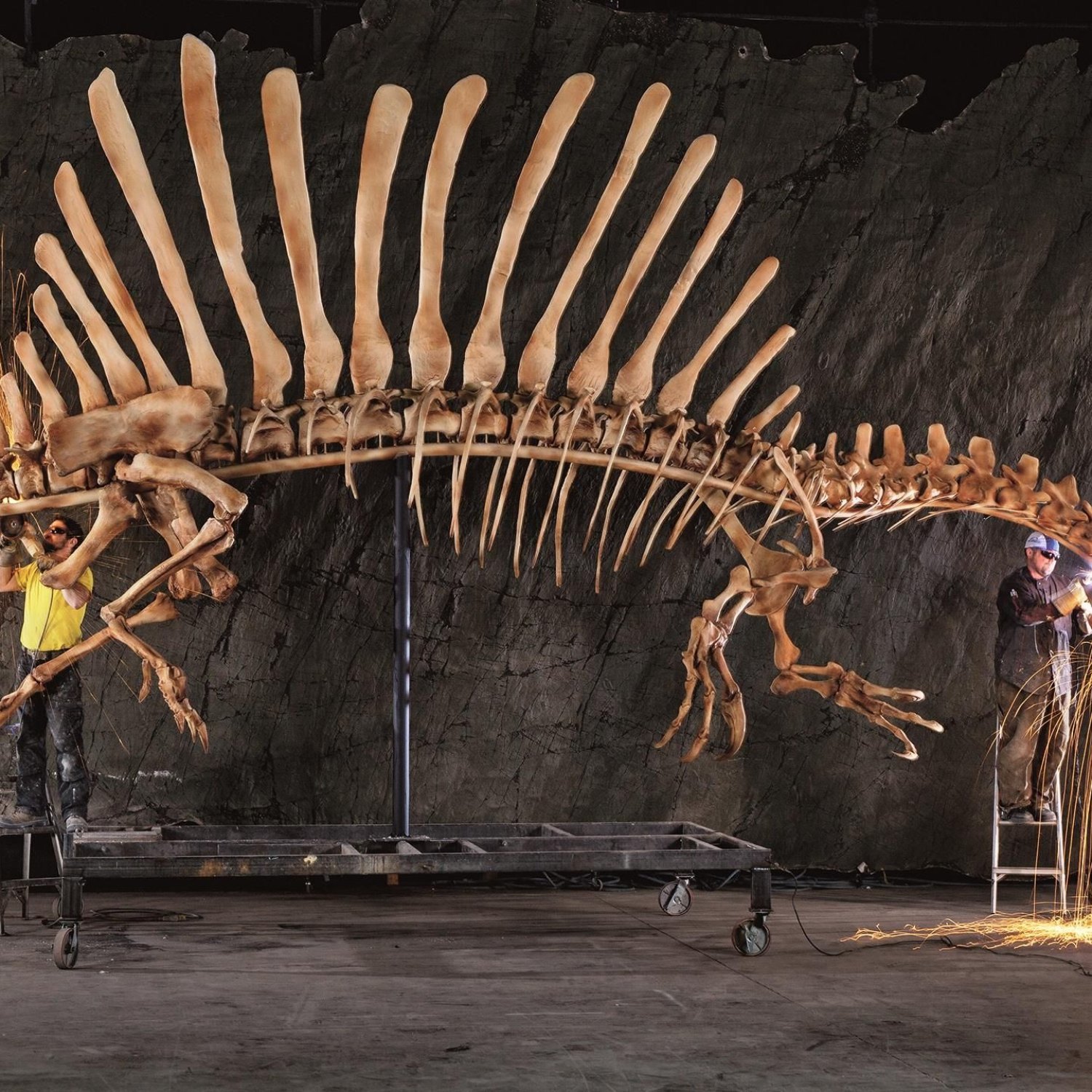
Fossil Type
Fossil Type
Meet the fiery T. rex, a carnivorous dinosaur with a whopping top speed of 20 mph! With its iconic skin color and widespread distribution in North America, this powerful predator ruled the land during the Cretaceous Period. Discover more about this fascinating fossil type and its fearsome diet in our latest article. #Trex #Cretaceous #FossilFinds #DinoFacts
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Fossil Type
Geological Era: Fossil Type
Feeding Behavior: Fossil Type
The Mighty Tyrannosaurus Rex: Exploring the King of the Dinosaurs
Millions of years ago, the world was a very different place. Vast continents collided and broke apart, oceans rose and fell, and the Earth was inhabited by creatures that are now only known through fossil records. Among these ancient creatures, there is one that stands out as the most iconic and feared of them all - the Tyrannosaurus Rex, or T. rex for short Fossil Type.This monstrous dinosaur has fascinated scientists and captured the imagination of people for decades. Its impressive size and sharp teeth have made it one of the most well-known dinosaurs in history. In this article, we will explore the standout features of this mighty reptile and discover what made it such a fearsome predator.
The Basics: What is a Tyrannosaurus Rex?
The name Tyrannosaurus Rex comes from the Greek words "tyrannos" meaning tyrant and "sauros" meaning lizard. Translated, it means "Tyrant Lizard King," which is a fitting name for this colossal beast. T. rex was a large carnivorous dinosaur that roamed the Earth during the Late Cretaceous period, about 68 to 66 million years ago.This fearsome predator was first discovered in 1902 in Montana, United States, by American paleontologist Barnum Brown. Since then, numerous T Fossil Location. rex fossils have been found in different parts of the world, including Canada and Patagonia.
Mighty Size and Impressive Stats
The T. rex was an incredibly large creature, measuring approximately 12 to 13 meters (40 to 43 feet) in length and standing at about 4 meters (13 feet) tall. It is estimated to have weighed around 5 to 7 tons, making it one of the heaviest land predators ever known.This massive size was supported by its powerful legs and muscular body, allowing it to move at impressive speeds. Scientists believe that the T. rex could reach a maximum speed of 18 miles per hour, which is considered fast for an animal of its size.
A Carnivorous Diet
The T. rex was a fierce predator and a top-of-the-food-chain carnivore. Its diet mainly consisted of other dinosaurs, such as hadrosaurs and ceratopsians, as well as smaller reptiles and mammals.One of the standout features of the T. rex was its massive jaws and sharp, serrated teeth, perfectly designed for tearing through flesh and crushing bones. It is estimated that an adult T. rex could exert a bite force of up to 12,800 pounds, which is the equivalent of a medium-sized elephant standing on a person's chest.
Feeding and Predatory Behavior
The T. rex was a formidable predator, and its feeding behavior was efficient and ruthless. Its massive size and powerful limbs allowed it to hunt down and overpower its prey with ease. Scientists believe that the T. rex was a solitary hunter and would ambush its prey with its powerful bite.One of the most distinctive features of the T. rex was its tiny arms, which have puzzled scientists for years. Some theories suggest that these arms were used for grasping onto mating partners or for holding onto prey while the T. rex tore into its flesh with its powerful jaws.
The T. Rex's Tooth Structure
The T. rex's impressive teeth were crucial to its success as a predator. It had about 50 to 60 large, curved teeth, each measuring up to 12 inches in length. These teeth were constantly growing, and as they wore down from frequent use, they would be replaced by new ones.The teeth were sharp and serrated, making it easier for the T. rex to pierce through tough hides and bones. It is estimated that the T. rex could bite down with a force of 7,800 pounds per square inch, which is more than twice the bite force of a lion.
A Native Habitat and Geographical Distribution
The T. rex had a diverse geographical distribution, as fossils have been found in Montana, Wyoming, and Alberta, Canada, among other places. Scientists believe that it inhabited a variety of ecosystems, including forests, swamplands, and open plains.Its native habitat was characterized by hot and humid climates, with plenty of vegetation and prey species. The T. rex was a versatile predator and could adapt to various environmental conditions, making it a dominant species during its time.
Preferred Temperature and Skin Color
The T. rex lived during a time when the Earth was much warmer than it is today. The preferred temperature for this giant dinosaur was around 86°F (30°C). This warm climate provided a suitable habitat for the T. rex's prey and allowed it to survive and thrive as a predator.Scientists believe that the T. rex had a scaly and reptilian skin, with a greyish-brown coloration. However, there is evidence that they may have had feathers on their bodies, especially on their backs, making them partially warm-blooded creatures.
A Fascinating and Continuing Legacy
The T. rex is undoubtedly one of the most iconic and fascinating creatures in history. Its impressive size, sharp teeth, and powerful bite have made it a subject of countless books, movies, and documentaries. This mighty dinosaur has also contributed significantly to our understanding of evolution and the Earth's ancient past.Today, scientists continue to study the T. rex and other dinosaurs to learn more about their behavior, biology, and why they eventually went extinct. With each new discovery and fossil find, we get closer to unlocking the secrets of these magnificent creatures and painting a clearer picture of the world they lived in.
In conclusion, the Tyrannosaurus Rex stands out as the King of the Dinosaurs, a fearsome predator that ruled the Earth with its impressive size and powerful jaws. Its legacy continues to captivate our imagination and inspire future generations to delve deeper into the mysteries of the past.

Fossil Type
Dinosaur Details Fossil Type - Scientific Name: Fossil Type
- Category: Dinosaurs F
- Scientific Name: Fossil Type
- Common Name: Fossil Type
- Geological Era: Fossil Type
- Length: Fossil Type
- Height: Fossil Type
- Weight: Fossil Type
- Diet: Fossil Type
- Feeding Behavior: Fossil Type
- Predatory Behavior: Fossil Type
- Tooth Structure: Fossil Type
- Native Habitat: Fossil Type
- Geographical Distribution: Fossil Type
- Preferred Temperature: Fossil Type
- Maximum Speed: Fossil Type
- Skin Color: Fossil Type
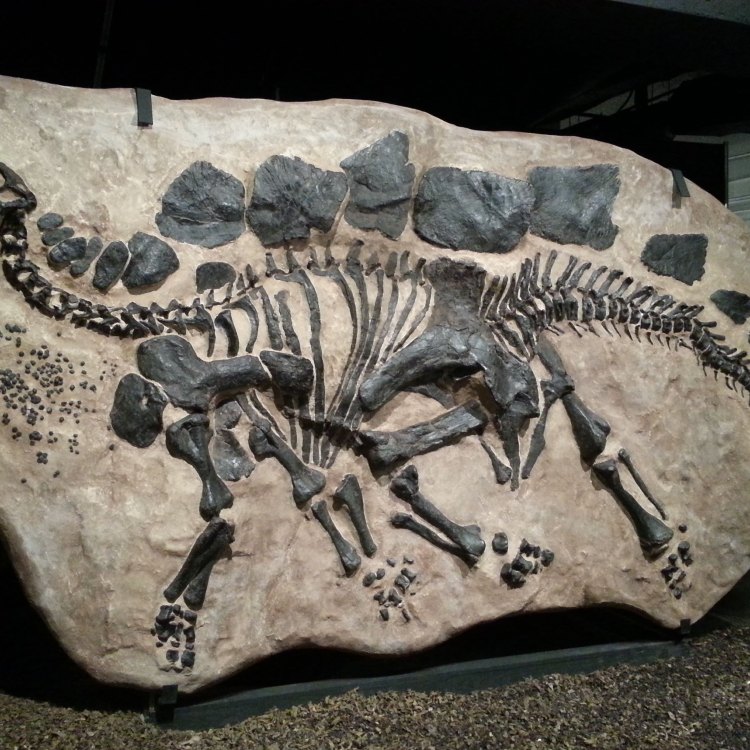

Fossil Type
- Bone Structure: Fossil Type
- Reproduction Type: Fossil Type
- Activity Period: Fossil Type
- Distinctive Features: Fossil Type
- Communication Method: Fossil Type
- Survival Adaptation: Fossil Type
- Largest Species: Fossil Type
- Smallest Species: Fossil Type
- Fossil Characteristics: Fossil Type
- Role in Ecosystem: Fossil Type
- Unique Facts: Fossil Type
- Predator Status: Fossil Type
- Discovery Location: Fossil Type
- Discovery Year: Fossil Type
- Discoverer's Name: Fossil Type
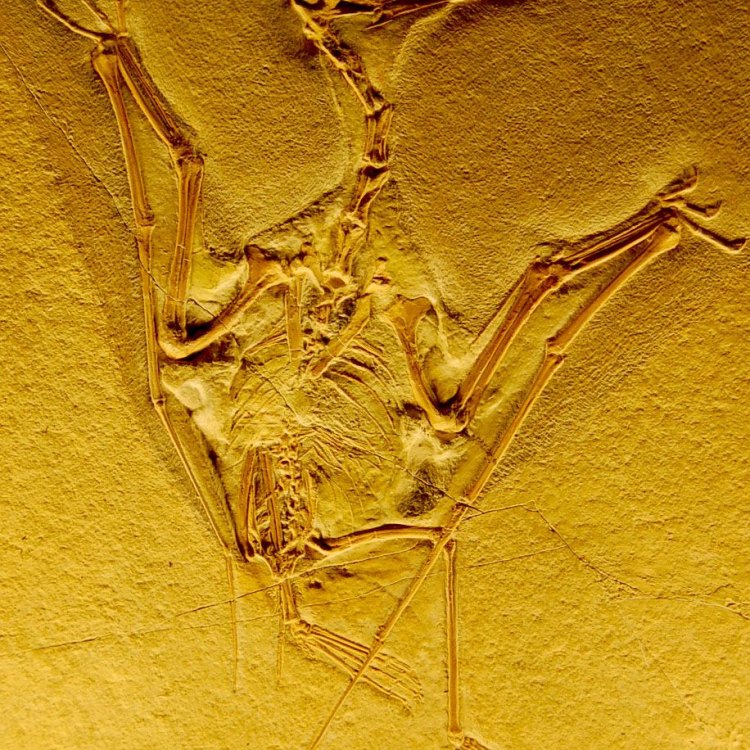

Fossil Type
The Fascinating World of Fossil Type: Exploring the Unique Features of These Ancient Remains
When we think of fossils, images of long-extinct dinosaurs and other prehistoric creatures come to mind. But did you know that there is a diverse world of fossils, and each one has its own unique features and characteristics? In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of fossil type and uncover the secrets of these ancient remains.Bone Structure: The Building Blocks of Fossils
Fossil type refers to the type of organism that has been preserved in the fossil record. These can range from plants and animals to microbes and even human remains OnTimeAiraz.Com. However, regardless of the organism, all fossils share a common feature – they are made up of bones.Bones are the hard, structural support system of an organism's body. They provide protection and give shape to the body, and they also serve as an attachment point for muscles, enabling movement. When an organism dies, its body begins to decompose, but the bones may remain intact for thousands, even millions of years. Over time, minerals seep into these bones, replacing the organic material and turning them into fossils.
The structure of bones is essential in understanding the anatomy and behavior of fossil type. For example, the bone structure of a dinosaur can reveal valuable information about its size, weight, and how it may have moved. Additionally, the presence of certain bones, such as wings or fins, can indicate the type of animal and its mode of locomotion.
Reproduction Type: The Story of Life in Fossil Type
Another crucial aspect of fossil type is their reproduction type Fossils. This refers to how the organisms were able to produce offspring and continue their species. The reproductive organs of an organism may not always be preserved in the fossil record, but scientists can make inferences based on the size, shape, and position of other preserved organs.For example, some fossils of marine invertebrates show evidence of external fertilization, where the egg and sperm are released into the water and combine to form an embryo. In contrast, others show evidence of internal fertilization, where the sperm is deposited inside the female's body. These small but significant details can help us understand the reproductive mechanisms of ancient organisms and how they contributed to the diversity of life on earth.
Activity Period: A Glimpse into the Lives of Fossil Type
One of the most intriguing things about fossils is that they provide a direct link to life on Earth millions of years ago. Fossil type can also reveal the activity period of an organism – the time of day or season when they were most active.For example, a fossilized plant may show signs of having adapted to a dry, arid climate, suggesting that it primarily grew during the summer months. Similarly, the presence of certain bones and muscles in a dinosaur's fossil can indicate whether it was a diurnal or nocturnal creature. These small details can help us piece together the complex puzzle of life on Earth and how it has evolved over time.
Distinctive Features: Uncovering the Unique Traits of Fossil Type
Every type of fossil has its own distinctive features that make it stand out from others. These features can range from anatomical or physiological characteristics to behavioral traits.For example, one of the most exciting fossil types is the ammonite, an extinct marine mollusk with a spiral shell. Ammonites are known for their intricate and beautifully preserved shells, which often feature intricate patterns and designs. These unique features not only make them visually stunning but also provide valuable information about their evolutionary history and adaptation to their environment.
Communication Method: How Fossil Type Expressed Themselves
Communication is an essential aspect of life for many animals, and fossil type are no exception. While it may be challenging to determine the exact communication method of a long-extinct species, scientists have been able to make educated guesses based on anatomical features and behavioral patterns.For instance, some fossils show evidence of vocalization, such as the larynx and vocal cords in primates, indicating that they may have used sound to communicate. Others may show evidence of visual communication, such as markings on the skin or feathers, revealing a means of displaying dominance or attracting a mate. The communication methods of ancient species may seem distant and unfamiliar, but they played a crucial role in their survival and adaptation to their environment.
Survival Adaptation: The Key to Longevity
One of the most remarkable aspects of fossil type is their ability to adapt and survive for millions of years. From the majestic Tyrannosaurus Rex to the tiny Trilobite, each organism had unique physical and behavioral adaptations that allowed them to thrive in their environment.For example, the pterosaur, a flying reptile that lived over 220 million years ago, had hollow bones, making it lighter and more efficient in flight. The woolly mammoth, a prehistoric ancestor of modern-day elephants, had a thick layer of fur to keep them warm in the harsh, cold climate of the Ice Age. Studying these survival adaptations can not only help us understand how these creatures lived but also provide insights into how species adapt and evolve over time.
Largest Species: Exploring the Giants of Fossil Type
Fossil type includes some of the largest and most impressive creatures that have ever lived on Earth. From giant marine reptiles to enormous land mammals, these species captivate our imaginations and leave us in awe with their sheer size and power.The largest fossil type known to date is the blue whale, an immense marine mammal that can reach lengths of up to 100 feet and weigh over 200 tons. It's hard to imagine a creature of such massive proportions, but the blue whale's fossil remains prove its existence and continue to fascinate scientists and researchers.
Smallest Species: The Intricacies of Tiny Fossil Type
On the other end of the spectrum, we have the tiniest fossil type, organisms that are often overlooked but just as crucial to understanding the history of life on Earth. These tiny creatures may not have the same impact or awe factor as their larger counterparts, but they hold a wealth of information within their microscopic bodies.One of the smallest fossil type is the microscopic diatom, a type of single-celled algae that has been found in rocks dating back millions of years. Although small, these tiny organisms played a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of marine ecosystems and continue to do so today. Their fossilized remains may not be as visually impressive, but they are just as valuable in understanding the complex web of life on Earth.
Fossil Characteristics: A Glimpse into the Past
Apart from their physical features, fossils also have unique characteristics that provide valuable information about the past. These characteristics can include the location in which they were found, the conditions in which they were preserved, and even their chemical composition.For example, fossils found in sedimentary rocks may indicate that the organism lived in a shallow marine environment, while fossils found in volcanic deposits can reveal that the organism lived near or on land. Similarly, the presence of certain elements, such as iron or calcium, in a fossil can provide clues about its diet and the environment in which it lived.
Role in Ecosystem: The Impact of Fossil Type on Their Environment
Fossil type not only provide valuable information about the organisms themselves but also about their role in the ecosystem. By studying the remains and behaviors of ancient species, scientists can gain a better understanding of how these organisms interacted with their environment and other species.For instance, fossilized footprints of dinosaurs have shown evidence of herding behavior, which may have contributed to the spread of vegetation and disruption of the soil. Fossils can also reveal important predator-prey relationships, shedding light on the dynamics of ancient ecosystems. By understanding these interactions, we can gain a better understanding of the impact of modern-day species on their environment and how we can preserve it for the future.
Unique Facts: Uncovering the Mysteries of Fossil Type
One of the most exciting things about fossils is that they constantly challenge our perceptions and knowledge of the past. While scientists have made significant discoveries and advancements in understanding fossils, there are still many unanswered questions and mysteries waiting to be uncovered.For example, the discovery of the feathered dinosaur, Archaeopteryx, provided compelling evidence for the evolution of birds from dinosaurs. However, the exact details of how this evolution occurred and the timeline of events are still being debated. These unique facts and revelations remind us that there is always more to learn and discover about the fascinating world of fossil type.
Predator Status: The Hunt for Fossil Type
Finally, we must not forget the important role that humans play in the search for and preservation of fossil type. From fossil hunters and researchers to museums and institutions that house these precious remains, humans are key in uncovering and studying the secrets of our ancient past.The hunt for fossil type is a delicate balance between discovery and preservation. It is essential to find and extract these remains carefully, ensuring that they are not damaged or lost in the process. Additionally, it is crucial to protect and preserve these fossils for future generations, maintaining their integrity and ensuring that they remain a source of wonder and knowledge.
Discovering the World of Fossil Type
Fossil type may be ancient remains, but they continue to fascinate and intrigue us with their unique features and characteristics. From the largest creatures to the tiniest organisms, each fossil has its own story to tell,

The Mighty Tyrannosaurus Rex: Exploring the King of the Dinosaurs
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.