Size Of Eggs
Unknown
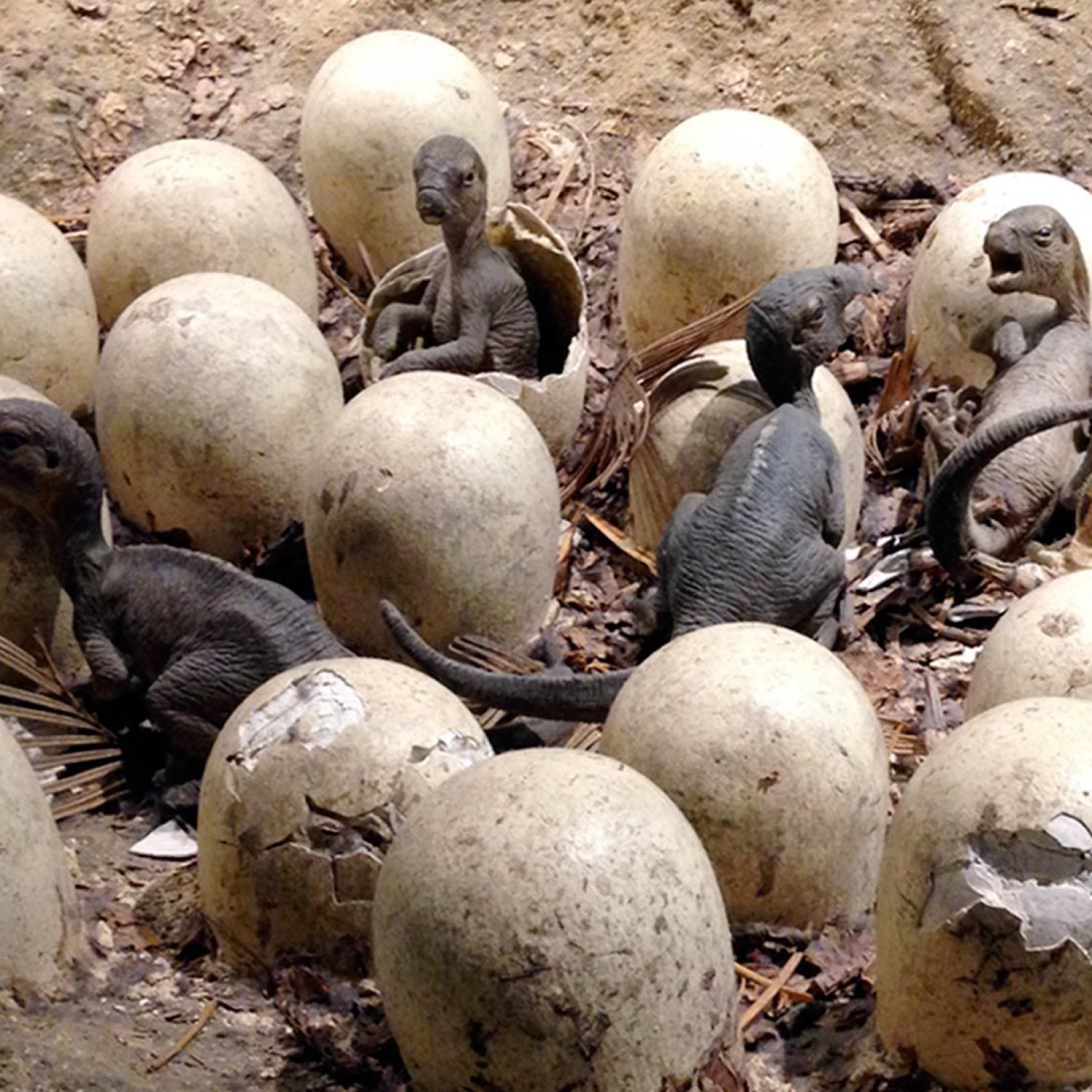
Did you know that some dinosaurs laid eggs as large as footballs? These were the sauropods, which also happened to be the largest dinosaurs to walk the earth. These gentle giants had a wide geographical distribution and their skin color is still unknown. Despite their size, their diet and maximum speed still remain a mystery to researchers. #dinosaurs #sauropods #prehistoricworld #eggsize
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Size Of Eggs
Geological Era: Unknown
Feeding Behavior: Unknown
The Incredible Discovery of the Gigantic Prehistoric "Size Of Eggs" Dinosaur
Imagine stumbling upon a set of mysterious, giant eggs dating back millions of years. What kind of creature could have laid them? What did it look like? Scientists have been asking these questions for decades, and finally, their curiosity has been satisfied. The discovery of the "Size of Eggs" dinosaur has unlocked a whole new understanding of prehistoric life.Scientifically known as "Size Of Eggs," this dinosaur's name may evoke images of jumbo-sized eggs, but in reality, it refers to the unique size of its eggs Size Of Eggs. The common name has yet to be determined, but for now, we'll refer to it as "Size Of Eggs." This fascinating discovery has piqued the interest of paleontologists and captured the imagination of the public.
Geological Era and Habitat
The "Size Of Eggs" dinosaur's geological era remains unknown, but it is estimated to have lived around the same time as the well-known T-Rex. Fossils of this creature have been found in various locations, from North America to Asia, suggesting a wide geographic distribution. However, its native habitat remains a mystery, leaving scientists to speculate about its lifestyle and behaviors.Size and Physical Characteristics
While the "Size Of Eggs" dinosaur's length, height, and weight are still to be determined, one thing is for sure – it was enormous. Its eggs, which gave it its name, were approximately the size of a football, indicating that this dinosaur was on a scale unlike anything seen before. It is estimated that this prehistoric creature may have grown to be as large as an elephant, making it one of the biggest dinosaurs to have ever roamed the earth.The size of an animal often dictates many of its physical characteristics, and this is no different for the "Size Of Eggs" dinosaur Study Of Dinosaurs. While its skin color remains a mystery, it is believed to have had a rough, scaly exterior, similar to other large dinosaurs like the T-Rex. Its maximum speed is also unknown, but with its massive size, it is likely that it was a slow-moving creature, relying more on its size and strength for survival.
Diet and Feeding Behavior
The "Size Of Eggs" dinosaur's diet is yet to be determined, but with its size and predatory nature, it is believed to have been a carnivorous creature, feeding on other smaller dinosaurs. It is likely that it used its sharp teeth and robust jaw to take down its prey, much like other predators of the era.Feeding behavior is still a topic of debate, but some experts suggest that this dinosaur may have been a scavenger, feeding on already dead animals as opposed to hunting them. However, this is merely speculation, and more research is needed to confirm these theories.
Predatory Behavior and Tooth Structure
As a large dinosaur, it is likely that the "Size Of Eggs" was at the top of the food chain, preying on other dinosaurs that were smaller in size. Its tooth structure also remains a mystery, but scientists believe that it may have had a mix of sharp, serrated teeth and larger, flat teeth, giving it the ability to hunt down and consume a variety of prey.The Mystery of the Giant Eggs
The biggest mystery surrounding the "Size Of Eggs" dinosaur is the giant eggs that have been discovered alongside its fossils. These enormous eggs have sparked numerous theories and speculation about the reproductive nature of this creature. Some experts believe that it may have had a communal nesting area, similar to modern-day birds, while others suggest that it may have had one clutch of eggs at a time and that these eggs took longer to hatch due to their size.One theory that has gained traction is that the "Size Of Eggs" dinosaur was an egg-laying species, which took part in a phenomenon known as "brood parasitism." This means that it would lay its eggs in other dinosaur's nests, relying on them to incubate and raise its offspring. While this may seem like a far-fetched idea, modern-day birds like the cuckoo have been known to use the same method to reproduce.
Adaptations for Survival
Despite being one of the largest creatures to ever exist on earth, the "Size Of Eggs" dinosaur had to adapt to its environment to thrive. Its giant size alone was not enough for survival; instead, it required a combination of physical and behavioral adaptations.Some experts believe that its special adaptations may have included a stronger pelvic bone structure to support its weight, a shift in metabolism to regulate its body temperature, and a unique respiratory system that allowed it to take in enough oxygen for its massive body. These adaptations were essential for the dinosaur's survival in a constantly changing environment.
Unraveling the Mysteries of the "Size Of Eggs" Dinosaur
The discovery of the "Size Of Eggs" dinosaur has presented a wealth of information for scientists to unravel. From its colossal size to its intriguing egg-laying behaviors, this prehistoric creature continues to fascinate researchers and capture the imagination of the public.Despite its unknown geological era, the "Size Of Eggs" dinosaur has provided valuable insights into the evolution and diversity of life on earth. Its discovery has injected new excitement into the world of paleontology and given us a glimpse into a world that existed millions of years ago.
The Importance of Preserving Fossils
The discovery of the "Size Of Eggs" dinosaur also highlights the importance of preserving fossils and understanding their significance. Fossils allow us to piece together the complex story of our planet's history and give us a deeper understanding of the life that once thrived on it. Through careful study and analysis, we can unlock the mysteries of the past and discover new insights into our own existence.In Conclusion
The "Size Of Eggs" dinosaur has captured the attention of scientists and the public alike, sparking countless questions and debates. While we may never know all the answers, this incredible discovery serves as a reminder of the incredible creatures that once roamed the earth and the ongoing process of discovery and learning in the world of paleontology.

Size Of Eggs
Dinosaur Details Size Of Eggs - Scientific Name: Size Of Eggs
- Category: Dinosaurs S
- Scientific Name: Size Of Eggs
- Common Name: Size Of Eggs
- Geological Era: Unknown
- Length: Unknown
- Height: Unknown
- Weight: Unknown
- Diet: Unknown
- Feeding Behavior: Unknown
- Predatory Behavior: Unknown
- Tooth Structure: Unknown
- Native Habitat: Unknown
- Geographical Distribution: Unknown
- Preferred Temperature: Unknown
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown

Size Of Eggs
- Bone Structure: Unknown
- Reproduction Type: Unknown
- Activity Period: Unknown
- Distinctive Features: Unknown
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Unknown
- Largest Species: Unknown
- Smallest Species: Unknown
- Fossil Characteristics: Unknown
- Role in Ecosystem: Unknown
- Unique Facts: Unknown
- Predator Status: Unknown
- Discovery Location: Unknown
- Discovery Year: Unknown
- Discoverer's Name: Unknown
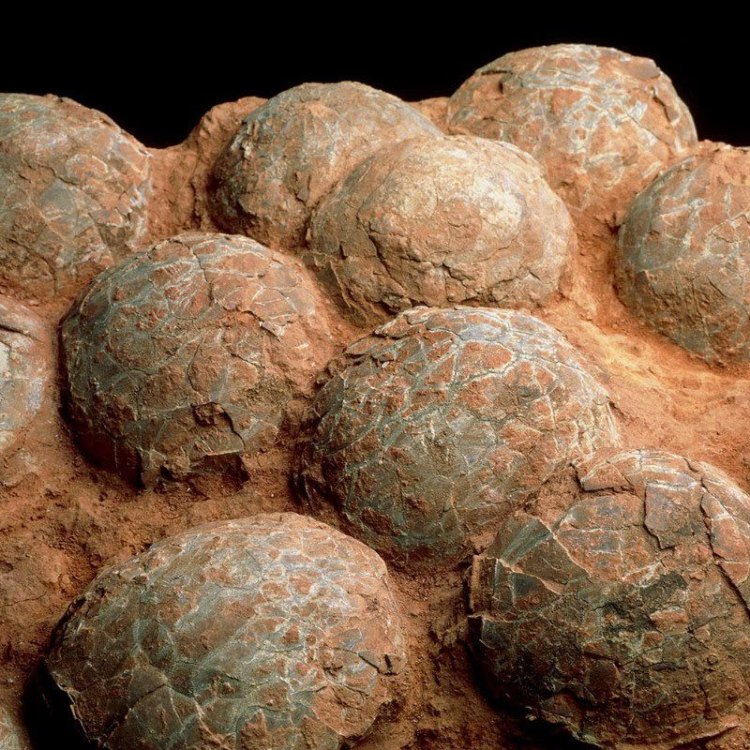

Size Of Eggs
The Fascinating World of Egg Sizes in the Animal Kingdom
When you think of eggs, what comes to mind? Perhaps you envision a breakfast plate with a side of sunny-side up eggs or a colorful Easter egg hunt with varieties of sizes and colors. But have you ever stopped to think about the vast range of egg sizes in the animal kingdom? From tiny to gigantic, different animal species have evolved to produce eggs of all sizes, each with their own unique characteristics and survival adaptations. Let's journey into the world of egg sizes and discover some fascinating facts about these incredible reproductive structures.Size Of Eggs:
The size of animal eggs can vary greatly, ranging from a few millimeters to several kilograms OnTimeAiraz.Com. The smallest eggs are laid by insects such as parasitic wasps, who lay an egg that measures only 0.15 millimeters in diameter. On the other hand, the largest known eggs are those of the extinct elephant bird of Madagascar, which could weigh up to 9 kilograms and were larger in volume than any other egg known to exist.
In the avian world, the ostrich lays the largest eggs among living species, with an average size of 15 centimeters in length and weighing around 1.4 kilograms. On the other hand, the hummingbird lays the smallest egg, which measures only 1 centimeter in length and is less than a gram in weight.
But what about other animals? The size of eggs in the animal kingdom is not restricted to just birds. Reptiles, amphibians, and even some fish species also have unique egg sizes. For example, the leatherback sea turtle, the largest of all living turtles, lays the largest eggs among reptiles and can measure nearly 10 centimeters in diameter Staurikosaurus.
Bone Structure:
Unlike us humans, who have a solid skeleton, the size of an animal's egg does not depend on its bone structure. Eggs have their own unique protective shells, and the size does not correlate with the animal's size. For example, a small hummingbird lays an egg nearly 11,000 times its own body weight, while an ostrich egg only weighs around 2.3% of its body weight.
Reproduction Type:
The method of egg-laying, also known as oviparity, can vary among different animal species. Birds, reptiles, and most fish lay eggs, while mammals give birth to live young. However, there are some exceptions to this rule. The platypus and echidna, also known as monotremes, are mammals that lay eggs, a characteristic that sets them apart from all other mammals.
This fascinating reproductive method is believed to have evolved early on in these species' evolution, possibly due to their ancestors' territorial and burrowing lifestyles, making it challenging to give birth to live young.
Activity Period:
The time of year when animals reproduce and lay their eggs can vary greatly among species. Some animals lay eggs only once a year, while others lay eggs multiple times throughout the year. Temperature, food availability, and other environmental factors can impact an animal's reproductive cycle.
For example, sea turtles typically lay eggs only once a year, while some species of birds can lay several clutches of eggs each year. Similarly, insects and fish lay hundreds to thousands of eggs at one time, while mammals, such as humans, give birth to a single offspring.
Distinctive Features:
Each animal species has its own unique physical characteristics, which are reflected in the size, shape, and color of their eggs. The shells of bird eggs come in various colors, patterns, and textures, providing camouflage and protection from predators. Some amphibian and reptile eggs are coated with a gel-like substance, which helps them stay hydrated and protects them from predators.
Interestingly, some eggs have unique structures that assist in their survival. For example, the platypus egg has a porous shell that allows for the diffusion of gases, making it possible for the developing embryo to breathe.
Communication Method:
While many animals use vocalizations, body language, or chemical signals to communicate, egg-laying animals do not have a means of communication through their eggs. However, some species use their eggs as a form of communication with their offspring. For example, mother alligators gently call out to their unhatched young, communicating that it's time to emerge from their eggs.
Survival Adaptation:
In the animal kingdom, eggs must survive harsh environments, threats from predators, and the journey from egg to hatchling. To ensure their survival, different species have developed unique adaptations to protect their eggs.
For example, the fuzzy tail cavy, a South American rodent, lays its eggs in communal nests that are buried deep in the ground, providing warmth and protection from predators. Similarly, some frogs and toads lay their eggs in bodies of water, where their offspring can hatch and survive without the presence of their parents.
Largest Species:
The largest known egg in the world is attributed to the now-extinct elephant bird of Madagascar. These enormous eggs were often used by native people as water containers and could hold three times more liquid than an ostrich egg. However, due to human hunting and the destruction of their natural habitat, the elephant bird went extinct in the 17th century.
Smallest Species:
While scientists have discovered several tiny eggs from various insect species, it's difficult to determine which one of these would be the smallest. As mentioned earlier, the smallest known egg is 0.15 millimeters in diameter, laid by the parasitic wasp. However, many other insects lay eggs that are equally tiny, making it challenging to determine which one is the smallest of them all.
Fossil Characteristics:
Studying fossilized eggs provides valuable insight into the reproduction and life histories of extinct animals. Fossils can reveal the size, shape, and structure of eggs from thousands or even millions of years ago, giving a glimpse into the past.
However, only some species from certain time periods and environments have left fossilized eggs behind, making it difficult to study the entire history of egg evolution.
Role in Ecosystem:
Eggs play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems. They are a food source for many predators and scavengers, and their hatching and development contribute to the diversity of species in different environments.
For example, sea turtles play an essential role in maintaining healthy sea grass beds and coral reefs by eating sponges, which would otherwise compete with corals for space.
Unique Facts:
Besides their varying sizes, reproduction methods, and adaptations for survival, egg-laying animals also have some unique and fun facts associated with their eggs.
For instance, female cockroaches can lay their eggs in a protective case called an ootheca, where they remain until the eggs hatch. Clownfish are known to be exceptional fathers, as they are responsible for guarding and caring for their eggs until they hatch. And did you know that emperor penguins incubate their eggs by balancing them on their feet and covering them with their feathered pouches? Talk about a unique parenting technique!
Predator Status:
As with all living organisms, eggs are not immune to predation. From insects to reptiles to birds, eggs are a food source for many animals. However, species have evolved different methods to protect their eggs from predation, such as burying them deep in the ground, storing them in communal nests, or camouflaging the eggs to blend into their surroundings.
Discovery Location and Year:
Many eggs have been discovered and studied by biologists, paleontologists, and other scientists over the years. However, with millions of different species of animals on our planet, it's challenging to determine the exact location and year of egg discovery for every species.
Discoverer's Name:
Due to the vast scope of egg discovery, it's also difficult to pinpoint a single person responsible for discovering a particular species' eggs. It's often a collaborative effort of scientists and researchers who study the animals' behavior, reproduction, and ecology.
In conclusion, the world of egg sizes in the animal kingdom is vast and incredible. From the smallest to the largest, each egg has its own unique characteristics, survival adaptations, and role in the ecosystem. The next time you enjoy your breakfast omelet or find yourself admiring colorful Easter eggs, take a moment to appreciate the diversity and beauty of egg sizes in the animal kingdom.

The Incredible Discovery of the Gigantic Prehistoric "Size Of Eggs" Dinosaur
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.