Tarbosaurus
Unknown
Meet the Tarbosaurus, a fierce and mysterious dinosaur. This carnivorous creature roamed the lands of Mongolia, China, and Russia and was known for its lightning-fast speed. While its skin color remains a mystery, its powerful jaws and sharp teeth make it a top predator in the prehistoric world. Learn more about this fascinating dinosaur and its prehistoric world today. #Tarbosaurus #Dinosaurs #Mongolia #China #Russia
Dinosaur Details Summary:
Common Name: Tarbosaurus
Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
Feeding Behavior: Active predator
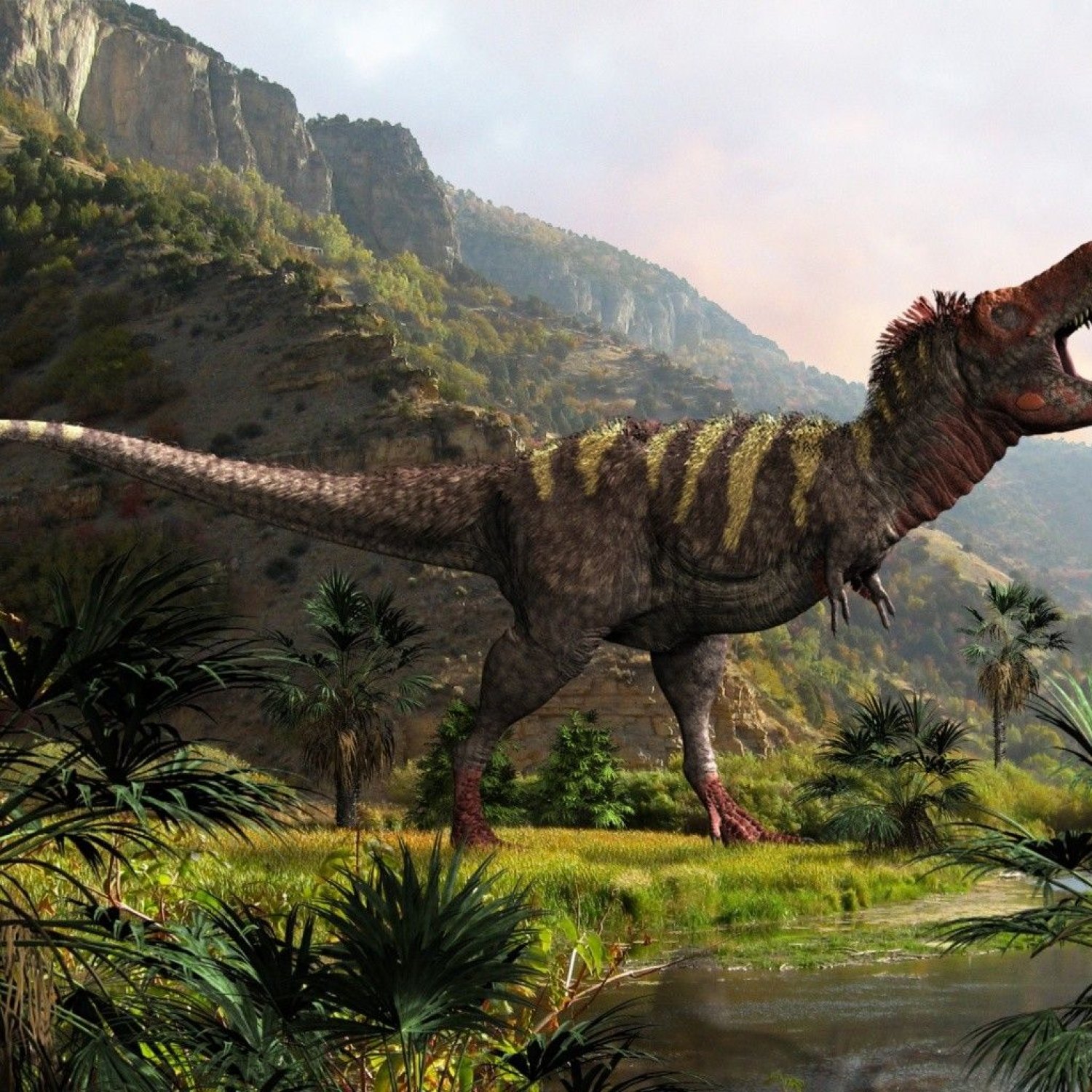
Tarbosaurus: The Ferocious King of Asia
Tarbosaurus, a dinosaur whose name literally translates to "alarming lizard", was a fierce predator that ruled the lands of Asia during the Late Cretaceous period. With its sharp teeth, active predatory behavior, and impressive size, this dinosaur was a formidable creature that struck fear in the hearts of its prey.Scientifically known as Tarbosaurus bataar, this species was first discovered in 1947 in Mongolia by a Soviet-Mongolian expedition. Its name was given due to its similarity to the infamous Tyrannosaurus rex, with whom it shared many physical characteristics Tarbosaurus. However, recent studies have shown that Tarbosaurus may have actually been a closer relative of the North American Daspletosaurus.
Appearance and Size
Tarbosaurus was a large and robust carnivorous dinosaur, measuring around 12-13 meters in length and standing at a height of 4-5 meters. It weighed approximately 4-5 tons, making it one of the largest predators of its time. Its body was covered in scales, with a muscular tail and two short arms with three-fingered hands.One of the most notable features of this dinosaur was its head, which was large and heavy compared to its body. It had a long, narrow snout with rows of sharp and serrated teeth, perfect for tearing through flesh and bones. Its skull was around 1.3 meters in length, making it one of the largest of any known theropod dinosaur.
Diet and Feeding Behavior
Being a carnivorous dinosaur, Tarbosaurus had a diet mainly consisting of other dinosaurs and smaller animals Theropods. Its sharp teeth and powerful bite allowed it to easily tear through the thick hides and bones of its prey. Its active predatory behavior, coupled with its impressive speed and agility, made it a fearsome hunter that could take down larger prey.Recent studies have also suggested that Tarbosaurus may have been a scavenger, feeding on the remains of dead animals as well. This adaptive behavior would have helped it survive during times of scarcity, giving it an edge over other predators.
Predatory Behavior and Hunting Techniques
Tarbosaurus was a solitary hunter, but also showed signs of pack behavior. This means that while it primarily hunted alone, it also had the ability to work with other members of its species to take down larger prey or in times of extreme competition for food.Its long, powerful legs allowed it to run at high speeds, making it a skilled predator that could chase down and catch its prey. It is believed that it used its keen sense of smell and hearing to locate prey, and then used its long, sharp claws and teeth to deliver a fatal blow.
Habitat and Distribution
Tarbosaurus was primarily found in Asia, with fossils being discovered in Mongolia, China, and Russia. These dinosaurs inhabited a variety of environments, from dry deserts to temperate forests. Their preferred habitat was near rivers or water sources, as it provided them with a consistent supply of food and water.Their wide distribution also suggests that they were highly adaptable to different habitats, thriving in various climates and terrains. This adaptation would have allowed them to survive millions of years in an ever-changing planet.
Temperature Range and Skin Color
Being found in places like Mongolia and Russia, it is believed that Tarbosaurus preferred a temperate climate. However, due to insufficient evidence, their exact preferred temperature range is still unknown.Similarly, their skin color remains a mystery. While it is widely believed that they had a scaly skin like most dinosaurs, the exact color or pattern cannot be confirmed without further evidence.
The Legacy of Tarbosaurus
Tarbosaurus may not be as well-known as its close relative, the Tyrannosaurus rex, but it has played an important role in our understanding of dinosaur evolution. Its fossils have provided valuable insights into the physical characteristics and behavior of large theropod dinosaurs, shedding light on the diversity of species that once roamed the Earth.However, the story of Tarbosaurus does not end with its extinction. In recent years, illegal fossil trade and poaching have threatened the preservation of these ancient creatures. Many Tarbosaurus fossils have been illegally smuggled out of Mongolia and sold to private collectors, leading to a significant loss of precious scientific information.
To combat this, efforts are being made to protect fossil sites and educate the public on the importance of preserving these artifacts for future generations. Museums around the world have also been conducting exhibition and research studies on Tarbosaurus, allowing people to learn more about this fascinating dinosaur.
The Mighty Tarbosaurus: A Legacy That Will Continue to Fascinate
Tarbosaurus may have gone extinct millions of years ago, but its legacy lives on through its fossils, which provide valuable insights into the world of dinosaurs. With the ongoing efforts to preserve and share knowledge about these creatures, we can continue to learn about and appreciate the fascinating history of Tarbosaurus and its role in the prehistoric world.
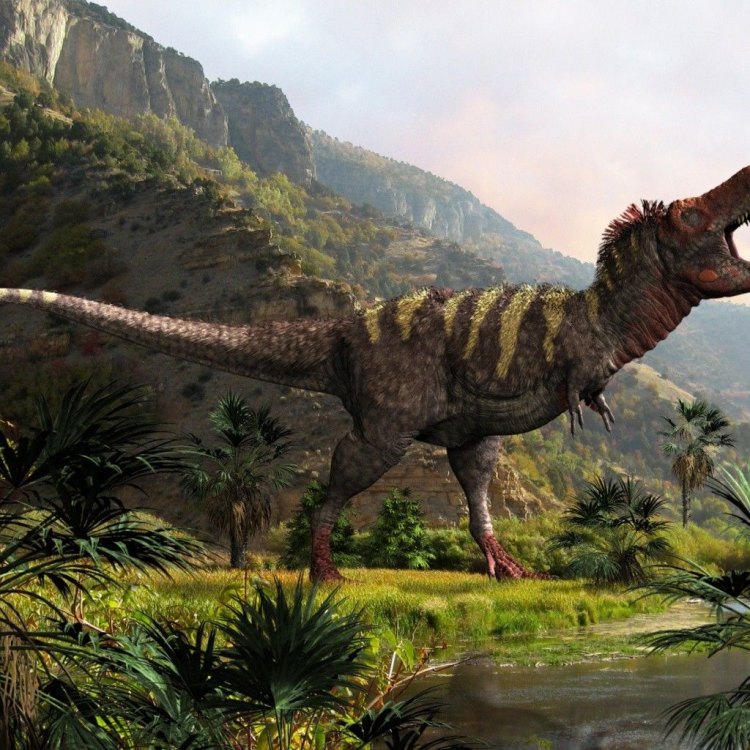

Tarbosaurus
Dinosaur Details Tarbosaurus - Scientific Name: Tarbosaurus
- Category: Dinosaurs T
- Scientific Name: Tarbosaurus
- Common Name: Tarbosaurus
- Geological Era: Late Cretaceous
- Length: 12-13 meters
- Height: 4-5 meters
- Weight: 4-5 tons
- Diet: Carnivorous
- Feeding Behavior: Active predator
- Predatory Behavior: Hunting in packs
- Tooth Structure: Sharp and serrated
- Native Habitat: Asia
- Geographical Distribution: Mongolia, China, and Russia
- Preferred Temperature: Temperate
- Maximum Speed: Unknown
- Skin Color: Unknown
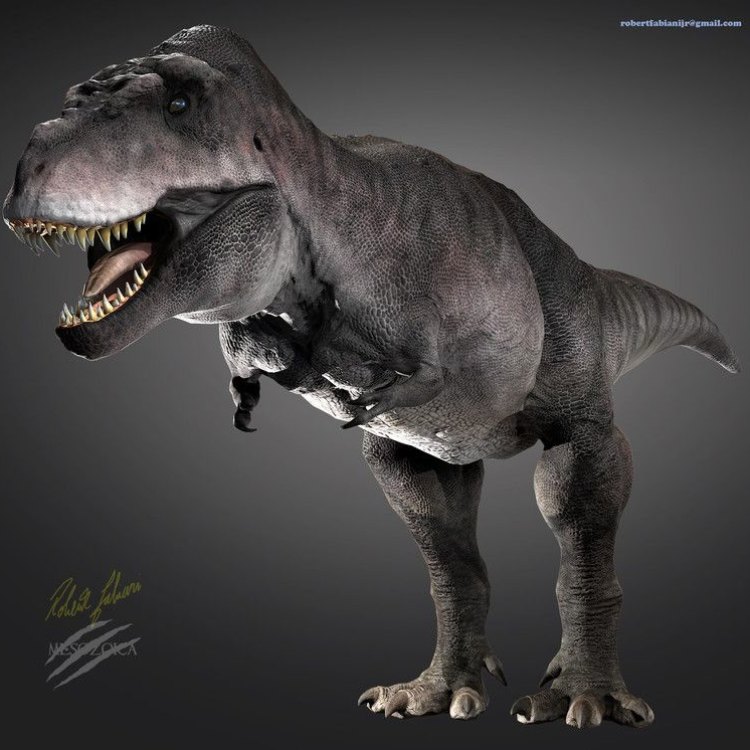

Tarbosaurus
- Bone Structure: Large and robust
- Reproduction Type: Egg-laying
- Activity Period: Diurnal
- Distinctive Features: Large head and long tail
- Communication Method: Unknown
- Survival Adaptation: Sharp teeth for hunting and eating
- Largest Species: Tarbosaurus bataar
- Smallest Species: Unknown
- Fossil Characteristics: Large skull with powerful jaws
- Role in Ecosystem: Top predator
- Unique Facts: Closely related to Tyrannosaurus rex
- Predator Status: Apex predator
- Discovery Location: Mongolia
- Discovery Year: 1946
- Discoverer's Name: Evgeny Alexandrovich Maleev
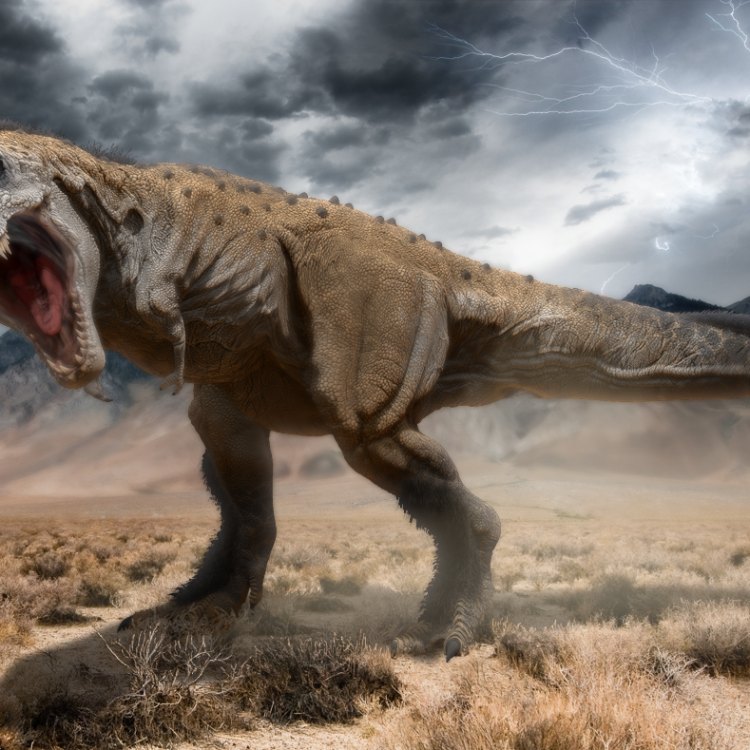

Tarbosaurus
The Powerful Tarbosaurus: King of the Mongolian Land
In the vast steppes of Mongolia, there once roamed a fierce and formidable predator, known as Tarbosaurus. This large and robust dinosaur ruled the land with its sharp teeth and powerful jaws, earning its place as the apex predator of its ecosystem. But what makes this dinosaur so unique and fascinating? Let's dive into the world of Tarbosaurus and discover its distinctive features, survival adaptations, and role in its ecosystem.When we think of dinosaurs, the first image that comes to mind is often the Tyrannosaurus rex, the king of all dinosaurs OnTimeAiraz.Com. But not far behind in terms of size and power is its closely related cousin, Tarbosaurus. In fact, Tarbosaurus bataar is the largest known species of Tarbosaurus, with the smallest species yet to be discovered. Its name translates to "alarming or frightening lizard," and it is easy to see why.
The most notable feature of Tarbosaurus is its large head and long tail. With a length of up to 12 meters and a weight of 5-7 tons, this dinosaur was a force to be reckoned with. Its large head housed powerful jaws, lined with sharp teeth, perfect for capturing and tearing apart its prey. This allowed Tarbosaurus to maintain its position as the top predator in its ecosystem.
Another feature of Tarbosaurus that sets it apart from other dinosaurs is its bone structure. It was built for strength and endurance, with robust bones that could support its massive body Thecodontosaurus. This adaptation was crucial for its hunting and survival, as it needed to be quick and agile to catch its prey and win battles against other predators.
Like most dinosaurs, Tarbosaurus was an egg-laying species. Its reproductive type was similar to that of modern-day birds, where females would lay eggs and incubate them until they hatched. These eggs were carefully buried or hidden in nests to protect them from predators, ensuring the continuation of their species. However, little is known about their communication methods, making Tarbosaurus a mysterious and intriguing creature.
One of the most interesting facts about Tarbosaurus is its close relationship to the famous Tyrannosaurus rex. They both belonged to the same family of dinosaurs, known as the tyrannosaurids, and shared many physical characteristics. It is believed that they evolved from a common ancestor and had a similar lifestyle, but Tarbosaurus had a few unique features that set it apart.
Tarbosaurus inhabited the land of Mongolia during the late Cretaceous period, approximately 70-65 million years ago. This discovery was first made in 1946 by a Russian paleontologist, Evgeny Alexandrovich Maleev. He unearthed the first Tarbosaurus fossils in the Nemegt Formation in Mongolia, and since then, several more discoveries have been made in the same location.
The fossils of Tarbosaurus provide valuable information about the dinosaur's physical characteristics and serve as a time capsule, giving us a glimpse into the prehistoric world. The most distinctive feature of these fossils is the large and powerful skull, with a skull length of up to 1.3 meters. It also had a short and thick neck, indicating its strong bite force and perfect for capturing its prey.
Tarbosaurus was a diurnal creature, meaning it was active during the day. Due to its large size and territorial nature, it would have required a considerable amount of food to sustain its energy levels. Its sharp teeth were essential for hunting and tearing apart its prey, making it a formidable and efficient predator. Its diet consisted of large herbivores, such as hadrosaurs, ceratopsians, and sauropods, which were also found in the same ecosystem. This highlights the vital role Tarbosaurus played in the balance of its ecosystem as the top predator.
While Tarbosaurus ruled the land, it was not without its own predators. It faced competition from other ferocious species, such as Therizinosaurus and Saurolophus, who preyed on its eggs and juveniles. This natural selection was essential for maintaining a balanced ecosystem, with each species playing a vital role in the food chain.
Unfortunately, the reign of Tarbosaurus was short-lived, along with most dinosaurs. The Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event, which occurred around 66 million years ago, wiped out almost all dinosaurs, including Tarbosaurus. This event was caused by a massive asteroid impact, leading to drastic changes in the climate and environment, ultimately resulting in their extinction.
In conclusion, Tarbosaurus was a powerful and fierce predator, closely related to the famous Tyrannosaurus rex. Its distinctive features, such as its large head and robust bone structure, set it apart from other dinosaurs, making it a unique and intriguing species. Its role as the top predator in its ecosystem highlights its crucial contribution to the balance of nature. Although it is long gone, the legacy of Tarbosaurus continues to fascinate and capture the imagination of scientists and dinosaur enthusiasts alike.
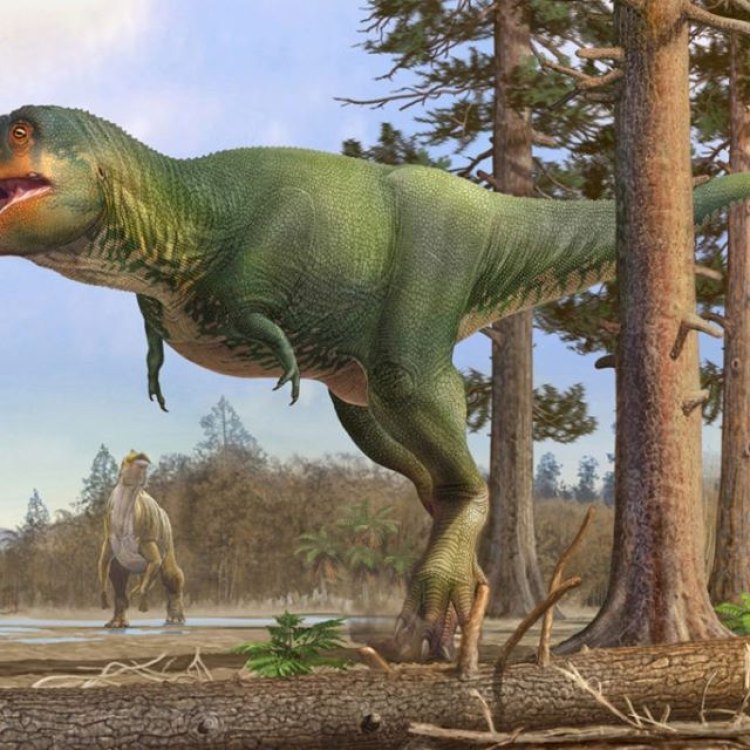

Tarbosaurus: The Ferocious King of Asia
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here is subject to change without notice.