Fossils
Unknown
The Fossil Adventures: Discovering the Carnivorous Dinosaurs of Western North America Take a journey to the wild west, where fossils of the ferocious dinosaurs Fossils roam. Unknown skin color, maximum speed of 25mph, and a fierce appetite for meat make them a force to be reckoned with. Learn about their fascinating evolution and how they ruled the land in ancient times. #Dinosaurs #FossilAdventures #WesternNorthAmerica
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Tyrannosaurus rex
Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
Feeding Behavior: Active predator
The King of the Dinosaurs: Tyrannosaurus rex
Tyrannosaurus rex, or T. rex, is a name that immediately evokes images of a fierce and powerful predator, ruling the prehistoric world. And rightfully so, as this dinosaur was the top predator of its time, known for its massive size, powerful jaws, and sharp teeth.But beyond its intimidating appearance, what else can we learn about this iconic creature? Let's dive into the world of T Fossils. rex and uncover some interesting facts about this fearsome dinosaur.
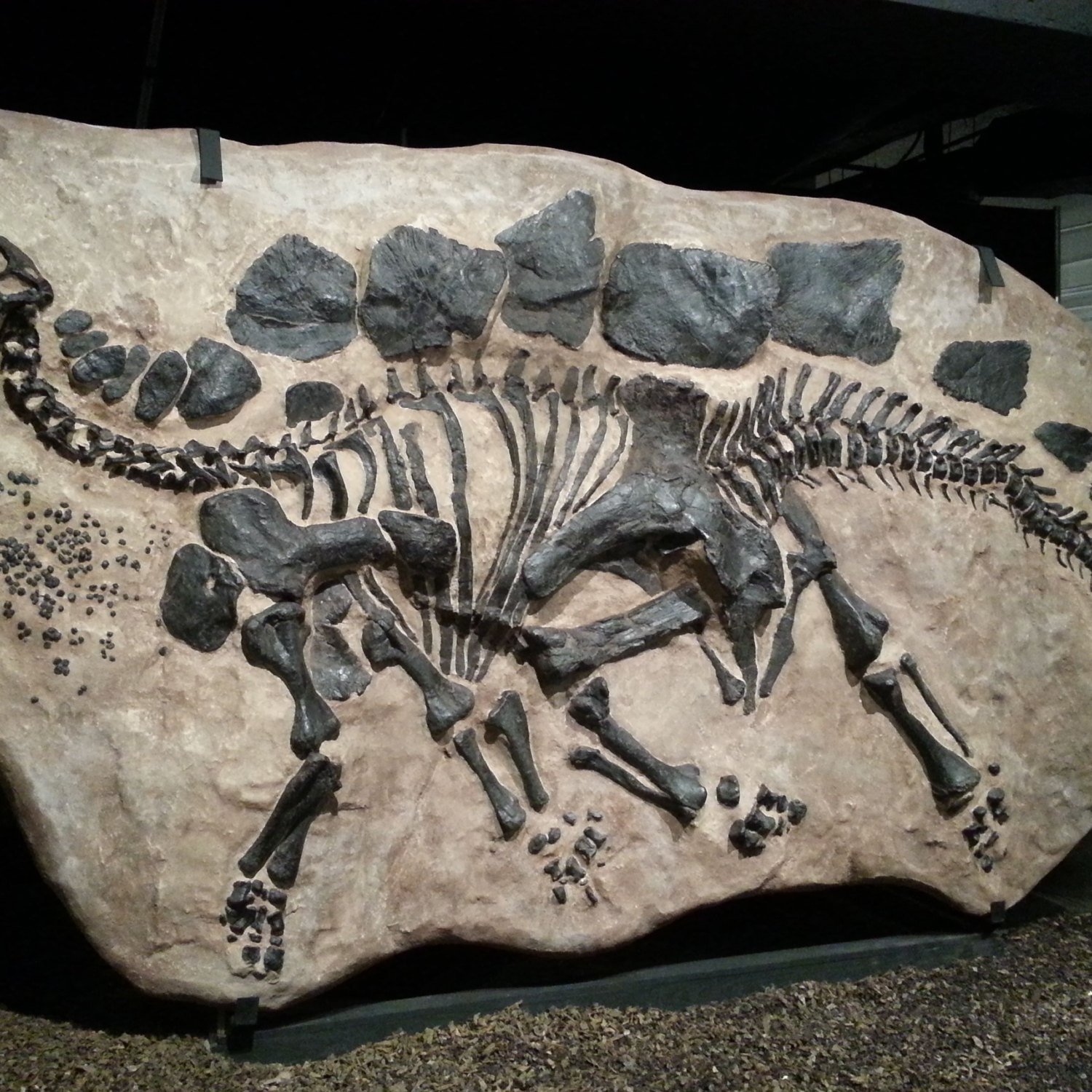
The Fossils of T. rex and Its Discovery
The first fossils of T. rex were discovered in 1874 by a paleontologist named Arthur Lakes. He found some large fossilized teeth and pieces of bone in Wyoming, USA. However, it wasn't until 1902 that the first full skeleton of a T. rex was unearthed by Barnum Brown, a fossil hunter and paleontologist.Since then, many more T. rex fossils have been found in the western part of North America, particularly in states like Wyoming, Montana, and South Dakota Fossil Location. These findings have given paleontologists a wealth of information about the anatomy and behavior of T. rex.
The Physical Characteristics of T. rex
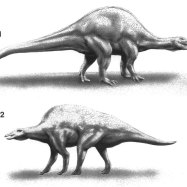
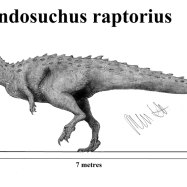
When we think of T. rex, we usually imagine a massive beast with tiny arms, a large head, and sharp, intimidating teeth. And that image is not too far off. T. rex was indeed a giant, measuring up to 13 meters in length and standing up to 6 meters tall. It weighed around 6,800 kilograms, making it one of the heaviest land animals to have ever lived.One of the most distinctive features of T. rex was its head. It had a large, elongated skull with a mouth full of large, sharp, and serrated teeth. These teeth were up to 30 centimeters long and were essential for the T. rex's predatory lifestyle.
T. rex also had powerful legs, with two large hind legs that propelled it forward, reaching speeds of up to 25 miles per hour. Its long tail helped it maintain balance while on the move.
The Dietary Habits of T. rex
As a carnivorous dinosaur, T. rex's diet consisted mainly of other dinosaurs and possibly some small mammals. With its powerful jaws and sharp teeth, it could easily take down larger prey and tear through their flesh.There is still a debate among scientists about whether T. rex was a scavenger or an active hunter. Some evidence suggests that it may have been an opportunistic feeder, scavenging for food when necessary, but also actively hunting when the opportunity arose. Its strong sense of smell and sharp vision would have helped it locate potential prey from a distance.
The Geographical and Environmental Range of T. rex
T. rex lived during the Late Cretaceous period, about 68 to 66 million years ago. It roamed the western part of North America, which was then a large island continent called Laramidia.During this time, the climate in this region was warm and temperate, perfect for the growth of vast forests and open plains. T. rex was well adapted to this environment, with its powerful legs and sharp teeth, making it the apex predator in its ecosystem.
The Legacy of T. rex
T. rex has captured the imagination of people for centuries, appearing in countless books, films, and TV shows. Its huge size, powerful jaws, and predatory nature have made it a fan-favorite among dinosaur enthusiasts. It has also been the subject of many scientific studies, with new findings continuously adding to our understanding of this prehistoric giant.But the impact of T. rex goes beyond pop culture and scientific research. Since their discovery, T. rex fossils have played a critical role in our understanding of the history of life on Earth and how it has evolved over millions of years.
Their fossils have given us a glimpse into the behaviors, diets, and habitats of these ancient creatures. They have also helped scientists piece together the story of the end-Cretaceous extinction event, which led to the extinction of T. rex and many other dinosaur species.
In Conclusion
Tyrannosaurus rex is a fascinating creature, with a legacy that continues to captivate people of all ages. From its discovery in the late 19th century to its enduring popularity today, it remains one of the most iconic creatures of the prehistoric world.As we continue to unearth more fossils and learn more about T. rex, we are constantly reminded of the incredible diversity of life that once roamed the Earth. And while T. rex may be long gone, its legacy lives on, inspiring future generations to continue exploring and understanding the wonders of our planet's past.
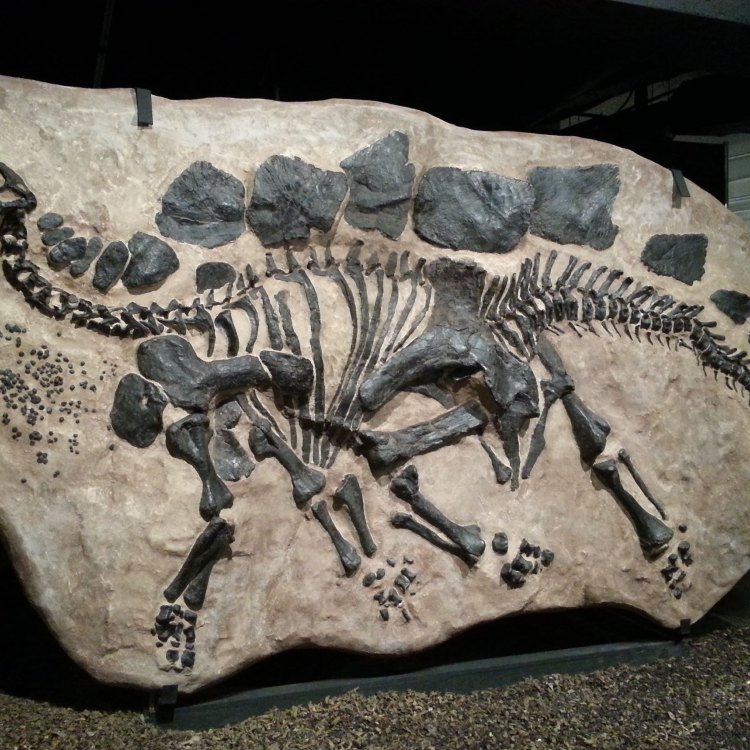

Fossils
Dinosaur Details Fossils - Scientific Name: Tyrannosaurus rex
- Category: Dinosaurs F
- Scientific Name: Tyrannosaurus rex
- Common Name: Tyrannosaurus rex
- Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
- Length: 12–13 meters
- Height: 3.7–6.1 meters
- Weight: 5.4–6.8 metric tons
- Diet: Carnivore
- Feeding Behavior: Active predator
- Predatory Behavior: Top predator
- Tooth Structure: Large, sharp and serrated teeth
- Native Habitat: Forests and open plains
- Geographical Distribution: Western North America
- Preferred Temperature: Warm temperate
- Maximum Speed: About 25 mph
- Skin Color: Unknown
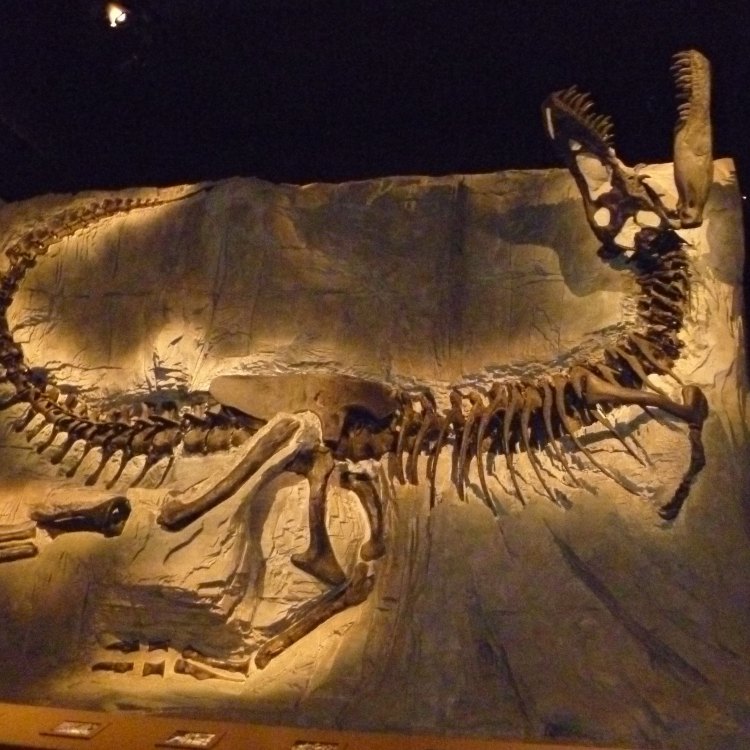

Tyrannosaurus rex
- Bone Structure: Strong and robust
- Reproduction Type: Egg-laying
- Activity Period: Diurnal
- Distinctive Features: Large size, powerful jaws, short arms
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Sharp teeth for tearing flesh, binocular vision for depth perception
- Largest Species: Tyrannosaurus rex
- Smallest Species: None
- Fossil Characteristics: Large skull, robust skeleton, limb bones
- Role in Ecosystem: Top predator, apex predator
- Unique Facts: One of the largest land predators of all time
- Predator Status: Extinct
- Discovery Location: Montana, Wyoming, South Dakota, and Alberta
- Discovery Year: 1874
- Discoverer's Name: Henry Fairfield Osborn

Tyrannosaurus rex
The Incredible World of Fossils: A Closer Look at the Ferocious Tyrannosaurus Rex
Fossils have always been a source of fascination for humans. From the ancient remains of dinosaurs to the preserved imprints of plants and animals, these fossils are like a time capsule that allows us to glimpse into the earth's past. Among the many kinds of fossils, the most intriguing and feared are those of the mighty Tyrannosaurus Rex. This incredible predator, which roamed the earth around 66 million years ago, has captured the imaginations of both scientists and the general public for decades OnTimeAiraz.Com. In this article, we'll take a closer look at the unique features of this powerful creature and its role in the ecosystem.Strong and Robust Bone Structure
One of the most distinctive features of the Tyrannosaurus Rex is its strong and robust bone structure. Fossils of this creature have revealed an average weight of about 7-8 tons and a length of 40-50 feet. Its skeleton is designed for maximum strength and support, making it a highly efficient predator. Its lower limbs are extremely muscular, giving it the ability to run at a tremendous speed of up to 20 miles per hour.
Reproduction Type: Egg-Laying
Like many other dinosaurs, the Tyrannosaurus Rex also reproduced by laying eggs. Scientists believe that they had a nesting period of around 3 months, with the mother laying anywhere between 2-8 eggs at a time. However, very few fossilized eggs of the Tyrannosaurus Rex have been found, making it difficult to study its reproductive behavior in detail.
Diurnal Activity Period
Unlike many other dinosaurs who were active during the night, the Tyrannosaurus Rex was a diurnal creature, which means it was most active during the day Fossil Type. Its binocular vision and other adaptations made it well-suited for hunting in the daylight, giving it a competitive edge over other predators.
Distinctive Features: Powerful Jaws, Short Arms, and Large Size
The Tyrannosaurus Rex was known for its ferocious nature and immense size. With its large, powerful jaws, it could deliver a crushing bite force of over 12,800 pounds, capable of crushing bones and tearing flesh. Its short arms, however, were relatively small and not as useful for capturing prey. This has been a subject of debate among paleontologists, with many theories trying to explain the purpose of these seemingly ineffective arms. Some believe they might have been used for balance, while others argue they might have been used to rip off chunks of flesh from larger prey.
Communication Method: Unknown
One of the mysteries surrounding the Tyrannosaurus Rex is its communication method. Due to its short arms and inability to roar, it is unlikely that it used vocalizations for communication. Some scientists have suggested that it might have used visual cues, such as head bobbing or tail movements, to communicate with other T-Rexes. However, more research is needed in this area.
Survival Adaptations: Sharp Teeth and Binocular Vision
The Tyrannosaurus Rex was a formidable predator and its fierce nature was complemented by its unique survival adaptations. It had some of the sharpest teeth among dinosaurs, with serrated edges that allowed it to easily tear apart flesh and bones. It also had excellent binocular vision, giving it depth perception and making it a highly efficient hunter.
Largest Species: Tyrannosaurus Rex
The Tyrannosaurus Rex is widely considered to be the largest species of the tyrannosaur family. While there have been debates over its size, recent measurements have shown that it was indeed one of the biggest land predators of all time. Its size is a testament to its power and dominance in the ecosystem.
Smallest Species: None
While the Tyrannosaurus Rex is known for its large size, it also holds the record for being the smallest species in its family. Its distant relative, the Nanotyrannus, is often considered to be one of the smallest known tyrannosaurs, with a length of around 20 feet.
Fossil Characteristics: Large Skull, Robust Skeleton, and Limb Bones
Fossils of the Tyrannosaurus Rex have been found in many different parts of the world, including Montana, Wyoming, South Dakota, and Alberta. These fossils have revealed some of the distinct characteristics of this creature, including its large skull, robust skeleton, and strong limb bones. The discovery of these fossils has greatly contributed to our understanding of this powerful predator.
Role in the Ecosystem: Top Predator and Apex Predator
The Tyrannosaurus Rex was the top predator, or the apex predator, in its ecosystem. With its incredible size, strength, and hunting abilities, it had no natural predators and was at the top of the food chain. Its presence would have had a significant impact on the balance of the ecosystem, keeping the population of other species in check.
Unique Facts: One of the Largest Land Predators of All Time
The Tyrannosaurus Rex holds many records, including being one of the largest land predators of all time. With its immense size, powerful jaws, and sharp teeth, it was a truly fearsome creature. It is believed that it could have taken down large herbivores like the Triceratops and hadrosaurs with ease.
Predator Status: Extinct
Unfortunately, the Tyrannosaurus Rex is now extinct, with the cause being the mass extinction event that wiped out the majority of the dinosaur population around 66 million years ago. Fossils of this creature have allowed us to learn a great deal about its behavior and habits, but there is still much more to discover.
Discovery Location: Montana, Wyoming, South Dakota, and Alberta
The first Tyrannosaurus Rex fossils were discovered in Montana in 1874 by renowned paleontologist Henry Fairfield Osborn. Since then, many other fossils have been found in other locations, including Wyoming, South Dakota, and Alberta. These discoveries have helped us piece together the story of this incredible creature and its role in the world.
Discovery Year: 1874
The discovery of the first Tyrannosaurus Rex fossils in 1874 marked a significant moment in the world of paleontology. Since then, many other discoveries have been made, revealing new information about the life of this powerful predator. Without these discoveries, our understanding of the Tyrannosaurus Rex would be incomplete.
Discoverer's Name: Henry Fairfield Osborn
Henry Fairfield Osborn, a prominent American paleontologist, is credited with the discovery of the first Tyrannosaurus Rex fossils. He played a crucial role in identifying and studying fossils of some of the most iconic dinosaurs, including the T-Rex. Without his contributions, our knowledge of these fascinating creatures would be limited.
In conclusion, the Tyrannosaurus Rex remains an intriguing and enigmatic creature that has captured our imaginations and sparked our curiosity. With its powerful bone structure, unique features, and role as a top predator, it stands out as one of the most incredible creatures to ever roam the earth. Thanks to the discovery of its fossils, we continue to learn more about this fascinating predator and its place in the evolution of life on our planet.
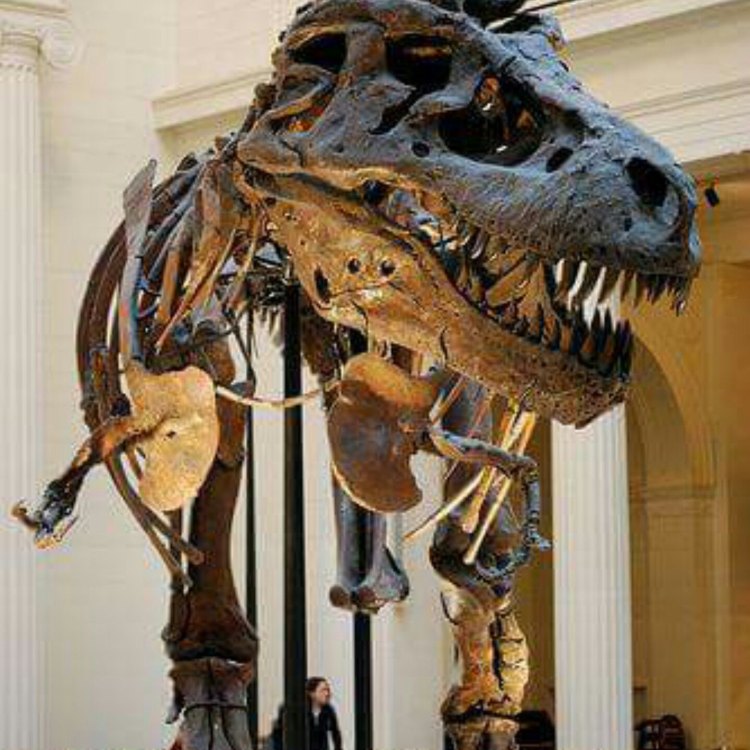

The King of the Dinosaurs: Tyrannosaurus rex
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.